Биология. 10 класс. Строение и функции гемоглобина и миоглобина человека /20.11.2020/
Summary
TLDRThis lesson focuses on the structure and functions of hemoglobin and myoglobin in humans. Hemoglobin, found in red blood cells, is responsible for oxygen transport and consists of globin and heme groups, allowing reversible oxygen binding. Myoglobin, located in muscle tissues, stores oxygen to meet metabolic demands. The lesson highlights their structural differences—hemoglobin's quaternary structure versus myoglobin's tertiary structure—and discusses the various types of hemoglobin, including fetal hemoglobin, which has a higher affinity for oxygen. Overall, it emphasizes the critical roles these proteins play in oxygen delivery and storage.
Takeaways
- 😀 Hemoglobin is an iron-containing respiratory pigment found in human and vertebrate blood, responsible for oxygen transport.
- 😀 The structure of hemoglobin consists of globin protein and heme groups, with the heme containing iron that binds oxygen.
- 😀 Hemoglobin can exist in two forms: oxyhemoglobin (oxygen-bound) and reduced hemoglobin (oxygen-released), which differ in color.
- 😀 The average hemoglobin content in adult human blood is approximately 13-16 grams per 100 milliliters.
- 😀 Adult hemoglobin (HbA) has a quaternary structure with four polypeptide chains: two alpha and two beta chains.
- 😀 Myoglobin is a protein found in skeletal and cardiac muscle, serving as an oxygen reserve during muscle activity.
- 😀 The structure of myoglobin is simpler than that of hemoglobin, consisting of a single polypeptide chain and a heme group.
- 😀 Myoglobin binds about 14% of the total oxygen in the body, which is critical for sustaining muscle function during oxygen deprivation.
- 😀 Different types of hemoglobin exist during embryonic development, with fetal hemoglobin (HbF) having a higher affinity for oxygen than adult hemoglobin.
- 😀 The interaction between hemoglobin and oxygen involves reversible binding, crucial for efficient oxygen delivery to tissues.
Q & A
What is the primary function of hemoglobin in the human body?
-The primary function of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen from the respiratory organs to the tissues of the body.
