Noam Chomsky - Why Does the U.S. Support Israel?
Summary
TLDRThis transcript examines the historical, religious, and geopolitical factors behind the United States' support for Israel. The speaker argues that Christian Zionism, rooted in both British and American culture, has played a key role, with influential leaders like Woodrow Wilson and Harry Truman supporting the Jewish return to Palestine based on biblical principles. Additionally, the strategic military alliance between the U.S. and Israel, particularly since the 1967 war, is highlighted. The speaker also critiques the media’s uncritical support of state power and intellectuals’ reluctance to challenge imperialistic actions, drawing parallels to other settler colonial societies.
Takeaways
- 😀 Christian Zionism, which predates Jewish Zionism, has been a significant influence on the U.S.'s support for Israel, with religious figures like Woodrow Wilson and Harry Truman playing key roles in shaping policy.
- 😀 The support for Israel in the United States aligns with a broader historical pattern of settler colonialism, shared with other Anglosphere nations like Britain, Canada, and Australia.
- 😀 The Biblical narrative, particularly the idea of the return of Jews to Palestine, has deeply influenced U.S. foreign policy, reflecting a literal interpretation of religious teachings.
- 😀 The U.S. military has viewed Israel as a strategic asset, with Israel’s military success in 1948 and beyond reinforcing its importance to American interests in the Middle East.
- 😀 In the early years of Israel's statehood, the Pentagon saw Israel as a potential military base, contributing to its continued support, despite differing views within the U.S. government.
- 😀 Israel's role in defeating secular Arab nationalism and supporting radical Islam in the 1960s further cemented its relationship with the United States.
- 😀 The U.S. has provided significant military aid to Israel, such as munitions during conflicts like the Gaza attacks, highlighting the deep military and intelligence cooperation between the two countries.
- 😀 Media coverage in the U.S. often supports government policy without critical questioning, especially regarding military actions like the Iraq War and Vietnam War.
- 😀 The speaker criticizes intellectuals and the broader intellectual community for their tendency to support state power, rather than challenge or critically examine historical and contemporary power dynamics.
- 😀 The discussion of U.S. and British imperialism and colonization highlights a pattern where mainstream intellectuals avoid confronting uncomfortable historical truths, such as the genocidal aspects of colonial practices.
Q & A
Why does the United States support Israel?
-The United States' support for Israel is rooted in both historical and cultural factors, including the influence of Christian Zionism, which has shaped American policies and attitudes toward Israel. Additionally, there are strategic and military considerations, with Israel being viewed as a vital ally in the Middle East.
What role does Christian Zionism play in the United States' support of Israel?
-Christian Zionism, particularly influential in the United States, is a powerful force that has contributed to American support for Israel. Leaders like Woodrow Wilson and Harry Truman were devout Christians who saw the return of Jews to Palestine as a fulfillment of biblical prophecy.
How did British elites influence the support for Jewish colonization of Israel?
-Christian Zionism among British elites was a major factor in supporting Jewish colonization of Israel. This ideological stance influenced Britain’s policies, such as the Balfour Declaration, which expressed support for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
What is meant by 'settler colonialism' in the context of Israel's establishment?
-Settler colonialism refers to a form of colonization where settlers move into a territory and establish control, often displacing indigenous populations. Israel is described as a settler colonial society, similar to other Anglo-settler societies like the United States, Canada, and Australia, driven by religious and imperial ideologies.
What were the differing perspectives within the U.S. government regarding Israel's establishment in 1948?
-In 1948, the U.S. government was divided on how to react to the establishment of Israel. The State Department was cautious, concerned about refugees and territorial issues, while the Pentagon viewed Israel as a valuable military ally in the region, recognizing its military potential.
How did Israel's military successes influence U.S. support for the country?
-Israel's military successes, particularly in conflicts like the 1948 Arab-Israeli War and the 1967 Six-Day War, helped solidify its strategic importance to the U.S. Israel's ability to defeat regional adversaries made it a key ally in the Middle East, contributing to continued U.S. support.
How did the U.S. view Israel’s role in countering Arab nationalism and radical Islam?
-Israel played a crucial role in weakening secular Arab nationalism, which was viewed as a threat to U.S. interests. At the same time, Israel's support for radical Islamic factions in the region aligned with U.S. goals, as both sought to counterbalance Arab nationalist movements.
What is the significance of U.S. military aid to Israel, particularly during conflicts like the Gaza attack?
-The U.S. provides significant military aid to Israel, including munitions and intelligence. For instance, during the Gaza conflict, the U.S. replenished Israel's munitions supply from U.S. stockpiles pre-positioned in Israel, reflecting the close military and strategic relationship between the two countries.
What is the relationship between U.S. intelligence and Israel?
-The U.S. and Israel share close intelligence ties, dating back to the early years of Israel's establishment. These ties have remained strong, with Israel playing a key role in supporting U.S. intelligence efforts in the Middle East.
How does the media in the U.S. shape public opinion on Israel?
-The U.S. media largely supports government policy regarding Israel, with little questioning or dissent. This reflects a broader tendency to align with state power, often portraying the U.S.-Israel relationship in a favorable light while downplaying criticism or alternative perspectives.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Iran, Pakistan, myth of Islamic bomb & why Muslim Ummah isn’t coming to Tehran’s aid against Israel

