Sistemas amortiguadores
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Andrea Medeiros discusses buffer systems, focusing on their role in maintaining pH balance in living organisms and various substances. She explains the concept of pH, the importance of buffers, and how they work to resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added. The video delves into the chemical principles behind buffering, the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, and various types of buffer systems, such as phosphate and bicarbonate buffers, in biological contexts. Real-world examples, like titration curves, are used to illustrate how buffers operate in different environments, emphasizing their importance in maintaining homeostasis in the body.
Takeaways
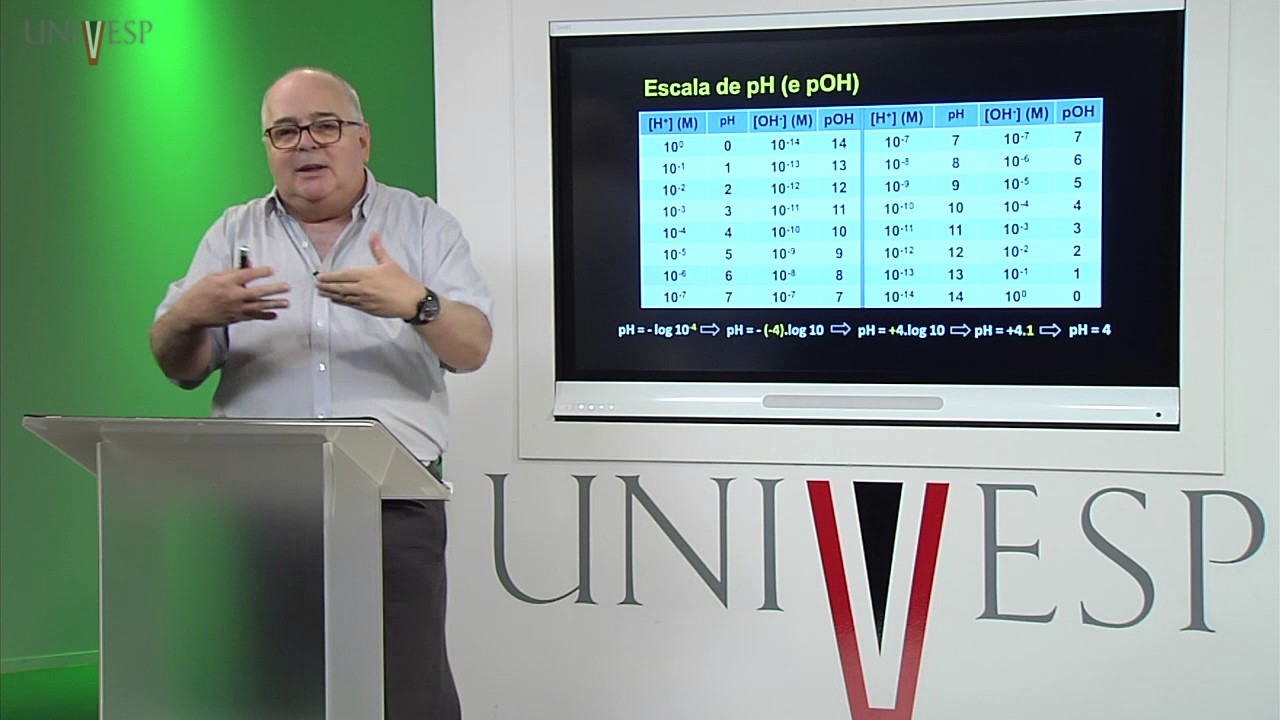
- 😀 The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of substances, with examples from household products, natural environments, and biological systems.
- 😀 pH is critical in the human body, as it influences enzyme activity and the function of various systems like digestion, lubrication, and oxygen transport.
- 😀 The pH of biological fluids like plasma is tightly regulated around 7.40, with a narrow range (7.35-7.45) essential for proper bodily function.
- 😀 Acidosis and alkalosis occur when the pH deviates from its normal range, affecting protein function and cellular stability.
- 😀 Metabolism produces acidic compounds, including fixed acids like sulfuric acid and volatile acids like carbon dioxide, which can alter pH levels.
- 😀 Buffer systems in the body, such as phosphate and bicarbonate buffers, help maintain pH balance by neutralizing added acids or bases.
- 😀 A buffer system consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base, and its effectiveness is maximized when the pH equals the pKa of the acid.
- 😀 The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates pH, pKa, and the ratio of acid to conjugate base, helping to predict buffer behavior in response to pH changes.
- 😀 The buffering capacity of a solution depends on the concentrations of acid and base; higher concentrations provide better buffering.
- 😀 Titration curves visually demonstrate the buffering capacity, showing the pH change when adding acid or base to a buffer solution.
- 😀 Different buffers are suitable for different pH ranges, and the selection of a buffer system depends on the target pH for maintaining stability.
Q & A
What is the role of pH in biochemical systems?
-pH plays a crucial role in biochemical systems by affecting chemical reactions, enzyme efficiency, and cellular functions. Most biochemical processes are pH-sensitive, requiring specific pH ranges for optimal activity.
What are the common pH ranges for substances in nature and living organisms?
-Substances in nature and living organisms show a wide range of pH values. For example, detergents and cleaning products have a basic pH, milk and egg whites are near neutral, while citrus juices like orange and lemon juice have acidic pH values. Natural water bodies can range from acidic in areas of acid rain to basic in saline lakes.