What are the main structural components of hemoglobin?
-Hemoglobin consists of a protein component called globin and a heme group that contains iron.
How does myoglobin differ from hemoglobin in terms of structure?
-Myoglobin has a tertiary structure and consists of a single polypeptide chain, while hemoglobin has a quaternary structure made up of four polypeptide chains.
What role does iron play in the function of hemoglobin?
-Iron in the heme group allows hemoglobin to bind and release oxygen efficiently.
How does the color of arterial blood differ from venous blood, and why?
-Arterial blood, which contains oxyhemoglobin, is bright red, while venous blood, which contains deoxygenated hemoglobin, appears dark red.
What types of hemoglobin are present during embryonic development?
-Embryonic development features different types of hemoglobin, including HbE, HbF, and HbA, with HbF having a higher affinity for oxygen.
What is the significance of myoglobin in muscle tissue?
-Myoglobin serves as an oxygen reserve in muscle tissues, supplying oxygen during periods of high demand when blood flow may be limited.
How does hemoglobin change its conformation during oxygen binding?
-Hemoglobin undergoes conformational changes between tense (T) and relaxed (R) states, which affects its affinity for oxygen.
What is the average concentration of hemoglobin in adult human blood?
-The average concentration of hemoglobin in adult human blood is about 13-16 grams per 100 milliliters.
What happens to myoglobin levels during muscle ischemia?
-During muscle ischemia, myoglobin can help maintain oxygen supply to muscle fibers, allowing them to function temporarily despite reduced blood flow.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Mioglobina: funzioni e differenze rispetto all'Emoglobina 🩸
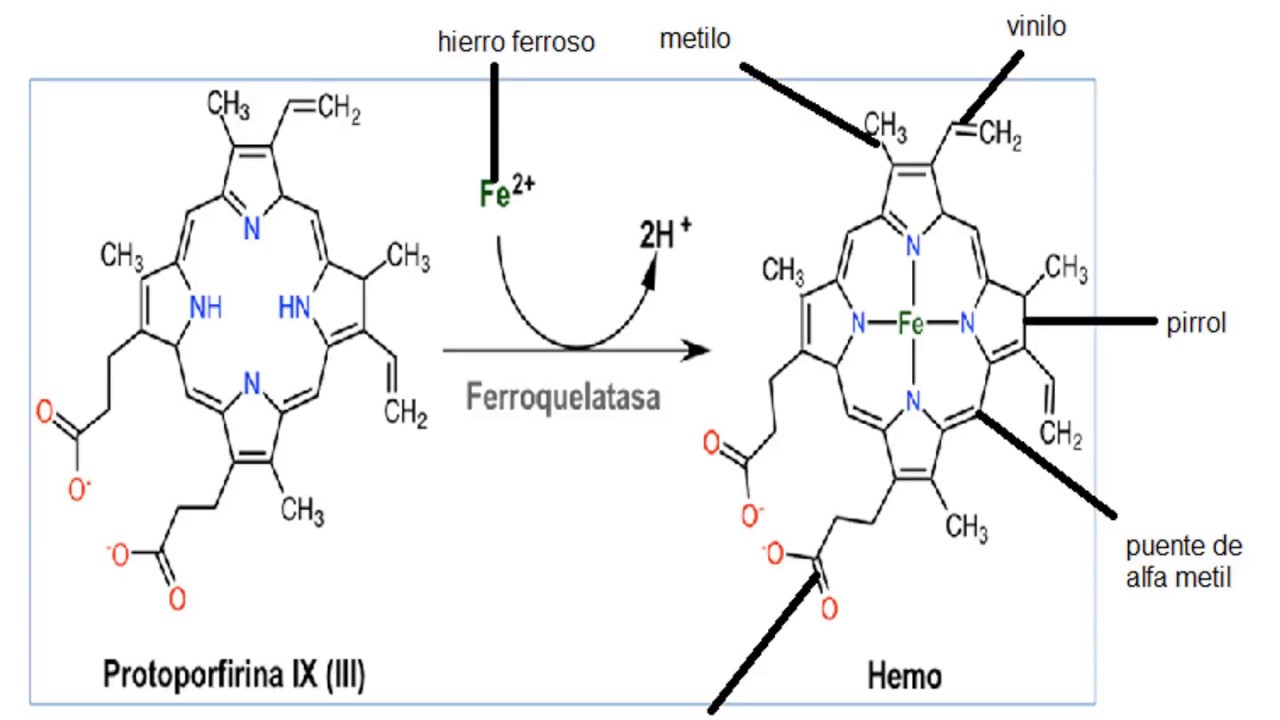
Hemoglobina parte 2(grupo hemo, union del hemo a la gb, efecto de cooperatividad )
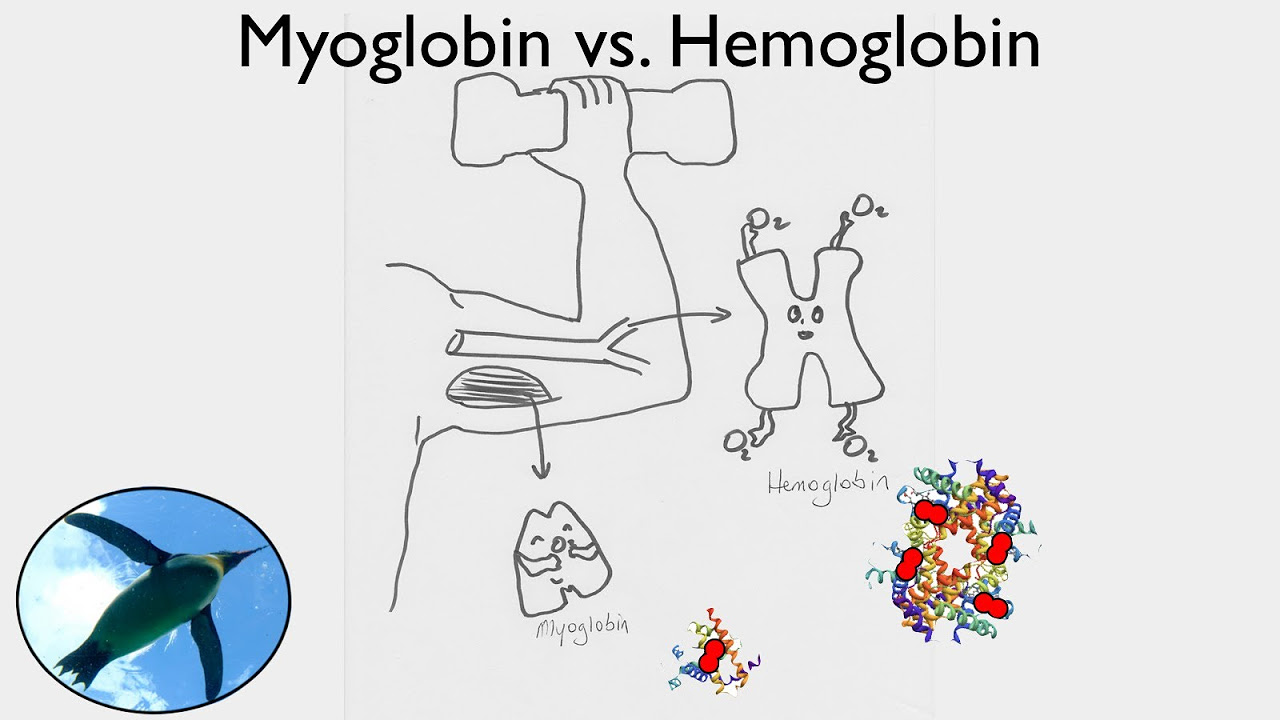
Getting Oxygen: Myoglobin vs. Hemoglobin

Structure of globin mRNA B. Sc Zoology Molecular Biology||Core XI||#bsczoology #globinmrna
Respiration. Part 3.

Iron Metabolism : Transportation and Storage, Absorption and Regulation, Daily loss of iron : USMLE
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
