GRAVIMETRY ANALYSIS CALCULATION - PART 2
Summary
TLDRIn this instructional video, the host explains the principles of gravimetric analysis, focusing on how to calculate the concentration of ions in a sample. Through clear examples, such as determining chloride and lead concentrations, viewers learn to use formulas that incorporate precipitate weights and gravimetric factors. The process involves adding reagents to form precipitates, weighing them, and performing calculations to find the percentage of the analyte in the original sample. This method, while straightforward, emphasizes precision and accuracy, encouraging viewers to practice for mastery.
Takeaways
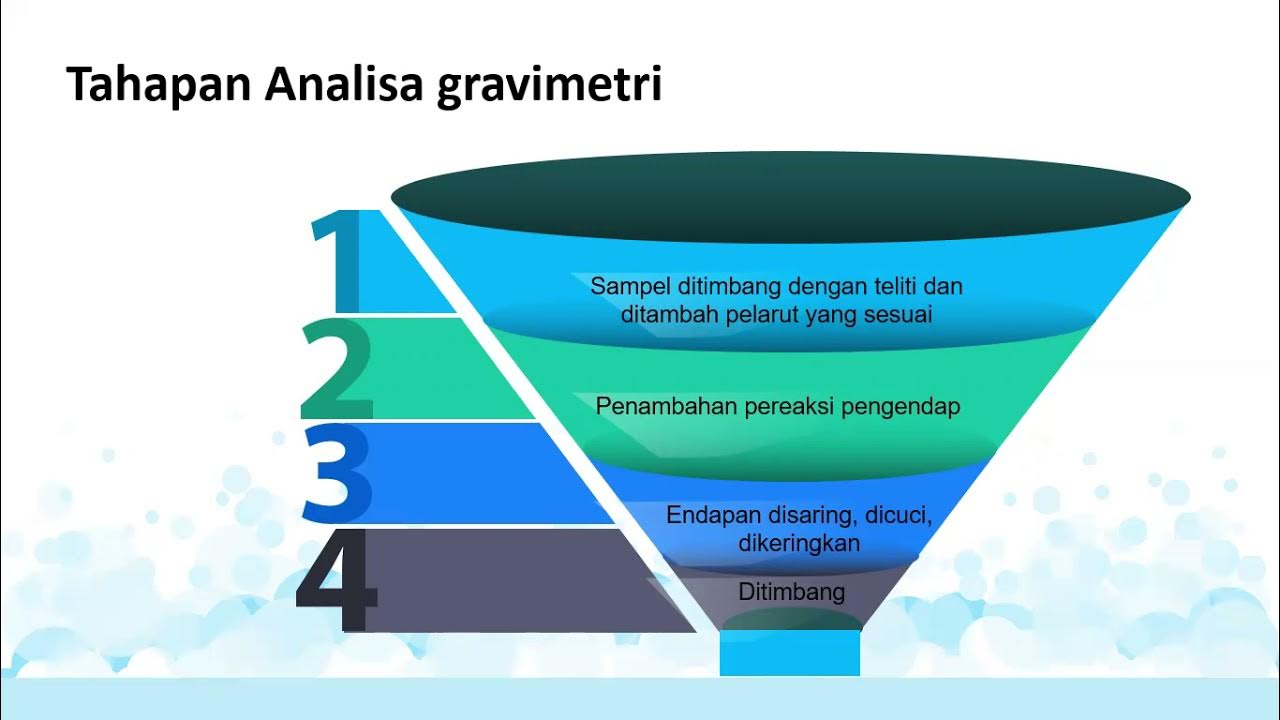
- 😀 Gravimetric analysis is a method used to determine the concentration of specific ions in a sample by measuring the mass of precipitates.
- 📊 The formula for calculating the concentration of an ion involves the mass of the precipitate, the gravimetric factor, and the mass of the sample.
- 🔬 The gravimetric factor is calculated using the atomic weight of the ion divided by the molar mass of the precipitate formed.
- 🧪 An example calculation was provided for determining the concentration of chloride ions using silver chloride (AgCl) as the precipitate.
- ⚖️ Accurate measurements of both the sample and precipitate are crucial for reliable results in gravimetric analysis.
- 📈 The video highlighted the importance of understanding and correctly applying formulas for gravimetric calculations.
- 📝 Step-by-step examples demonstrated how to derive the gravimetric factor and calculate ion percentages.
- 💡 The presenter emphasized that the concentration of ions can be significant, especially for toxic elements like lead.
- 🔍 Practice problems were encouraged to enhance understanding and application of the gravimetric analysis method.
- 🎓 The session aimed to build foundational knowledge for students in analytical chemistry regarding gravimetric techniques.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video focuses on calculating the concentration of substances in a sample using gravimetric analysis.
How is the gravimetric factor used in calculations?
-The gravimetric factor is calculated by dividing the atomic mass of the component being analyzed by the molar mass of the precipitate formed.
What is the formula for calculating the percentage of a component in a sample?
-The formula is: (weight of precipitate × gravimetric factor / weight of sample) × 100.
What is the significance of weighing the precipitate?
-Weighing the precipitate allows for the determination of the amount of the target ion in the original sample.
In the example provided, what was the sample weight and what ion was being analyzed?
-The sample weight was 8.5 grams, and the ion being analyzed was chloride (Cl).
How do you calculate the molar mass of a compound in gravimetric analysis?
-To calculate the molar mass, sum the atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound's formula.
What was the calculated percentage of lead (Pb) in the second example given?
-The calculated percentage of lead (Pb) in the sample was 15.32%.
Why is it important to ensure the accuracy of measurements in gravimetric analysis?
-Accuracy is crucial because small errors in measurement can lead to significant discrepancies in the final concentration calculations.
What can the presence of heavy metals in water samples indicate?
-The presence of heavy metals, such as lead, in water samples can indicate pollution and pose serious health risks.
What is the conclusion drawn about the analysis methods discussed in the video?
-The video concludes that gravimetric analysis is a straightforward method for determining the concentration of substances, provided the calculations and procedures are followed accurately.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

PEKI4205 Kimia Analitik I - Analisis Gravimetri

How to do Gravimetric Analysis in Chemistry (with calculations and examples!)

ANALISIS GRAVIMETRI (PART 2) Perhitungan Gravimetri Metode Pengendapan

Melaksanakan Analisis Gravimetri Konvensional Mengikuti Prosedur - Teknik Kimia

Analisis kuantitatif potensiometri
Analisa Gravimetri
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
