Fisika Kelas 7 - Ekspansi Thermal
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the concept of thermal expansion, focusing on how heat affects the size and shape of materials. It explains the processes of thermal expansion in solids, liquids, and gases, highlighting how heat causes atoms to vibrate, leading to changes in distance between them. The script explores formulas for calculating changes in length, area, and volume due to temperature changes, and provides a detailed breakdown of the coefficients of thermal expansion for different dimensions. The video concludes with practical applications and emphasizes the importance of understanding these principles for solving related problems.
Takeaways
- 😀 Thermal expansion occurs when a material increases in size due to heat, causing the atoms or molecules to vibrate more and move apart.
- 😀 The change in length (ΔL) of a material is directly proportional to the coefficient of linear expansion (α), the initial length (L₀), and the change in temperature (ΔT).
- 😀 The formula for linear expansion is: ΔL = α * L₀ * ΔT, where ΔL is the change in length, α is the coefficient of linear expansion, L₀ is the initial length, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
- 😀 For area expansion, the formula is ΔA = β * A₀ * ΔT, where β is the coefficient of area expansion and A₀ is the initial area. It was derived that β ≈ 2α.
- 😀 For volumetric expansion, the formula is ΔV = γ * V₀ * ΔT, where γ is the coefficient of volumetric expansion and V₀ is the initial volume. γ ≈ 3α.
- 😀 The relationship between the coefficients of thermal expansion are: β ≈ 2α for area expansion and γ ≈ 3α for volumetric expansion.
- 😀 Thermal expansion is a key concept in understanding how materials change with temperature. It applies to solids, liquids, and gases, but behaves differently in each.
- 😀 In solids, atoms are arranged in a regular, ordered structure, and thermal expansion occurs predictably as atoms move apart.
- 😀 In liquids, the molecular arrangement is more disordered, which makes expansion less predictable compared to solids.
- 😀 Gases expand rapidly in all directions due to their molecules being far apart and moving freely. The coefficient of volumetric expansion (γ) is the most relevant for gases.
- 😀 The lesson emphasizes understanding the relationships between the coefficients of linear, area, and volumetric expansion, rather than memorizing derivations, to solve problems effectively.
Q & A
What is the primary concept discussed in this script?
-The script focuses on the concept of thermal expansion, explaining how materials expand when heated, and the resulting changes in length, area, and volume.
How does heat affect the molecular structure of solids?
-When a solid is heated, its atoms or molecules vibrate more intensely, causing the distance between them to increase, leading to the expansion of the material.
What is the formula for linear thermal expansion?
-The formula for linear thermal expansion is ΔL = α * L₀ * ΔT, where ΔL is the change in length, α is the coefficient of linear expansion, L₀ is the initial length, and ΔT is the temperature change.
What happens to the dimensions of an object during thermal expansion in 2D and 3D?
-In 2D, the area of an object expands according to the formula A = A₀ * (1 + β * ΔT), where β is the coefficient of area expansion. In 3D, the volume expands according to the formula V = V₀ * (1 + γ * ΔT), where γ is the coefficient of volumetric expansion.
How are the coefficients of expansion (α, β, γ) related?
-The coefficients of expansion are related by the following relationships: β = 2α (for area expansion), and γ = 3α (for volumetric expansion), where α is the coefficient of linear expansion.
Why are the squared and cubic terms in the formulas for expansion often neglected?
-The squared and cubic terms are often neglected because the coefficients of expansion are typically very small (around 10^-5), making these terms negligible in comparison to the linear term.
What distinguishes the thermal expansion behavior of solids, liquids, and gases?
-In solids, the atoms are closely arranged and can only vibrate, leading to expansion. In liquids and gases, the molecular arrangement is more disordered, allowing for greater expansion in all directions, with gases having the most significant thermal expansion.
What role does the coefficient of expansion play in the design of materials?
-The coefficient of expansion is critical in designing materials for specific applications because it dictates how a material will respond to temperature changes. For instance, materials with a low coefficient of expansion are used where stability is crucial, while those with higher coefficients might be used in environments where expansion is beneficial.
How is the formula for volumetric expansion derived?
-The formula for volumetric expansion is derived by considering the expansion in all three dimensions (length, width, and height). The final formula is V = V₀ * (1 + γ * ΔT), where γ is the coefficient of volumetric expansion.
What can be ignored when calculating thermal expansion in practical scenarios?
-In most practical scenarios, the squared and cubic terms in the expansion formulas can be ignored, as they contribute very little due to the small size of the coefficients of expansion (α, β, γ).
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

