Physical Features of India | 10 Minutes Rapid Revision| Class 9 SST
Summary
TLDRThe video provides an engaging and detailed overview of the physical features of India, focusing on its physiographic divisions. It covers the Himalayan mountains, the Northern plains, the Peninsular plateau, the Indian desert, the coastal plains, and the island groups. The speaker highlights the formation, structure, and significance of these regions, encouraging viewers to visualize and deeply understand India's diverse geography. Additionally, the video emphasizes the importance of mountains, plains, plateaus, deserts, and islands for agriculture, resources, and natural beauty, making India a uniquely diverse nation.
Takeaways
- 🗻 The chapter on India's physical features is meant to be visualized and experienced rather than just read from a book.
- 🏔️ The Himalayas are one of the most prominent mountain ranges in the world, geologically young and still growing, formed by the collision of the Eurasian and Indo-Australian plates.
- ⛰️ The Himalayan ranges consist of three divisions: the Inner Himalayan (Himadri), Middle Himalayan (Himachal), and Outer Himalayan (Shivalik), each with distinct features and elevations.
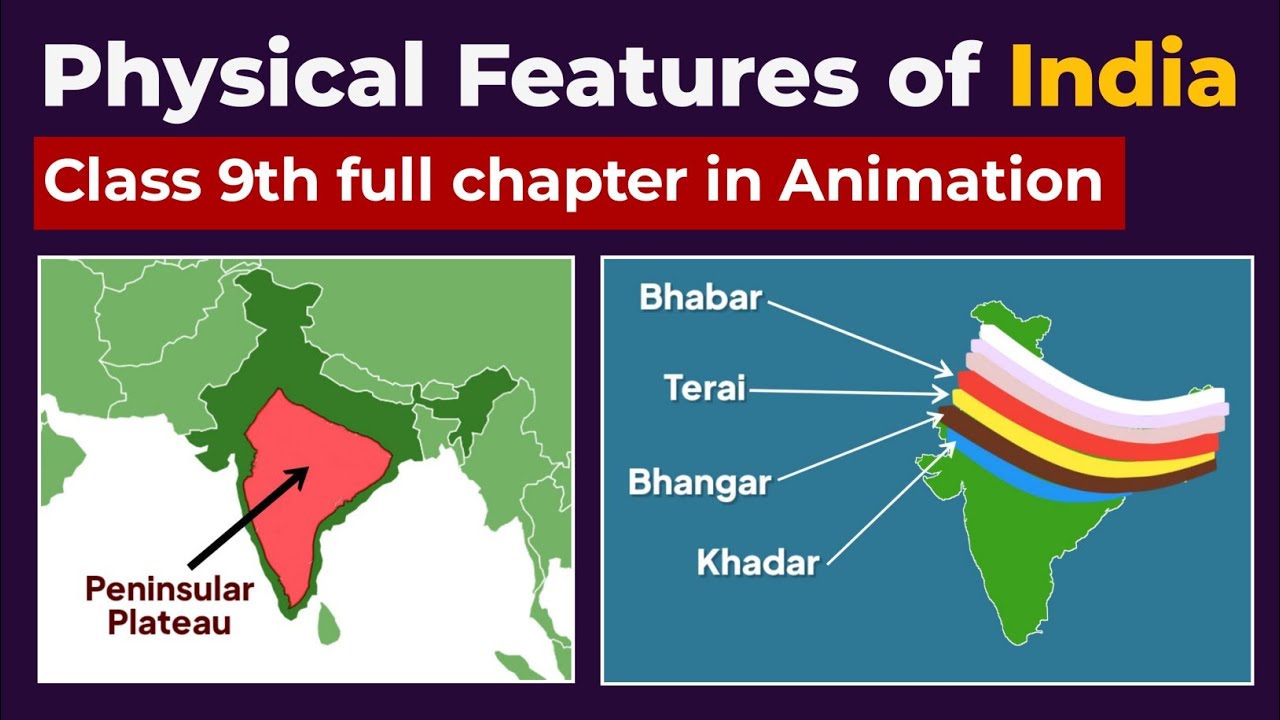
- 🌊 The Northern Plains, covering 7,000 square kilometers, were formed by the interplay of three rivers: the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra, making the region extremely fertile.
- 🏞️ The Northern Plains are divided into three sections: the western Indus river system, the central Ganga plains, and the eastern Assam plains around the Brahmaputra river.
- 🏜️ The Indian Desert lies west of the Aravalli Range and is an arid region with sand dunes and the Luni River being the only significant river.
- 🌍 The Peninsular Plateau is the oldest landmass in India, divided into the Central Highlands (north of the Narmada River) and the Deccan Plateau (south of the Narmada River), with rich mineral wealth.
- 🌴 India’s coastal plains include the Western Coastal Plains and Eastern Coastal Plains, with distinct characteristics such as estuaries on the western side and deltas on the eastern side.
- 🏝️ The two main island groups of India are the Lakshadweep Islands (coral origin) in the west and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (submerged mountain ranges) in the east, strategically significant due to their location.
- 🌾 The diverse physical features of India contribute to its greatness, providing fresh water, fertile land for agriculture, mineral wealth, and seafood resources.
Q & A
What is the main topic of this script?
-The main topic of the script is the geographical features of India, specifically covering the physical divisions such as the Himalayan Mountains, Northern Plains, Peninsular Plateau, Indian Desert, Coastal Plains, and the Island groups.
What are the three main ranges of the Himalayan Mountains?