Why The US South Is Insanely Religious
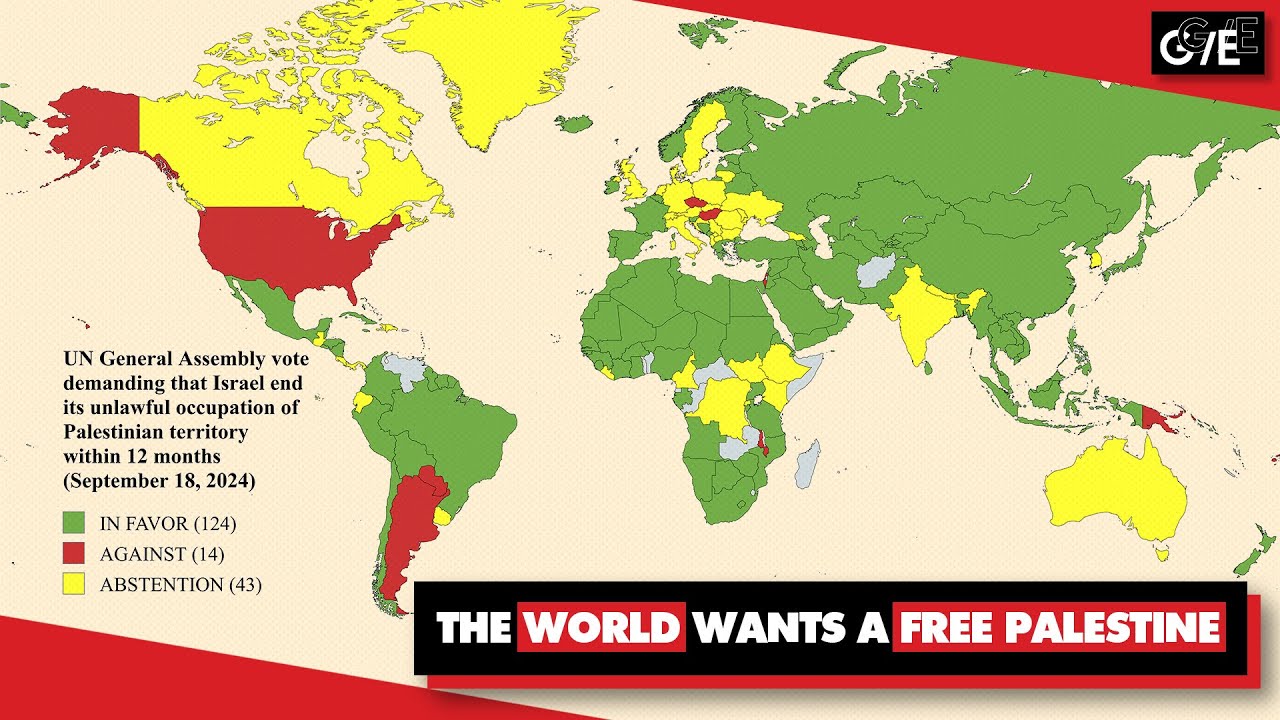
World demands end to Israel’s illegal occupation of Palestine, in landslide UN vote

अमेरिका-इस्राईल का ईरान पर हमला, क्या इस बार बच पाएगा ईरान?

Douglas Macgregor Warns: U.S Is Supporting Despite - Israel Firepower Has Reached Terrifying Levels

Truth about SYRIA! You won't believe what's REALLY going on!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