LEY DE FOURIER-TRANSFERENCIA DE CALOR EN UNA SUPERFICIE PLANA-AMF

Heat | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 4 Part 1

FISIKA Kelas 11 - Suhu & Kalor (PART 1) | GIA Academy
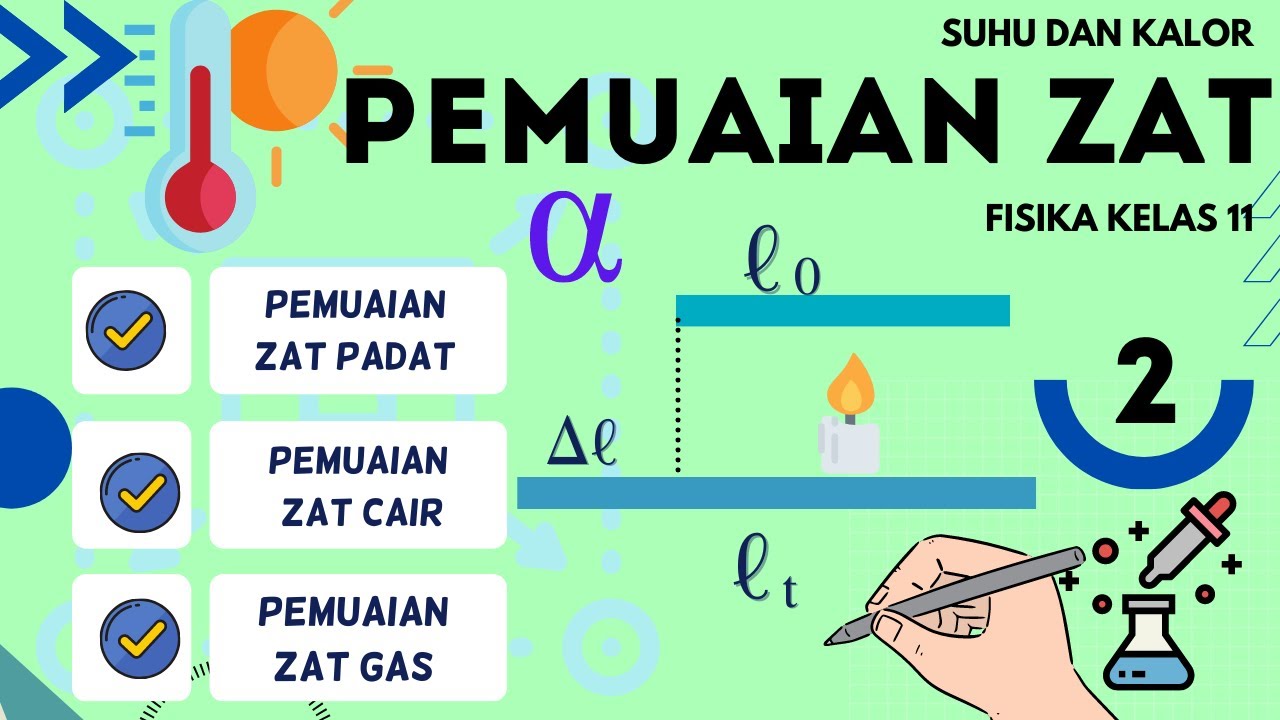
Suhu dan Kalor Fisika Kelas 11 - Part 2 : Pemuaian Zat Padat, Zat Cair, Zat Gas

KALOR DAN PERPINDAHAN KALOR SERTA CONTOH SOAL DAN PENYELESAIANNYA|| Kelas XI SMA || Gasal

Video PPL 1 FISIKA Model Problem Based Learning (PBL)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