-The three main ranges of the Himalayan Mountains are the Himadri (also known as Inner Himalayas or the Great Himalayas), the Himachal (Middle Himalayas), and the Shivalik (Outer Himalayas).
How did the formation of the Himalayan Mountains occur?
-The formation of the Himalayan Mountains occurred due to the collision between the Eurasian Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The mountain range is still growing as these plates continue to move.
What makes the Northern Plains of India fertile?
-The Northern Plains are fertile due to the deposition of silt and sediment by rivers originating from the Himalayan Mountains. These rivers, such as the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra, create rich alluvial soil ideal for agriculture.
How are the Northern Plains divided?
-The Northern Plains are divided into three broad sections: the Punjab Plains (dominated by the Indus River system), the Ganga Plains (between the Ghaghra and Teesta rivers), and the Assam Plains (along the Brahmaputra River).
What is unique about the Peninsular Plateau?
-The Peninsular Plateau is the oldest landmass of India, divided into the Central Highlands (north of the Narmada River) and the Deccan Plateau (south of the Narmada River). It is rich in minerals and features important rivers flowing towards the Bay of Bengal.
What distinguishes the Western and Eastern Ghats?
-The Western Ghats are higher, continuous, and form a steep edge, while the Eastern Ghats are lower, more broken, and are frequently interrupted by rivers like the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri.
What are the characteristics of the Indian Desert?
-The Indian Desert, located west of the Aravalli Mountains, is characterized by its arid climate, low rainfall, and sand dunes, with the Luni River being the only major river in the region.
What are the two major island groups of India?
-The two major island groups of India are the Lakshadweep Islands (in the Arabian Sea) and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (in the Bay of Bengal). Lakshadweep is of coral origin, while the Andaman and Nicobar Islands are considered submerged parts of mountains.
How do the different physiographic divisions of India contribute to the country’s resources?
-The mountains provide fresh water, the plains are fertile for agriculture, the plateau is rich in minerals, the deserts contribute to the country's ecosystem, the coastal regions support fishing, and the islands offer strategic and ecological importance.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

North & North East Mountains of India | Physiography of India | UPSC GS1

BENUA EROPA - Materi IPS SMP Kelas 9

WB Geography - 6 মিনিটে 1 ঘন্টার লেকচার কভার. Basic info, boundary, location, everything.
Physical Features of India Class 9 full Chapter in Animation | Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 | CBSE

ADR Law Lecture Revision Notes - Part 2. Alternative Dispute Resolution LLB Syllabus

Histologia do Pâncreas
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
