Grade 8 Social sciences: Scramble for Africa
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the causes of the Scramble for Africa, highlighting economic interests, technological superiority, political rivalries, and ideological motivations among European powers. The Industrial Revolution spurred demand for African resources, while advances in military technology facilitated colonial expansion. Key figures like Otto von Bismarck played significant roles, particularly in organizing the Berlin Conference, which partitioned Africa without African representation. The legacy of this scramble continues to impact the continent, raising important discussions about colonialism's effects and the dynamics of global power.
Takeaways
- 🌍 European interest in Africa began during the Age of Exploration in the 15th century, driven by economic motives and the transatlantic slave trade.
- 🛠️ The Industrial Revolution increased demand for raw materials from Africa, prompting European nations to expand their colonial empires.
- 🚢 Technological advancements in transportation and military technology provided Europeans with significant advantages over African states.
- 🏛️ Nationalism and imperialism fueled competition among European powers, leading to a scramble for African territories as a symbol of prestige and power.
- 💰 Economic interests were the primary motivation for colonization, focusing on the exploitation of Africa's natural resources.
- ⚔️ Political rivalries among European nations intensified the competition for dominance in Africa, impacting international relations.
- ✝️ Ideological motivations, including a perceived civilizing mission and missionary activities, played a role in justifying colonization efforts.
- 📜 Bismarck's role in the Berlin Conference of 1884-1885 was crucial in regulating the partitioning of Africa among European powers.
- 🔍 Despite Germany's initial disinterest in colonialism, Bismarck recognized its strategic and economic benefits by the 1880s.
- 🗺️ Africans were not consulted in the Berlin Conference; they were viewed as obstacles to be 'civilized' rather than partners in the process.
Q & A
What was the main economic motivation behind the Scramble for Africa?
-The primary economic motivation was the increased demand for raw materials driven by the Industrial Revolution, as European powers sought to exploit Africa's vast resources.
How did technological advancements influence European colonization of Africa?
-Technological advancements, such as steamships, railways, and military technologies like machine guns, gave European powers a significant advantage, enabling them to penetrate deeper into Africa.
What role did nationalism play in the Scramble for Africa?
-Nationalism fueled competition among European nations to acquire colonies, which were seen as symbols of national prestige and power.
What were the ideological motivations that justified the colonization of Africa?
-Europeans believed in the superiority of their culture and civilization, seeing their mission as a civilizing effort to save Africans from perceived barbarism.
What was the significance of the Berlin Conference in the context of the Scramble for Africa?
-The Berlin Conference, called by Bismarck in 1884-1885, regulated the partitioning of Africa among European powers, allowing them to divide the continent without African consent.
How did the transatlantic slave trade impact European interests in Africa?
-The transatlantic slave trade established European presence in Africa, leading to the creation of coastal trading ports, which later transitioned to resource extraction after the abolition of slavery.
In what ways did political rivalries among European powers contribute to the Scramble for Africa?
-Political rivalries intensified competition for colonial acquisitions, as nations sought to enhance their influence and power on the global stage through territorial expansion.
What role did missionaries play in the colonization of Africa?
-Missionaries justified colonization by promoting the conversion of Africans to Christianity and supporting European values, often collaborating with colonial authorities.
How did Bismarck's views on colonialism change over time?
-Initially skeptical of colonial ventures, Bismarck recognized their strategic and economic benefits by the 1880s and began to support Germany's colonial ambitions in Africa.
Were Africans involved in the decision-making processes during the Berlin Conference?
-No, Africans were not invited to the Berlin Conference and had no say in the decisions regarding the partition of their continent, which was treated as a resource to be exploited by European powers.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Causes of Colonization in Africa | Industrial Revolution, Imperialism, and Racism.

Second Wave IMPERIALISM, Explained [AP Euro Review—Unit 7 Topic 6]

Scramble for Africa | World History | Lecture - 7 | UPSC | GS History by Aadesh Singh

Imperialism's GLOBAL EFFECTS [AP Euro Review—Unit 7 Topic 7]

Imperialismo na África
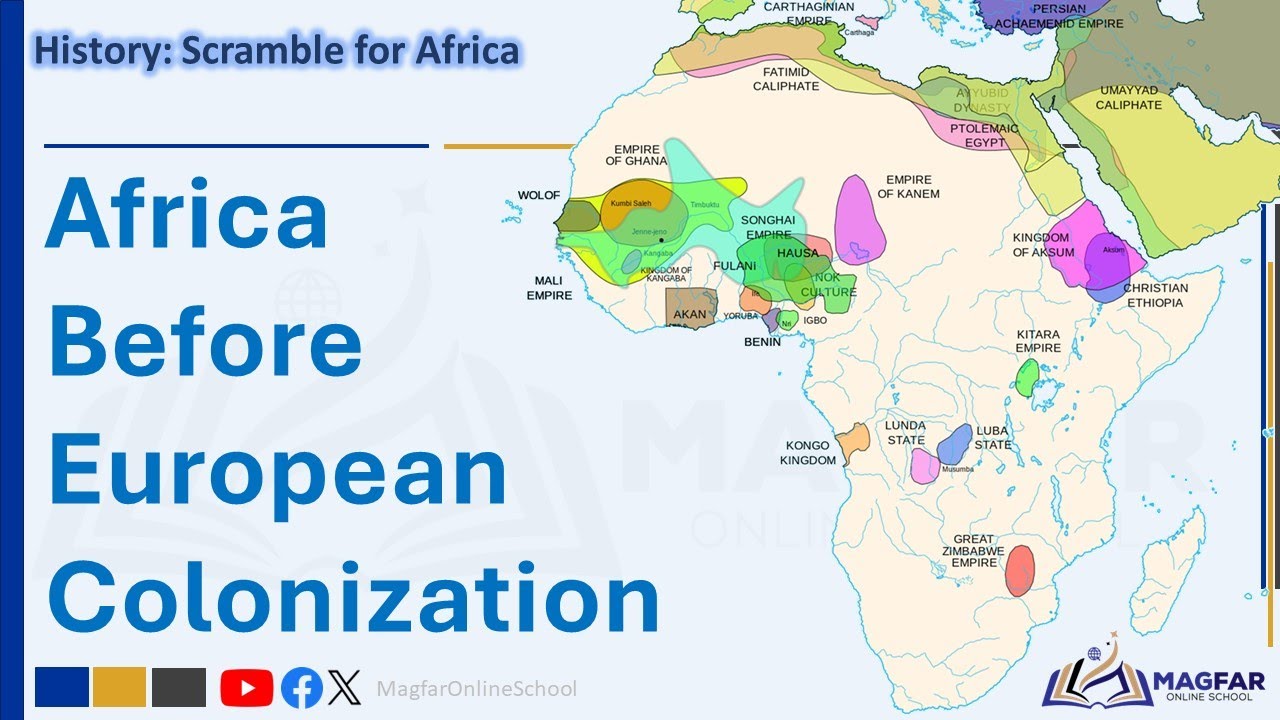
Scramble for Africa: Africa before European Colonization. Grade 8 Term 3 History.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