What is acidosis, and how does it affect the body?
-Acidosis occurs when the pH of the blood drops below 7.35, indicating an excess of protons. This condition can disrupt various physiological processes, including enzyme activity, membrane stability, and protein function.
What is the pH range compatible with human life?
-The pH range compatible with human life is between 6.8 and 7.8. Any significant deviation from this range can affect critical bodily functions and even be life-threatening.
What are buffer systems and why are they important in the human body?
-Buffer systems are mixtures of weak acids and their conjugate bases that help resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added. These systems are essential in the body to maintain stable pH levels in fluids like blood, which is necessary for proper enzyme function and metabolic processes.
How does the bicarbonate buffer system work?
-The bicarbonate buffer system helps regulate pH by balancing carbonic acid (H2CO3) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). When excess protons are added to the blood, bicarbonate neutralizes them, forming carbonic acid, which is then exhaled as CO2.
What is the equation of Henderson-Hasselbalch and why is it important?
-The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is: pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]). It relates the pH of a buffer solution to the concentrations of the acid (HA) and its conjugate base (A-). This equation is crucial for calculating the pH of buffer systems and understanding their buffering capacity.
What is the significance of the pKa value in buffer systems?
-The pKa value represents the pH at which an acid and its conjugate base are present in equal concentrations. It is important because the buffering capacity of a solution is highest when the pH is equal to the pKa value, ensuring maximum effectiveness in maintaining stable pH.
What happens during the titration of an acid with a strong base?
-During the titration of an acid with a strong base, the pH gradually increases as the base neutralizes the acid. At the equivalence point, all the acid has been neutralized, and the pH sharply rises. The region around the equivalence point is where buffering occurs.
Why is the phosphoric acid buffer system effective at pH 7?
-The phosphoric acid buffer system is effective at pH 7 because one of its dissociation equilibria has a pKa value close to 7, making it capable of buffering pH changes in this range, which is essential for maintaining blood pH.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Acid Base Physiology | Part One | Basics | Buffers | Renal Physiology

SOLUÇÃO TAMPÃO | EQUILÍBRIO QUÍMICO | Aula 26

Buffers (A-level IB Chemistry)

Larutan Penyangga • Part 1: Sifat, Komponen & Peran Larutan Buffer / Penyangga
Bioquímica - Aula 03 - Alguns conceitos químicos importantes - 2

PERANAN LARUTAN PENYANGGA DALAM KEHIDUPAN SEHARI-HARI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
