Pewarnaan Gram
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive guide to performing Gram staining on bacteria, a crucial microbiological technique for distinguishing between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The procedure involves several key steps: preparing a bacterial smear, applying primary and secondary stains (crystal violet and safranin), using iodine as a mordant, and decolorizing with alcohol. The video also emphasizes the importance of safety precautions and the proper handling of materials. Ultimately, Gram staining helps classify bacteria based on their cell wall structure, aiding in bacterial identification and diagnosis. The method was developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884.
Takeaways
- 😀 Gram staining is a microbiological technique used to distinguish between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria based on their cell membrane structure.
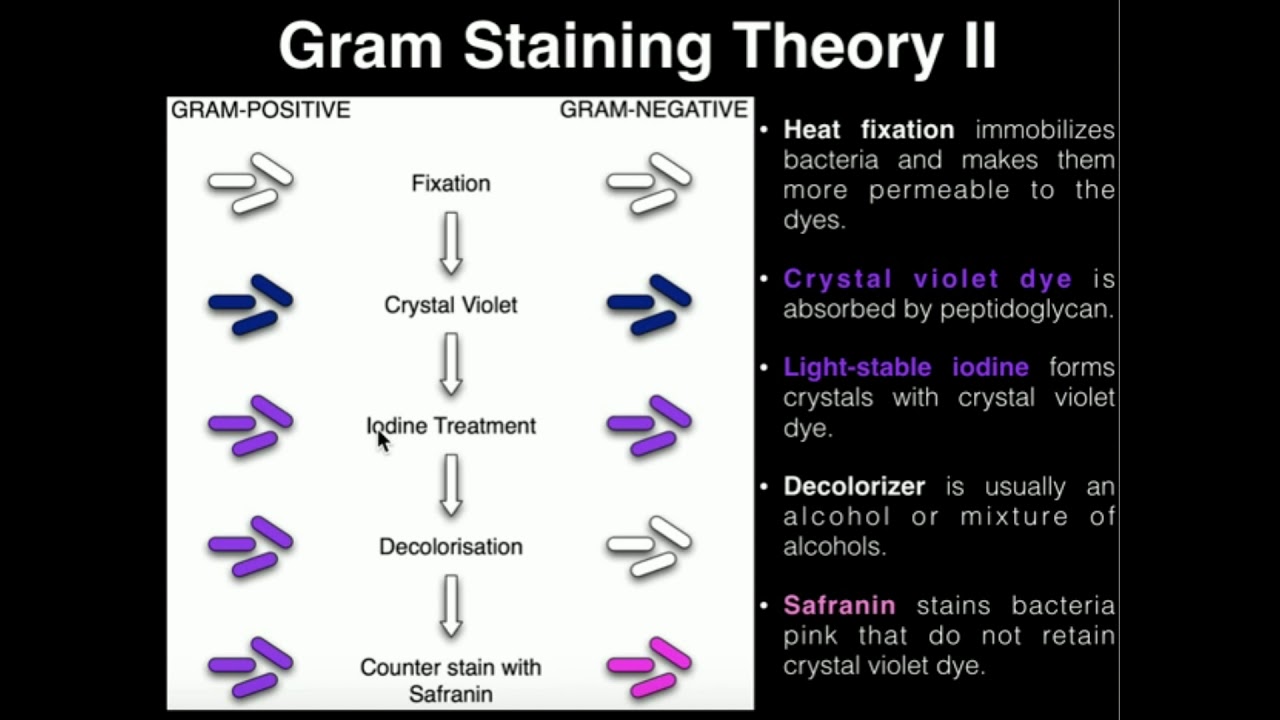
- 😀 Gram-positive bacteria retain the primary violet stain due to their thick peptidoglycan layer, appearing blue under the microscope.
- 😀 Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer and a complex outer membrane, causing them to appear pink after the counterstain (safranin).
- 😀 The Gram stain involves four key reagents: crystal violet (primary stain), Lugol's iodine (mordant), alcohol (decolorizer), and safranin (secondary stain).
- 😀 Before staining, bacteria are fixed to the slide by passing it through a flame to prevent loss during the process.
- 😀 The staining process begins with applying crystal violet for 1 minute, followed by iodine solution for another minute, which helps retain the violet stain in Gram-positive bacteria.
- 😀 Alcohol is used as a decolorizer, removing the crystal violet stain from Gram-negative bacteria, which makes them susceptible to the red safranin stain.
- 😀 After decolorization, safranin is applied for 30 seconds, which stains the Gram-negative bacteria red or pink, contrasting with the blue of Gram-positive bacteria.
- 😀 The slide is rinsed between steps to ensure that the stains are applied properly without contamination or loss of sample.
- 😀 The Gram stain technique was developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884 and remains fundamental for classifying bacteria and determining appropriate treatments.
Q & A
What is the main principle behind Gram staining?
-The main principle behind Gram staining is to color the bacterial membrane, which typically shows two types of colors: blue for Gram-positive bacteria and pink for Gram-negative bacteria.
What are the primary stains used in Gram staining?
-The primary stains used in Gram staining are crystal violet (the primary stain), Lugol's iodine (the mordant), alcohol (the decolorizer), and safranin (the secondary stain).
Why does Gram-positive bacteria retain the blue color after staining?
-Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall, which allows them to retain the crystal violet dye even after decolorization with alcohol.
What happens to Gram-negative bacteria during Gram staining?
-Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer and lack the thick cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria. This causes the crystal violet dye to wash out during decolorization, and they will retain the pink color from the secondary stain (safranin).
What is the purpose of the alcohol in the Gram staining process?
-Alcohol is used as a decolorizer in Gram staining. It washes away the crystal violet dye from Gram-negative bacteria, but not from Gram-positive bacteria, because of the differences in their cell wall structure.
What role does Lugol's iodine play in the Gram staining procedure?
-Lugol's iodine acts as a mordant in Gram staining. It binds with crystal violet to form a complex that helps the dye stick to the bacterial cell wall, especially in Gram-positive bacteria.
What are the necessary safety precautions when performing Gram staining in the laboratory?
-Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is necessary when performing Gram staining. This includes wearing a mask, gloves, a laboratory coat, and closed-toe shoes to ensure safety during the experiment.
How should bacterial samples be prepared before starting the Gram staining process?
-Before Gram staining, a bacterial smear is prepared on a glass slide. The sample is spread in a small drop of sterile saline and air-dried. It is then heat-fixed by passing the slide through a flame to kill the bacteria and adhere them to the slide.
What is the significance of Gram staining in microbiology?
-Gram staining is an important microbiological technique used to classify bacteria into two main categories: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. This classification helps in identifying bacterial species and determining the appropriate treatment.
What is the historical significance of Gram staining?
-Gram staining was developed by Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram in 1884. It revolutionized microbiology by providing a simple method to differentiate bacterial species based on their cell wall structure.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)