Photosynthesis and Respiration
Summary
TLDRThis Biology Essentials video explores free energy capture and storage, focusing on photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Photosynthesis, prevalent in areas like the Amazon and northern regions, involves autotrophs capturing sunlight to produce sugars and oxygen. Heterotrophs, like humans, rely on cellular respiration, using oxygen and sugars to generate ATP. The video also touches on chemosynthesis in deep-sea organisms and fermentation in winemaking, illustrating life's diverse energy strategies.
Takeaways
- 🌿 Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules.
- 🌍 The highest rates of photosynthesis occur in regions like the Amazon, eastern North America, and northern Europe and Asia, as well as in the ocean near the equator.
- 🔋 Autotrophs, such as plants, produce their own food through photosynthesis, while heterotrophs, like animals, obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
- 🌑 Chemosynthesis is a process used by some organisms in the deep ocean where light is scarce, utilizing chemical energy from compounds like hydrogen sulfide to produce carbohydrates.
- 🍇 Cellular respiration is how heterotrophs break down sugars in the presence of oxygen to release energy, resulting in carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
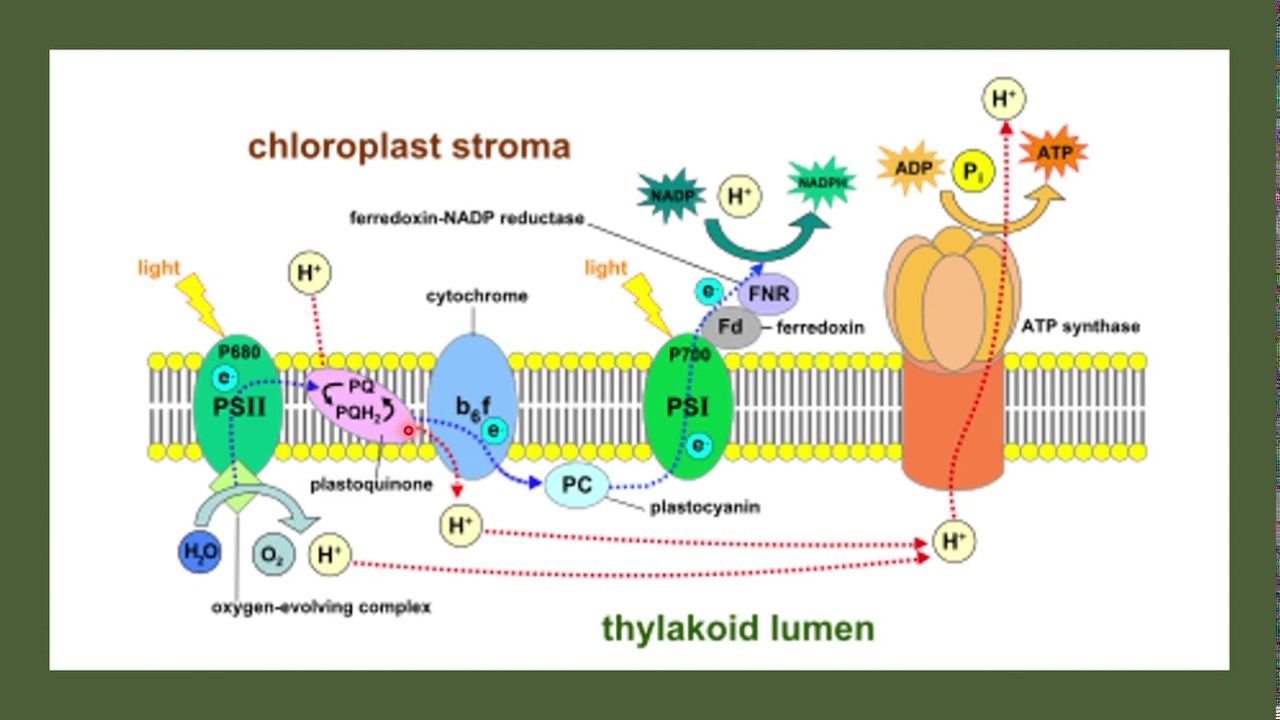
- 🌱 The Calvin Cycle is the part of photosynthesis that takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts, where carbon dioxide is fixed into glucose using the energy from ATP and NADPH.
- 💧 The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, where water is split to release oxygen and electrons, which are used to produce ATP and NADPH.
- 🔗 The process of photosynthesis can be summarized as the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, with energy from light stored in the glucose bonds.
- 🔄 Evolutionarily, the first life forms on Earth likely used photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, and around 2 billion years ago, significant amounts of oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere due to photosynthetic activity.
- 🔋 Cellular respiration involves glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, and the electron transport chain, which together break down glucose to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Q & A
What is the main focus of Biology Essentials Video 13?
-The main focus of Biology Essentials Video 13 is free energy capture and storage, with a significant emphasis on photosynthesis.
Where are the highest rates of photosynthesis found on Earth?
-The highest rates of photosynthesis are found in areas such as the Amazon in South America, eastern North America, northern Europe, and northern Asia, as well as in the ocean near the equator.
What is the role of respiration in the context of this video?
-Respiration is discussed as the process by which heterotrophs, including humans, use cellular respiration to convert sugars and oxygen into ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
What are the two life strategies mentioned in the video?
-The two life strategies mentioned are autotrophy, where organisms like plants make their own food through photosynthesis, and heterotrophy, where organisms like humans consume food made by others.
How do autotrophs capture energy from the sun?
-Autotrophs capture energy from the sun through two main processes: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin Cycle, which together are known as photosynthesis.
What is chemosynthesis and where does it occur?
-Chemosynthesis is a process used by certain organisms, like deep-sea tube worms, to capture energy from chemicals instead of light. It occurs in environments with limited light, such as deep ocean regions.
What is the role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
-The electron transport chain in cellular respiration is responsible for transferring electrons through a series of proteins, using their energy to pump protons and ultimately produce ATP.
How does fermentation differ from cellular respiration?
-Fermentation is an anaerobic process that does not require oxygen and is used by organisms when oxygen is scarce, such as in the production of wine or in muscle cells during intense exercise.
What is the significance of the red bands in 2.1 billion-year-old rocks mentioned in the video?
-The red bands in 2.1 billion-year-old rocks indicate the presence of appreciable amounts of oxygen, suggesting that photosynthesis was producing oxygen at that time.
What is the Calvin Cycle and where does it take place within a plant cell?
-The Calvin Cycle is the light-independent reaction of photosynthesis that uses the energy from ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into sugars. It takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast.
How does the process of photosynthesis relate to the production of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere?
-Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and certain bacteria produce oxygen as a byproduct, which has been a significant contributor to the oxygen levels in Earth's atmosphere over billions of years.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Celademhaling en fotosynthese

ATP - ADENOSINA TRIFOSFATO - ESTRUTURA E FUNÇÃO | Biologia com Samuel Cunha

VIE METABOLICHE - Respirazione Cellulare e Fotosintesi

Cell Structure and Function - Important Organelles | AP Biology 2.2

Molecular structure of glucose | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy
AP Biology Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Complete Review
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
