JENIS GAYA PADA HUKUM NEWTON
Summary
TLDRIn this physics lesson, the instructor, Pak Kahfi, explores Newton's laws and the various types of forces. He explains fundamental concepts such as weight, normal force, friction, and tension, illustrating each with clear examples. The session emphasizes the difference between mass and weight, highlighting how gravitational forces affect objects differently on Earth and the Moon. Engaging visuals and practical demonstrations accompany the explanations, making complex ideas accessible. The lesson encourages viewers to participate by completing exercises related to the types of forces discussed, promoting interactive learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 Forces are defined as pushes or pulls that cause a change in an object's position or shape.
- 😀 Force is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
- 😀 The unit of force is the Newton (N), and it can be measured using a dynamometer.
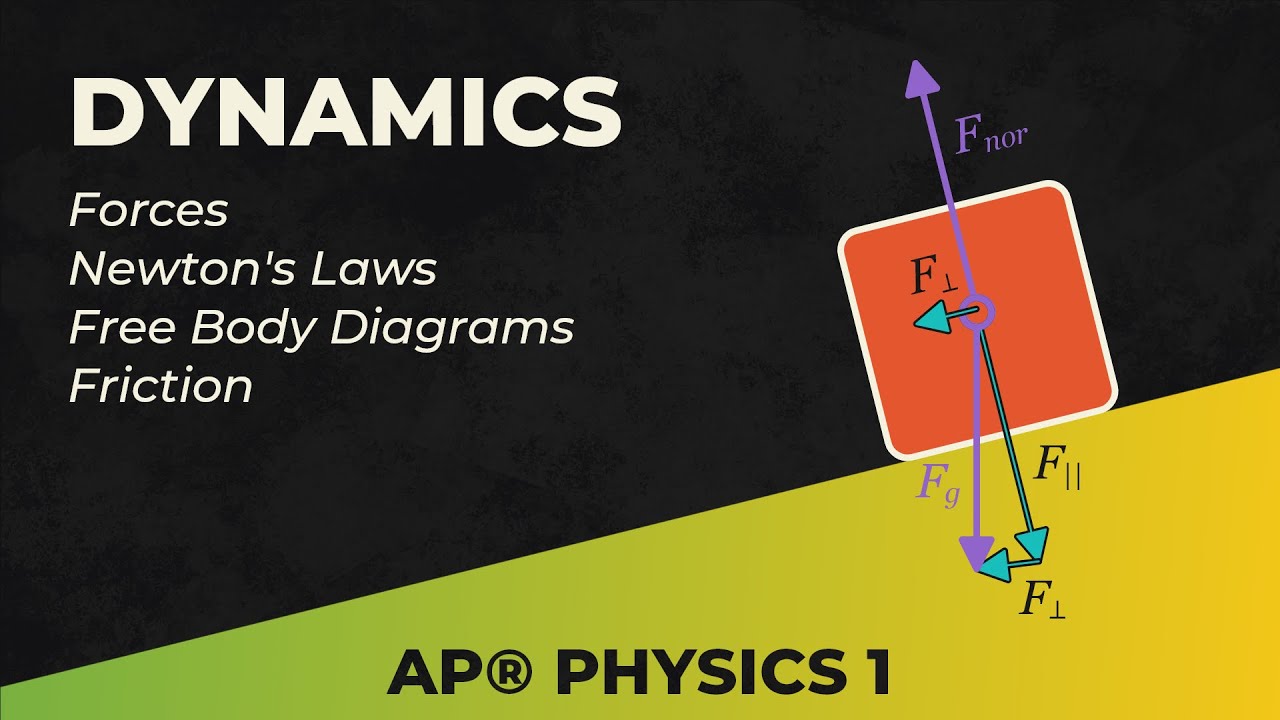
- 😀 Different types of forces include gravitational force (weight), normal force, frictional force, and tension force.
- 😀 Weight is calculated using the formula W = m × g, where m is mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
- 😀 Mass remains constant regardless of location, while weight varies depending on the gravitational field strength.
- 😀 Normal force acts perpendicular to the surface on which an object rests, counteracting gravity.
- 😀 Frictional force opposes the motion of an object and depends on the nature of the surfaces in contact.
- 😀 Tension force occurs in ropes or strings when they are pulled taut, acting in the direction of the rope.
- 😀 Understanding these forces is crucial for analyzing motion according to Newton's laws.
Q & A
What is the definition of force in physics?
-Force is defined as a push or pull on an object that results in a change in its position or shape.
What are the units of force and how are they represented?
-The unit of force is the Newton, represented by 'N'.
What is the difference between mass and weight?
-Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant regardless of location, while weight is the force exerted by gravity on that mass and can vary based on gravitational pull.
How is weight calculated?
-Weight is calculated using the formula W = m × g, where W is weight, m is mass, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
What is the direction of gravitational force?
-Gravitational force always acts towards the center of the Earth.
What does 'normal force' refer to?
-Normal force is the support force exerted by a surface that is perpendicular to the object resting on it.
What is the role of frictional force?
-Frictional force opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact, acting in the opposite direction of the movement.
What is tension in the context of forces?
-Tension is the force transmitted through a string, rope, or cable when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends.
How does the angle of inclination affect the forces acting on an object?
-The angle of inclination affects the components of gravitational force acting along the slope, which influences both normal force and friction.
What are the key types of forces discussed in the lesson?
-The key types of forces discussed include gravitational force, normal force, frictional force, and tension force.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)