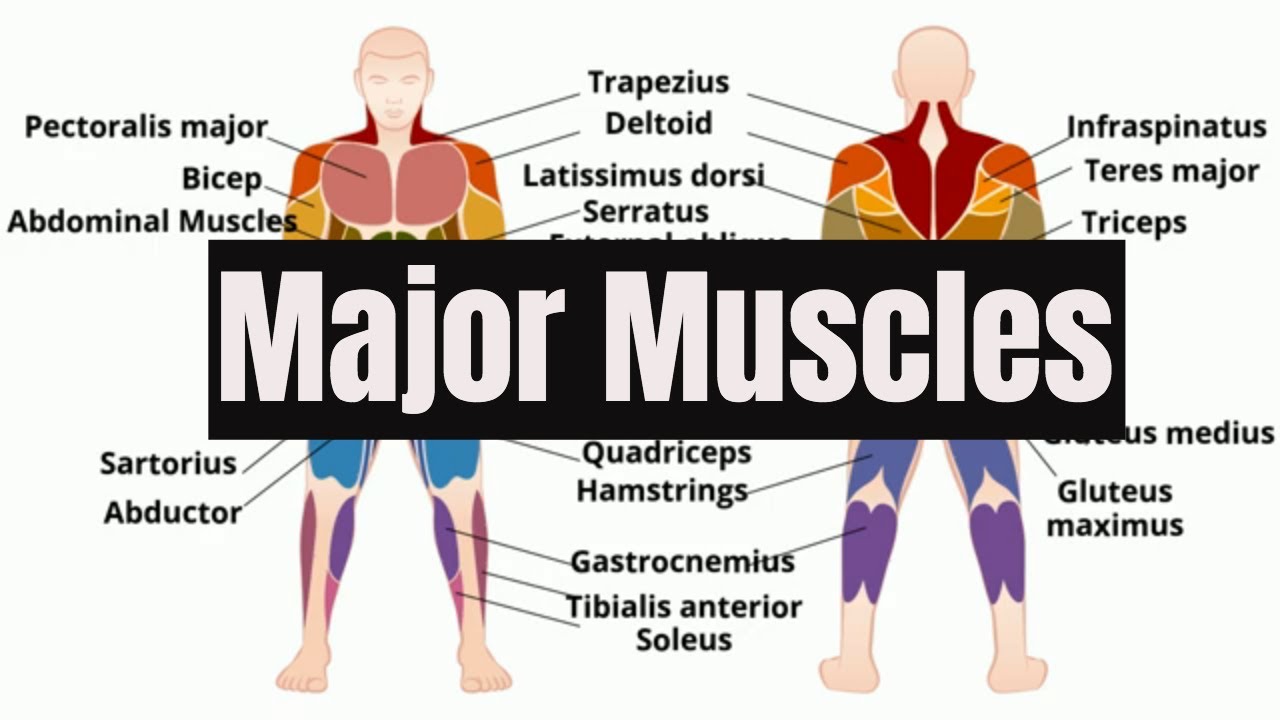
Regio Pectoralis, Deltoidea, Dorsalis (Video 15)
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides an in-depth exploration of the musculoskeletal system, focusing on the muscles of the superior extremity, including the pectoralis, deltoid, subclavius, and others. The script details the origin, insertion, function, and innervation of key muscles like pectoralis major and minor, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres major. It also touches on clinical conditions related to the rotator cuff and discusses the role of various muscles in arm movement and stability. The detailed anatomical descriptions aim to enhance understanding for students in the field of medical education.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script discusses the anatomy of the upper extremities, focusing on the musculoskeletal system, particularly in the pectoral, deltoid, and rotator cuff regions.
- 😀 The pectoralis major muscle originates from the medial half of the clavicle, the anterior surface of the sternum, and costal cartilages 1 to 7, and functions in abduction and rotation of the arm.
- 😀 The pectoralis minor muscle, located beneath the pectoralis major, originates from ribs 3, 4, and 5 and functions to elevate these ribs.
- 😀 The subclavius muscle is located below the clavicle and helps pull the shoulder towards the ventral side.
- 😀 The deltoid region contains the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor muscles, which are key to shoulder movement and stabilization.
- 😀 The rotator cuff, formed by the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor muscles, stabilizes the shoulder and helps with humeral rotation.
- 😀 Injury to the rotator cuff is common in individuals who frequently engage in overhead activities, such as tennis, badminton, or golf.
- 😀 The teres major muscle functions in medial rotation of the arm, with its origin at the inferior angle of the scapula.
- 😀 The deltoid muscle, which is responsible for arm abduction, originates from the acromion and clavicle, and inserts at the deltoid tuberosity on the humerus.
- 😀 The script provides a detailed overview of various upper extremity muscles, their origins, insertions, innervation, and primary functions.
- 😀 The importance of the rotator cuff muscles in maintaining shoulder joint stability is emphasized, particularly in preventing injuries during dynamic movements.
Q & A
What is the focus of this anatomical lecture?
-The lecture focuses on the musculoskeletal system, particularly the muscles found in regions such as the pectoralis, deltoid, and rotator cuff of the upper extremities.
What is the origin and insertion of the pectoralis major muscle?
-The pectoralis major muscle originates from the medial half of the clavicle, the anterior surface of the sternum, and the cartilage of ribs 1 to 7. It inserts at the greater tubercle of the humerus.
What are the functions of the pectoralis major muscle?
-The pectoralis major is involved in abduction and medial rotation of the humerus (brachium).
Which nerves innervate the pectoralis major muscle?
-The pectoralis major is innervated by the medial and lateral pectoral nerves, which originate from the brachial plexus.
Where is the pectoralis minor muscle located, and what is its function?
-The pectoralis minor is located behind the pectoralis major. It originates from the third, fourth, and fifth ribs and inserts at the coracoid process of the scapula. Its function is to elevate the third to fifth ribs.
What is the role of the rotator cuff muscles?
-The rotator cuff, consisting of muscles such as supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor, stabilizes the shoulder joint by fixing the humeral head in the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
How is the supraspinatus muscle involved in shoulder movement?
-The supraspinatus muscle originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts at the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is responsible for initiating abduction of the arm.
What distinguishes the teres minor from the teres major muscle?
-The teres minor is smaller and more superior in position compared to the teres major. It is responsible for lateral rotation of the arm, while the teres major performs medial rotation.
Which muscle functions as the primary abductor of the shoulder?
-The deltoid muscle is the primary abductor of the shoulder. It originates from the clavicle, acromion, and scapula, and inserts at the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus.
What is the clinical significance of rotator cuff injuries?
-Rotator cuff injuries, often caused by repetitive overhead movements in activities such as tennis or badminton, can lead to shoulder instability, pain, and difficulty in shoulder movements.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)