[BASIC FEATURES] Tax closing
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of tax closing, a legal process for businesses to settle taxes either monthly or quarterly. It covers how to calculate the balance between taxes received from customers and taxes paid to vendors, and how to submit the tax report. The video also demonstrates the process of settling tax accounts, using VAT accounts as an example. The steps for automating this in Odoo software, including setting up tax configurations, closing journal entries, and sending reports to tax authorities, are also detailed.
Takeaways
- 📊 Tax closing is a necessary process for companies to submit their tax reports, either monthly or quarterly.
- 💡 The tax closing involves calculating the total taxes received from customer invoices and paid through vendor bills, determining if more tax needs to be paid or refunded.
- 📋 In the software (ODOO), taxes paid and received are accumulated in the tax report using the tax grid for proper calculations.
- 🔄 The tax closing entry is crucial for settling tax accounts and transferring any remaining amounts into the VAT current account.
- 🔍 Accounting-wise, customer invoices and vendor bills increase the tax paid or received in respective tax accounts, which need to be settled at the end of the period.
- 📈 At the end of each period, tax accounts should be balanced to zero, with the remaining difference moved to the VAT current account, representing either a payable or receivable amount.
- 🔧 The periodicity of tax reports can be configured within the software, accommodating different reporting requirements like monthly, quarterly, or even bi-monthly.
- 📑 You can generate a tax closing journal entry automatically through the tax report function, ensuring that all tax accounts are settled correctly.
- ⚠️ Once the tax closing entry is posted, a tax lock date is set, preventing further changes to the tax report for that period.
- 🌐 The software supports direct submission of tax reports to certain legal authorities' websites (e.g., HMRC in the UK) or allows for exporting the necessary XML files for manual submission.
Q & A
What is tax closing?
-Tax closing is the process of settling all tax accounts at the end of a reporting period (monthly or quarterly) by calculating the total taxes received from customer invoices and the taxes paid on vendor bills. The difference determines if you need to pay or reclaim taxes.
How does a company determine whether to pay additional tax or reclaim tax during tax closing?
-A company compares the total tax received from customer invoices with the total tax paid on vendor bills. If the tax received exceeds the tax paid, the company needs to pay the difference to the government. If the tax paid is higher, the company can reclaim the excess tax.
What role do tax credits play in tax closing?
-Tax credits are recorded in the tax configurations and are used to compute the total tax amounts in the tax report. The tax closing entry ensures that these amounts are settled in the tax accounts.
What happens to the tax accounts during the tax closing entry?
-During tax closing, the tax accounts are settled to ensure their balances are zero. The remaining amount, representing the difference between taxes paid and received, is transferred to the VAT current account.
What is the VAT current account, and when is it used?
-The VAT current account records the remaining balance after settling the tax accounts. If a company has received more tax than it has paid, it records the balance as an amount owed to the government. If it has paid more, it records the balance as a receivable.
How does the tax closing process work automatically in Odoo?
-In Odoo, the tax closing process can be done automatically through the tax report feature. Once the configuration is complete, the system calculates the closing journal entry, settles the accounts, and transfers the remaining amount to the VAT current account.
What is a tax log date, and why is it important?
-The tax log date ensures that no entries affecting the tax report are made after the tax period has been closed. Once the tax report is submitted, the log date prevents any further changes to avoid altering the declared taxes.
Is it possible to change the tax periodicity in Odoo?
-Yes, Odoo allows you to configure different tax periodicities, such as monthly, quarterly, or every two months, depending on the legal requirements of the country.
Can Odoo directly send tax reports to legal authorities?
-Yes, in some countries, Odoo can directly send tax reports to the relevant authorities. For example, in Belgium, Odoo generates an XML file that can be uploaded to the tax platform, and in the UK, Odoo can send the report directly to HMRC.
What happens if a mistake is found in the tax report after submission?
-If a mistake is found in the tax report after submission, it cannot be altered for that period. Corrections must be made in the next reporting period.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

TUTORIAL PEMBUATAN E-BILLING DAN PELAPORAN PPH 25 DI CORETAX | KELOMPOK 2
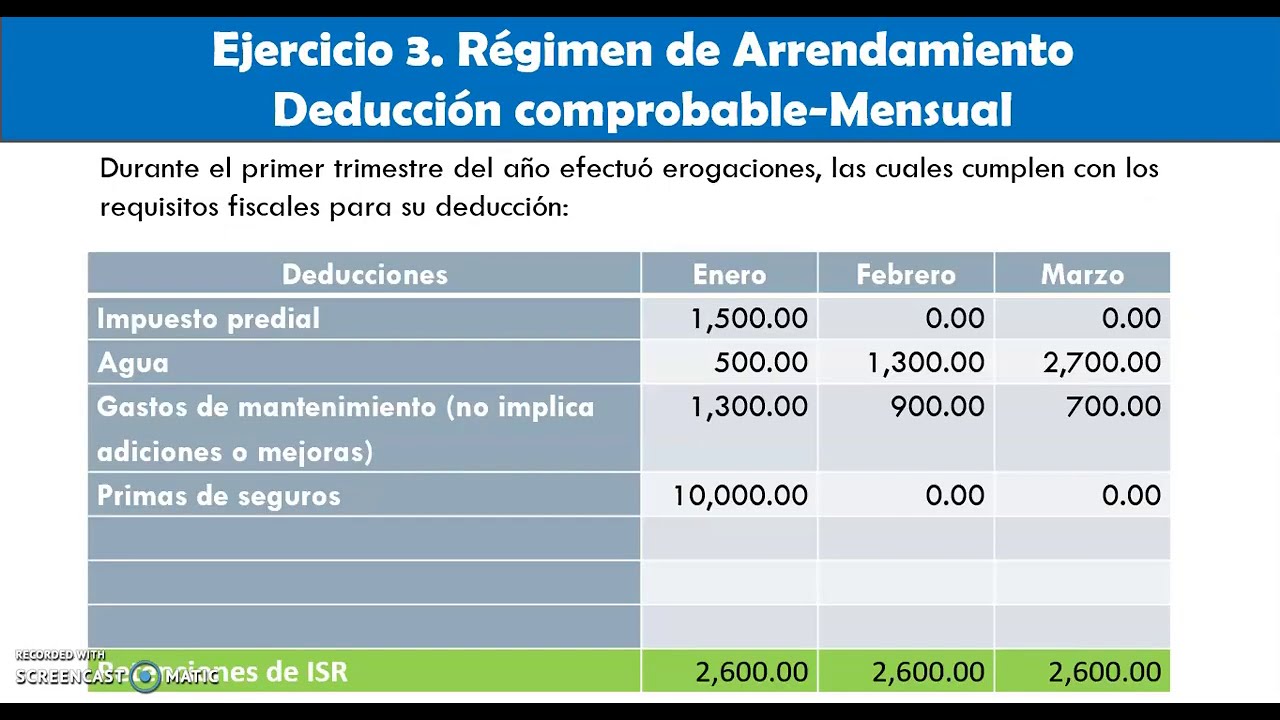
Pagos provisionales de ISR en Régimen de Arrendamiento parte 2

Pemilik UD Pramono Pilih Tutup Usaha Usai Ditagih Pajak Rp 670 Juta, Ini Kata Dirjen Pajak

Apa Itu Pajak Masukan dan Pajak Keluaran dalam PPN? - ConTAXtual Eps 9

Prestação de SERVIÇOS para o EXTERIOR | Saiba como PAGAR MENOS IMPOSTOS na prática!

PPh Pasal 25: Pengertian, Perhitungan, Penyetoran dan Pelaporan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
