Uji Chi Square (Part 1) | Genetika Tanaman
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the theory of probability and chi-square tests in the context of plant genetics, specifically genetic crossbreeding. It covers how probability theory helps predict the expected ratios in plant breeding experiments, like Mendel's laws of inheritance. The chi-square test is introduced as a method to compare experimental results with expected outcomes, determining whether deviations from expected ratios are due to chance. Through an example of a monohybrid cross, the video demonstrates how to apply these concepts to assess genetic results and understand whether observed deviations are significant or not.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script explains the concepts of probability theory and chi-square testing, both crucial in genetic cross studies.
- 😀 Probability theory helps in calculating the expected ratios of different genetic crosses, like Mendel’s laws of inheritance (e.g., 3:1, 9:3:3:1).
- 😀 Chi-square testing is used to compare experimental data with expected ratios to determine whether observed results deviate significantly from expectations.
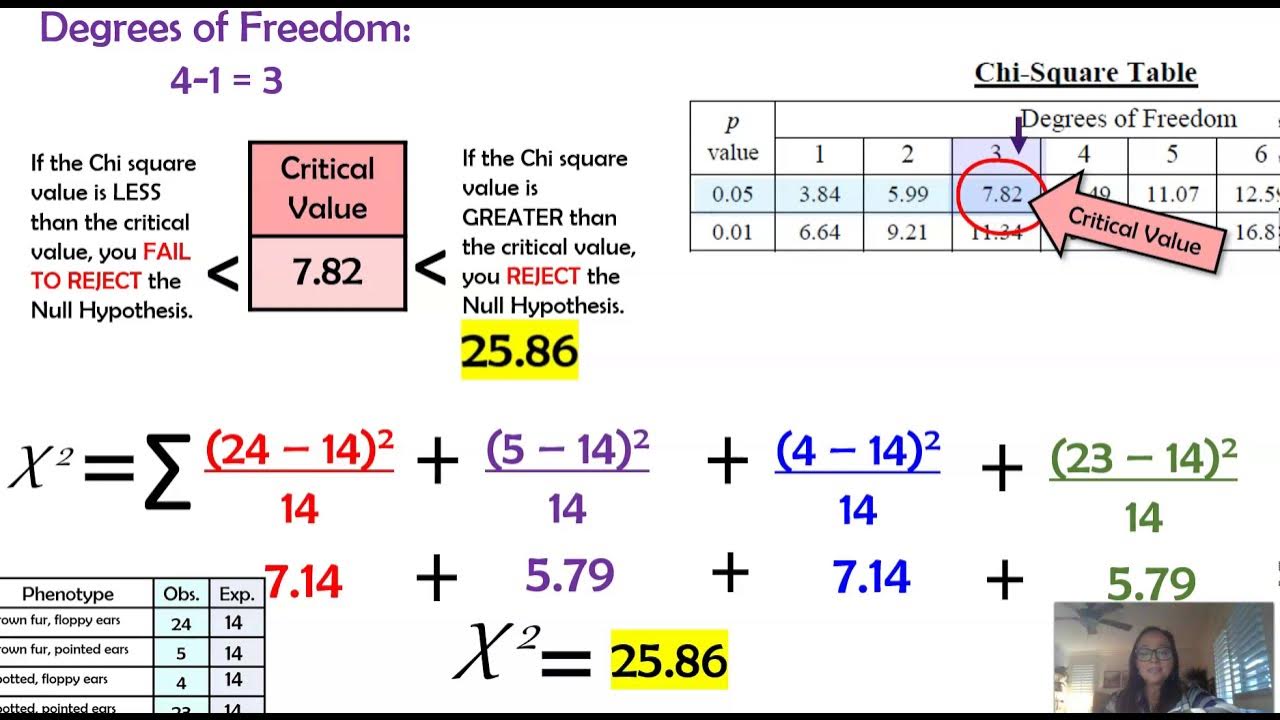
- 😀 Chi-square is calculated by comparing the observed data with the expected values, where deviations are squared and summed to determine if the hypothesis is accepted or rejected.
- 😀 If the calculated chi-square value (X²) is smaller than the critical value from the chi-square table (X² table), the hypothesis is accepted, indicating no significant deviation.
- 😀 If the calculated chi-square value (X²) is larger than the critical value (X² table), the hypothesis is rejected, indicating a significant deviation.
- 😀 A probability value (p-value) of 5% is commonly used as the threshold to decide whether to accept or reject a hypothesis in chi-square testing.
- 😀 The example of a monohybrid cross is used to demonstrate chi-square testing, with observed ratios compared to the expected 3:1 ratio for dominant and recessive traits.
- 😀 The process of calculating chi-square involves determining the observed and expected values, calculating deviations, and then computing the chi-square statistic.
- 😀 The degrees of freedom (df) are used to interpret the chi-square table, where df equals the number of classes minus one, and the critical value depends on the chosen significance level (e.g., 0.05).
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video script?
-The main focus of the video is explaining the concepts of probability theory and the chi-square test, specifically in the context of genetics and Mendelian inheritance.
How is probability theory related to genetics?
-Probability theory in genetics helps predict the expected ratios of offspring in genetic crosses, such as Mendel's laws of inheritance. It is used to estimate the likelihood of specific traits appearing in the offspring.
What does probability represent in the context of genetics?
-Probability represents the likelihood or chance of a certain genetic trait appearing in offspring, expressed as a percentage or a value between 0 (impossible) and 1 (certain).
What is the chi-square test used for?
-The chi-square test is used to compare observed results with expected results to determine if there is a significant deviation, helping to test hypotheses about genetic ratios in breeding experiments.
What is the formula for calculating the chi-square value?
-The chi-square value (χ²) is calculated by summing the squared differences between observed and expected frequencies, divided by the expected frequencies.
How do you interpret the chi-square value?
-The chi-square value is compared to a critical value from a chi-square distribution table. If the calculated value is less than the critical value, the hypothesis is accepted, indicating that deviations are due to random chance. If the value is higher, the hypothesis is rejected, suggesting a real deviation.
What does an observed result of 290 red flowers and 110 white flowers indicate in the example?
-The observed result of 290 red flowers and 110 white flowers is used to compare against the expected 3:1 ratio for a monohybrid cross, to see if the data fits Mendelian genetics.
Why is the chi-square value of 1.2 considered acceptable in this example?
-The chi-square value of 1.2 is considered acceptable because, when compared to the chi-square distribution table, it is smaller than the critical value, meaning the observed data aligns well with the expected ratio, and the hypothesis is accepted.
What happens if the chi-square value exceeds the critical value?
-If the chi-square value exceeds the critical value, it means that the observed deviation from the expected results is statistically significant, and the hypothesis is rejected, suggesting that the difference is not due to chance.
How does the chi-square test help in understanding Mendelian inheritance?
-The chi-square test helps confirm if the observed genetic ratios in offspring follow Mendelian inheritance patterns. It provides a statistical method to test whether the results of genetic crosses align with the predicted ratios (e.g., 3:1 or 9:3:3:1).
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

HEREDITAS - BIOLOGI - KELAS 12

BIOLOGI SMA Kelas 12 - Pewarisan Sifat PART 1 (Hukum Mendel) | GIA Academy

Distribusi Chi-square, Weibull, t dan F
Chi Square in Genetics & Examples (AP Biology)

Understanding Chi-Square and Fisher's Exact Tests

028 Gregor Mendel & die klassische Genetik Meilensteine der Naturwissenschaft & Technik
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
