Frekuensi Pernapasan, Volume Pernapasan dan Gangguan pada Sistem Pernapasan
Summary
TLDRThis educational video on the respiratory system explores key concepts such as respiratory frequency, influenced by age, gender, activity level, body position, and temperature. It details various respiratory volumes, including tidal volume and reserves, highlighting their importance in lung capacity. Additionally, the video addresses several respiratory disorders like asthma, pneumonia, and tuberculosis, explaining their impacts on breathing. The speaker invites viewers to continue learning about related topics, making the content both informative and engaging for students interested in biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Breathing frequency varies among individuals and is influenced by factors like age, gender, activity level, body position, and body temperature.
- 😀 As people age, their breathing frequency generally decreases due to reduced energy expenditure.
- 😀 Men typically have a higher breathing frequency than women, attributed to greater energy demands.
- 😀 Physical activities increase breathing frequency, as more oxygen is needed for energy production.
- 😀 Standing requires more energy than sitting or lying down, resulting in higher breathing frequency in that position.
- 😀 Elevated body temperature, such as during fever, leads to an increased breathing frequency due to higher oxygen needs.
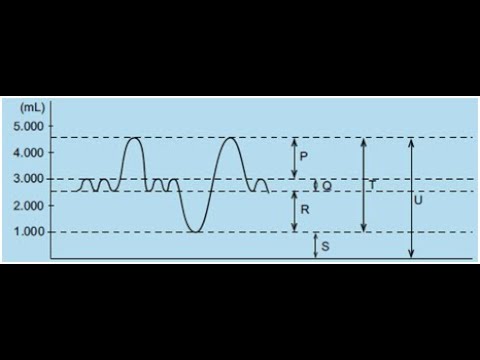
- 😀 Tidal volume refers to the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing, averaging around 500 ml.
- 😀 Complementary volume is the maximum air intake during deep inhalation, about 1500 ml.
- 😀 Residual volume is the air remaining in the lungs after exhalation, typically around 1000-1500 ml, preventing lung collapse.
- 😀 Total lung capacity combines vital capacity and residual volume, averaging around 4500 ml.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video discusses the respiratory system, including respiratory frequency, volume, and disorders.
What factors influence respiratory frequency?
-Respiratory frequency is influenced by age, gender, activity level, body position, and body temperature.
How does age affect respiratory frequency?
-As a person ages, their respiratory frequency tends to decrease due to lower energy expenditure.
What difference exists in respiratory frequency between genders?
-Generally, men have a higher respiratory frequency than women because they require more energy.
How does physical activity affect respiratory rate?
-Physical activities, such as sweeping or watering plants, increase respiratory frequency compared to inactivity.
What body position has the highest respiratory frequency?
-Standing has the highest respiratory frequency, followed by sitting, with lying down having the lowest.
What is tidal volume?
-Tidal volume is the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing, typically around 500 ml.
What are the components of lung capacity mentioned in the video?
-The lung capacity includes tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and expiratory reserve volume, totaling about 3500 ml.
What is the significance of residual volume?
-Residual volume is the air that remains in the lungs after exhalation, preventing lung collapse.
What are some respiratory disorders mentioned?
-The video mentions disorders such as pharyngitis, laryngitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, pleuritis, influenza, asthma, pneumonia, tuberculosis, and asphyxia.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

IPA Kelas 8 : Sistem Pernapasan 3 (Frekuensi dan Volume Pernapasan)

Faktor yang mempengaruhi Frekuensi Pernapasan

Mekanisme Pernapasan Manusia, Frekuensi Pernapasan dan Volume Pernapasan

FAKTOR YANG MEMPENGARUHI FREKUENSI PERNAPASAN MANUSIA
SISTEM PERNAPASAN MANUSIA PART 2 (Mekanisme, Frekuensi dan Volume Pernapasan)

FREKUENSI PERNAPASAN | SISTEM PERNAPASAN MANUSIA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
