Plant Layout, Objectives of Plant Layout, Types of Plant Layout [Animated video]
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the concept of plant layout, which involves strategically arranging equipment, material, and manpower to optimize productivity. It outlines the objectives of plant layout, such as eliminating bottlenecks, minimizing material handling, and enhancing workspace safety. The video categorizes plant layouts into four types: process, product, combination, and fixed position, each with its advantages and disadvantages. For a detailed exploration, viewers are directed to part two and encouraged to download the PDF for further insights.
Takeaways
- 🌿 **Plant Layout Definition**: It's the strategic arrangement of equipment, materials, manpower, and services within a plant to optimize productivity.
- 🏭 **Scope of Plant Layout**: It encompasses everything from building design to the movement of worktables and material handling systems.
- 🔄 **Variability in Layout**: Even plants with similar operations may have different layouts due to factors like size, process nature, and management's approach.
- 🚫 **Objectives of Plant Layout**: Key goals include eliminating bottlenecks, minimizing material handling, reducing waiting time, increasing flexibility, utilizing space efficiently, improving work methods, ensuring workplace safety, and enhancing productivity.
- 🔄 **Line Balancing**: It's a method to prevent congestion by ensuring a smooth flow of work, thus minimizing unnecessary movements and delays.
- 🛠️ **Workstation Design**: It's crucial for reducing the physical effort of workers by minimizing their movements within the workspace.
- 🔄 **Productivity and Quality**: A well-planned layout can lead to increased productivity and better product quality while reducing production costs.
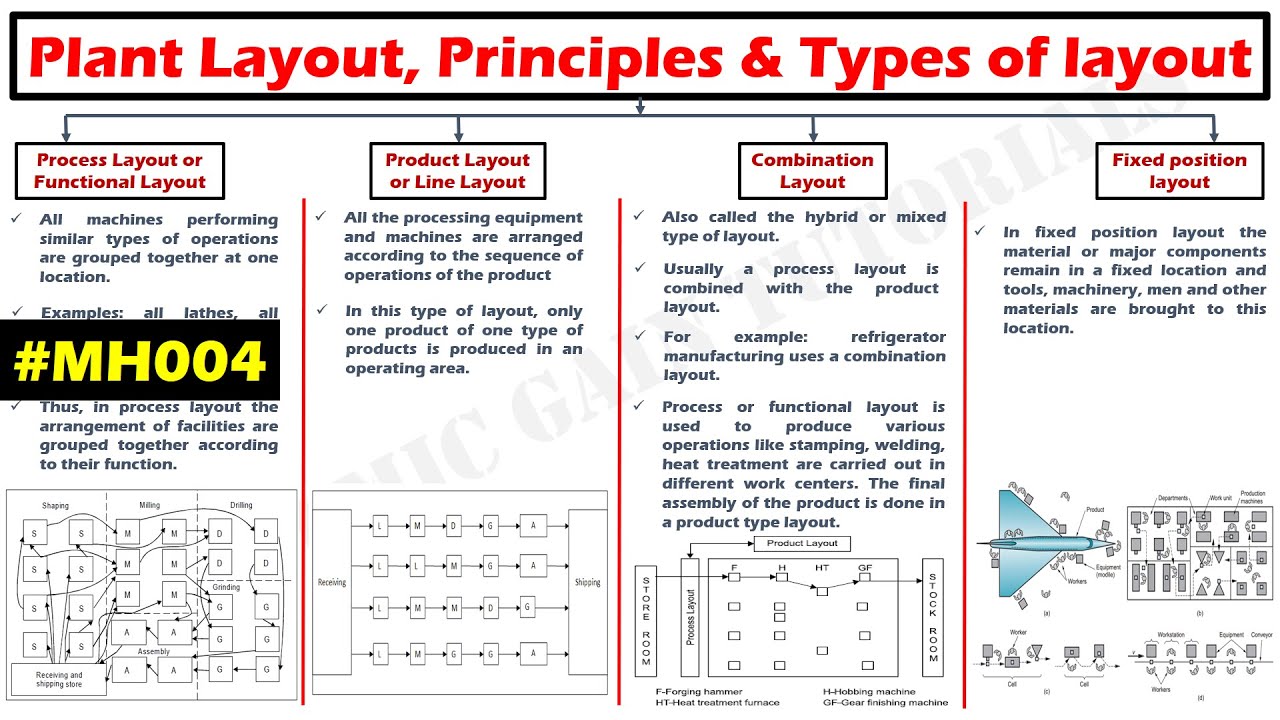
- 🏗️ **Types of Plant Layout**: The four main types are process layout, product layout, combination layout, and fixed position layout.
- 🔧 **Process Layout**: Machines are grouped by function, keeping similar machines and operations together for efficiency.
- 🔗 **Product Layout**: Also known as line layout, it sequences machines based on the production flow of the product.
- 🤝 **Combination Layout**: It merges the benefits of process and product layouts to optimize both functionality and flow.
- 🔩 **Fixed Position Layout**: Here, the product remains stationary while the equipment moves around it, which is ideal for large or immobile products.
Q & A
What is meant by plant layout?
-Plant layout refers to the strategic arrangement of equipment, materials, manpower, and other facilities and services within a plant's designated work area to optimize productivity.
What are the objectives of a good plant layout?
-The objectives of a good plant layout include eliminating bottlenecks, minimizing material handling and transportation, reducing worker movement, minimizing semi-finished product waiting time, increasing flexibility for product design changes, utilizing cubic space effectively, improving work methods, ensuring workplace safety, and increasing productivity with reduced production costs.
How does plant layout start and what does it encompass?
-Plant layout begins with building design and extends to the movement of work tables and material handling systems, covering all aspects of the physical arrangement within a plant.
Why might two plants with similar operations not have identical layouts?
-Two plants with similar operations may not have identical layouts due to differences in plant size, nature of the process, and management's approach and capabilities.
What is the purpose of line balancing in plant layout?
-Line balancing in plant layout aims to eliminate bottlenecks and points of congestion, ensuring a smooth workflow that minimizes material handling and transportation.
How does a good plant layout contribute to worker satisfaction?
-A good plant layout contributes to worker satisfaction by creating a safe, ventilated, and dust-noise-fume-free environment, which leads to better employer-employee relations.
What are the four types of plant layout mentioned in the script?
-The four types of plant layout mentioned are process layout, product layout, combination layout, and fixed position layout.
How are machines arranged in a process layout?
-In a process layout, similar machines and similar operations are kept in one place, with machines arranged according to their function.
What is the main characteristic of a product layout?
-A product layout, also known as line layout, involves arranging machines in a sequence that matches the production flow of raw materials through various operations.
What is the key difference between a fixed position layout and other types of layouts?
-In a fixed position layout, the product remains stationary while the equipment moves around it, which is the opposite of other layouts where the product moves past stationary equipment.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of each plant layout type discussed in part 2 of the video?
-The advantages and disadvantages of each plant layout type are explained in detail in part 2 of the video, which can be accessed by checking the 'i' button or the description for a link to the PDF or further information.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Key Factors in Plant Layout Selection

Types of Plant Layout, Explanation with Advantages and Dis-advantages, Plant layout part 2

Hierarki Visual - Seberapa penting itu ?

Facility Layout - Introduction and Types

Lec 19: Plant Layout: Types of Layout
#MH004 Plant Layout, Principles of plant layout & Types of layout.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
