Noções de Embriologia Animal
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, Professor Isabela explains the developmental stages of animals, starting from the fertilized egg (zygote) and progressing through various embryonic phases such as blastula, gastrulation, and the formation of germ layers. She discusses key evolutionary concepts, including the significance of the notochord and the differentiation between protostomes and deuterostomes. The lesson also covers the formation of the digestive system and the classification of animals based on their embryonic development. The professor emphasizes the importance of understanding these processes for comprehending the evolutionary relationships between major animal groups.
Takeaways
- 😀 All living organisms, including animals, are classified based on their evolutionary relationships and similarities.
- 😀 Taxonomists study the relationships between living beings and illustrate these connections through diagrams known as phylogenetic trees.
- 😀 The origin of all animals traces back to a single colonial organism that developed traits like multicellularity and embryonic development.
- 😀 The initial stages of embryonic development, including gastrulation and tissue formation, are crucial for the diversification of animal groups.
- 😀 Early stages of embryonic development, such as the formation of tissues, are remarkably similar across all animals, regardless of their final form.
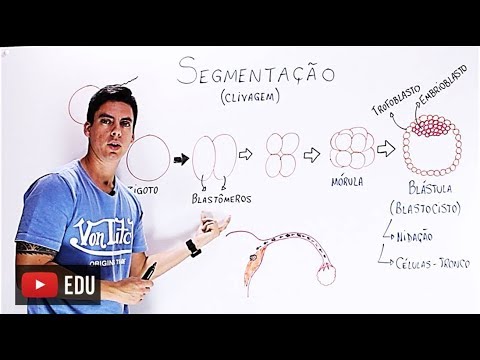
- 😀 The development of animals begins with the fertilized egg (zygote), which undergoes multiple divisions, forming a mass of cells known as a morula.
- 😀 As embryonic development progresses, cells continue to divide and migrate, forming structures like the blastula and the blastocoel.
- 😀 Gastrulation leads to the formation of the germ layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) and the primitive gut, marking the beginning of the digestive system in animals.
- 😀 The blastopore, formed during gastrulation, can either become the mouth or the anus, which helps classify animals as either protostomes or deuterostomes.
- 😀 Protostomes have the mouth formed first, while deuterostomes have the anus formed first; this is an important distinction in embryology.
- 😀 The presence of a true coelom (body cavity) formed by mesodermal cells is a key feature of more advanced animal groups, allowing for more specialized organs and efficient digestion.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lesson in the transcript?
-The main topic of the lesson is the classification and development of animals in the animal kingdom, focusing on their embryonic development and evolutionary relationships.
How are animals classified in the animal kingdom?
-Animals are classified based on their evolutionary relationships and shared characteristics. Taxonomists use these traits to create diagrams that illustrate the relationships between different species.
What is the significance of embryonic development in the evolution of the animal kingdom?
-Embryonic development plays a crucial role in the evolution and diversification of the animal kingdom. Early stages of development show greater similarities among animals, while later stages reflect more specific evolutionary changes.
What is a blastula, and why is it important in embryonic development?
-A blastula is a stage in embryonic development where the embryo forms a mass of cells around a cavity called the blastocoel. This stage is important as it marks the transition from a solid mass of cells to a structure that begins to form distinct layers.
What is gastrulation, and how does it affect the embryo?
-Gastrulation is the process during which the blastula undergoes significant changes, including the formation of three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. This stage is critical for the development of the digestive system and other body structures.
What is the difference between protostomes and deuterostomes?
-The primary difference lies in the fate of the blastopore during embryonic development. In protostomes, the blastopore becomes the mouth, while in deuterostomes, it becomes the anus. This distinction is crucial in understanding evolutionary relationships.
What is the role of the notochord in chordates?
-The notochord is a structure found in chordates that provides support to the body. In vertebrates, it is eventually replaced by the vertebral column. It plays a significant role in body structure and development.
What are the different types of body cavities found in animals?
-There are three main types of body cavities in animals: acoelomates (without a cavity), pseudocoelomates (with a cavity partially lined by mesoderm), and coelomates (with a fully mesoderm-lined cavity). These cavities are critical for the organization of organs and biological functions.
What is the significance of the mesoderm in embryonic development?
-The mesoderm is the middle layer of the embryo and is crucial for forming various body structures, including muscles, bones, and the circulatory system. It also plays a role in the formation of the coelom.
How do protostomes and deuterostomes differ in their embryonic development and digestive system?
-In protostomes, the blastopore becomes the mouth, and their digestive system develops with the mouth first. In deuterostomes, the blastopore forms the anus, and the mouth develops later, making the two groups different in their embryonic development and the formation of the digestive system.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Fase embrionik pertumbuhan dan perkembangan pada hewan - materi biologi sma kelas 12

Embryology Animated - the First Three Weeks

Pertumbuhan dan perkembangan pada hewan - Biologi kelas 12 SMA

General Embryology Review in 20 minutes
Embriologia humana

Desenvolvimento Embrionário - Aula 03 - Módulo VI: Zoologia | Prof. Guilherme
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
