Alpha, Beta and Gamma Radiation demo - GCSE Physics
Summary
TLDRThis video demonstrates the penetration and ionizing abilities of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation using a Geiger-Muller tube. The presenter shows how different sources, such as americium (alpha emitter), strontium-90 (beta emitter), and radium-226 (which emits all three), interact with materials like paper, aluminum, and lead. Safety precautions, like distance and exposure time, are emphasized to minimize radiation risk. The video also explains the difference between radiation and contamination, highlighting the importance of shielding and how ionization relates to the danger posed by different types of radiation.
Takeaways
- 💡 Radiation safety is important, but there’s no need to fear it as long as you follow safety precautions such as minimizing exposure time and keeping distance from radioactive sources.
- 📊 Background radiation is always present at low levels, and radiation exposure from sources should be compared to this baseline.
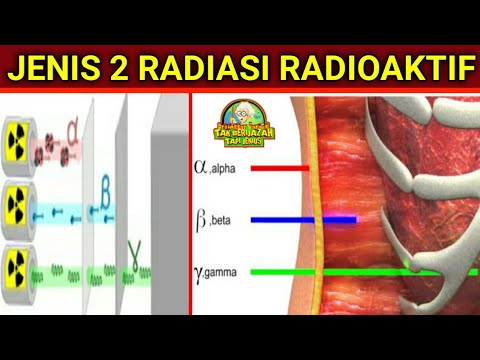
- 🔍 Americium is mainly an alpha emitter with low penetration, easily stopped by thin paper, and has a very short range in air (about 4 cm).
- 🧪 Strontium-90 is a beta emitter, with beta particles being more penetrating than alpha particles but stoppable by 2 mm of aluminum.
- ⚛️ Radium-226 emits alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. Gamma radiation can only be blocked by thick lead, whereas paper and aluminum reduce alpha and beta emissions.
- 🚧 Gamma radiation is highly penetrating but less ionizing compared to alpha and beta, making it more dangerous over long distances but less ionizing.
- 🛡️ The ionizing ability of radiation is inversely proportional to its penetrating power: alpha particles are highly ionizing but have low penetration, while gamma radiation is the opposite.
- ⚠️ Alpha radiation is only dangerous if ingested or inhaled, while beta particles can penetrate the body but are less ionizing.
- 👗 Clothing and skin are effective barriers against external alpha radiation, but contamination with radioactive material can cause internal exposure.
- ⏲️ To minimize radiation exposure, always limit your time near sources and maintain a safe distance to reduce the radiation dose.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the demonstration in the script?
-The purpose of the demonstration is to show the different penetrating abilities of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation using various radioactive sources, and to explain how their ionizing abilities are linked to their penetration power.
How does the presenter ensure safety when handling radioactive sources?
-The presenter ensures safety by limiting time of exposure, maintaining a good distance from the sources, and keeping the radioactive materials a couple of meters away when not in use.
What is background radiation, and how is it relevant to the experiment?
-Background radiation refers to the natural radiation present in the environment, typically around 15-20 counts per minute. It is relevant to the experiment as a baseline for comparing the radiation levels from the radioactive sources.
What is the primary radiation emitted by the americium source, and how is it stopped?
-The americium source primarily emits alpha radiation. Alpha particles have a short range in air and can be stopped by a thin piece of paper.
How does the beta radiation emitted by strontium-90 differ in penetration from alpha radiation?
-Beta radiation from strontium-90 can penetrate further than alpha radiation. It is not significantly blocked by paper, but it can be stopped by about two millimeters of aluminum.
Why does radium emit all three types of radiation (alpha, beta, and gamma)?
-Radium-226 is a radioactive isotope that decays by emitting all three types of radiation—alpha, beta, and gamma—allowing the demonstration to showcase the different penetrating abilities of each radiation type.
What material is used to block gamma radiation, and why is it needed?
-Thick lead is used to block gamma radiation because gamma rays have a very high penetrating ability. A few centimeters of lead are needed to stop most of the gamma radiation.
How is ionization related to the penetration power of radiation?
-Ionization and penetration power are inversely related. More ionizing radiation, like alpha particles, has less penetrating power because it loses energy quickly by ionizing atoms in its path. Less ionizing radiation, like gamma rays, penetrates further because it ionizes less and retains more energy.
Why is alpha radiation considered dangerous inside the body but less so outside?
-Alpha radiation is highly ionizing but has very low penetration power, so it is not dangerous outside the body as it can be stopped by skin or even air. However, if alpha-emitting material enters the body, it becomes dangerous because it can ionize cells internally, potentially causing significant damage.
What is the difference between radiation and contamination in this context?
-Radiation refers to the emission of energy from a radioactive source, while contamination occurs when radioactive material physically attaches to a person or object. In the video, the presenter avoids contamination by not touching the radioactive sources and staying at a safe distance, ensuring no radioactive material gets on his body.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)