RUANGGURU - BIAYA PRODUKSI - EKONOMI KELAS 10 SMA
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains essential concepts in production cost analysis, using a shoe manufacturing example. It covers fixed and variable costs, total costs, and average costs, demonstrating how these factors impact the profitability of a business. The script highlights how to calculate average costs, fixed costs, and variable costs, helping viewers understand how to determine the cost per unit produced. The video also introduces the concept of marginal cost, which is crucial for business decision-making in production scaling. The content is designed to help viewers grasp cost calculations and their significance in assessing business performance.
Takeaways
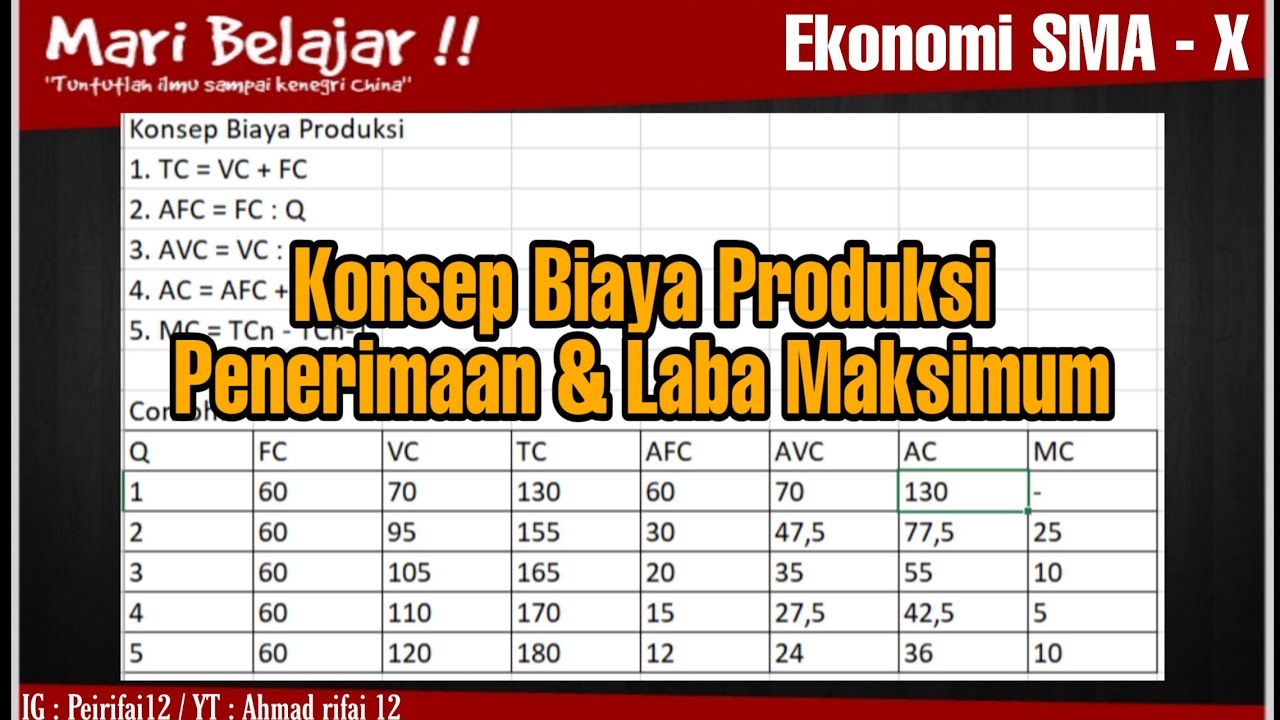
- 😀 Fixed costs (FC) remain constant regardless of the number of units produced, such as rent for the factory.
- 😀 Variable costs (VC) change in proportion to the quantity of units produced, like raw materials for manufacturing.
- 😀 Total cost (TC) is the sum of fixed costs and variable costs: TC = FC + VC.
- 😀 Average cost (AC) is the total cost per unit produced, calculated as TC divided by the number of units (Q).
- 😀 Average fixed cost (AFC) is the fixed cost per unit produced, calculated as FC divided by Q.
- 😀 Average variable cost (AVC) is the variable cost per unit produced, calculated as VC divided by Q.
- 😀 To calculate average cost, you can divide the total cost (TC) by the number of units (Q) produced.
- 😀 When calculating AFC and AVC, the sum of both equals the average cost (AC).
- 😀 Fixed costs do not change even if production levels vary or stop altogether.
- 😀 To determine the profitability of production, compare costs (FC + VC) with the revenue generated from sales.
- 😀 Marginal cost (MC), a key concept that will be discussed later, is related to the additional cost of producing one more unit.
Q & A
What are the two main types of costs in production?
-The two main types of costs in production are Fixed Costs (FC) and Variable Costs (VC). Fixed Costs remain constant regardless of the production volume, while Variable Costs change depending on the quantity of products produced.
What is the formula to calculate Total Cost (TC)?
-Total Cost (TC) is calculated by adding Fixed Costs (FC) and Variable Costs (VC): TC = FC + VC.
How do you calculate Average Cost (AC) per unit produced?
-Average Cost (AC) per unit is calculated by dividing the Total Cost (TC) by the quantity of products produced: AC = TC / Quantity Produced.
What does Average Fixed Cost (AFC) represent, and how is it calculated?
-Average Fixed Cost (AFC) represents the fixed cost per unit produced. It is calculated by dividing Fixed Costs (FC) by the quantity of products produced: AFC = FC / Quantity Produced.
What is the formula for Average Variable Cost (AVC)?
-Average Variable Cost (AVC) is calculated by dividing Variable Costs (VC) by the quantity of products produced: AVC = VC / Quantity Produced.
What is Marginal Cost (MC), and why is it important?
-Marginal Cost (MC) refers to the additional cost incurred to produce one more unit of a product. It is important because it helps businesses determine the most efficient level of production and optimize profitability.
How would you determine the production cost of a single unit if the total cost is 25 million IDR for 100 units?
-To find the cost per unit, divide the Total Cost (25,000,000 IDR) by the quantity of units produced (100): 25,000,000 IDR / 100 = 250,000 IDR per unit.
Why is it important for a business to calculate Average Fixed Costs and Average Variable Costs?
-Calculating Average Fixed Costs and Average Variable Costs is essential for understanding the cost structure of a business. It helps in pricing products, optimizing production, and ensuring profitability by managing costs effectively.
What is the relationship between Average Fixed Cost (AFC) and Average Variable Cost (AVC)?
-The sum of Average Fixed Cost (AFC) and Average Variable Cost (AVC) equals the Average Cost (AC). In other words, AC = AFC + AVC.
How can a business use these cost concepts to optimize pricing and profitability?
-By understanding and calculating costs such as Total Cost, Average Cost, and Marginal Cost, a business can set competitive prices that cover production costs while ensuring profitability. Cost optimization, like reducing fixed or variable costs, further enhances profit margins.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

LAPORAN HARGA POKOK PRODUKSI

INVENTORY COSTING AND CAPACITY ANALYSIS

Mini video: Absolute advantage and comparative advantage (1)
Cara Menghitung Biaya Produksi, Penerimaan dan Laba Maksimum

Managerial Accounting 6.7: Using Variable Costing to Make Decisions

Biaya Produksi | Biaya Non Produksi | Menganalisis Biaya Prototype Produk Barang/Jasa
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
