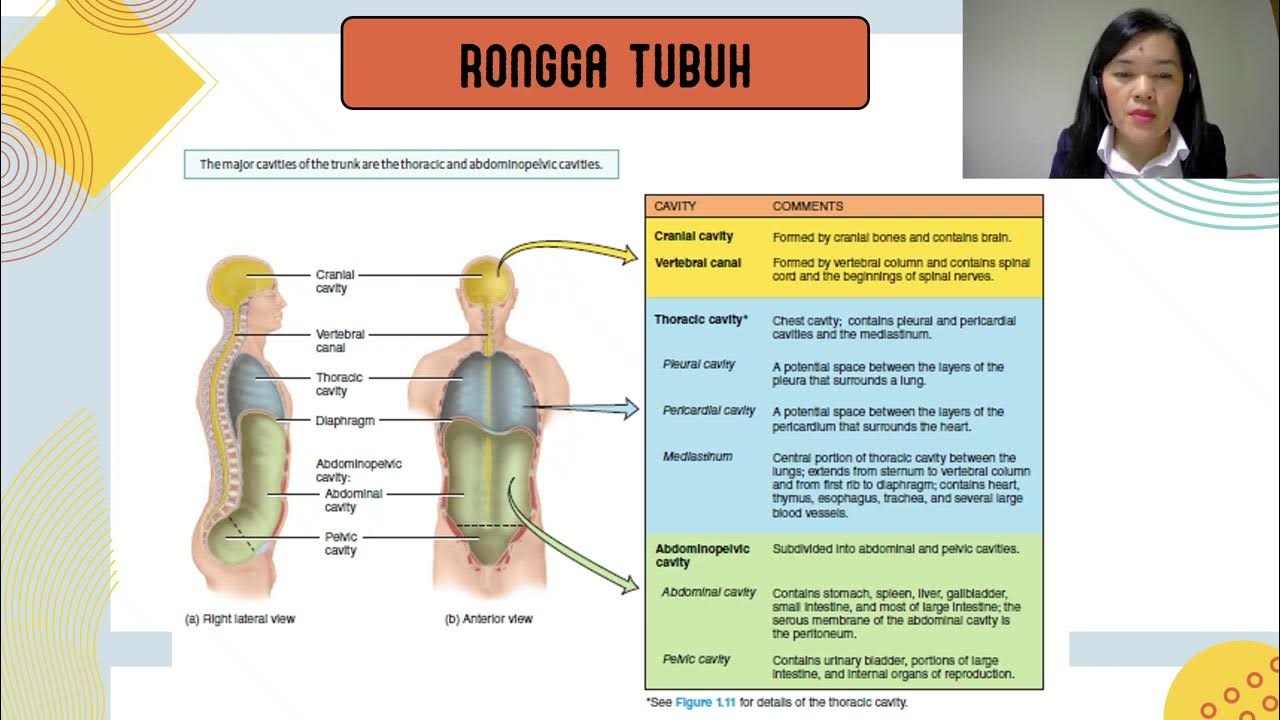
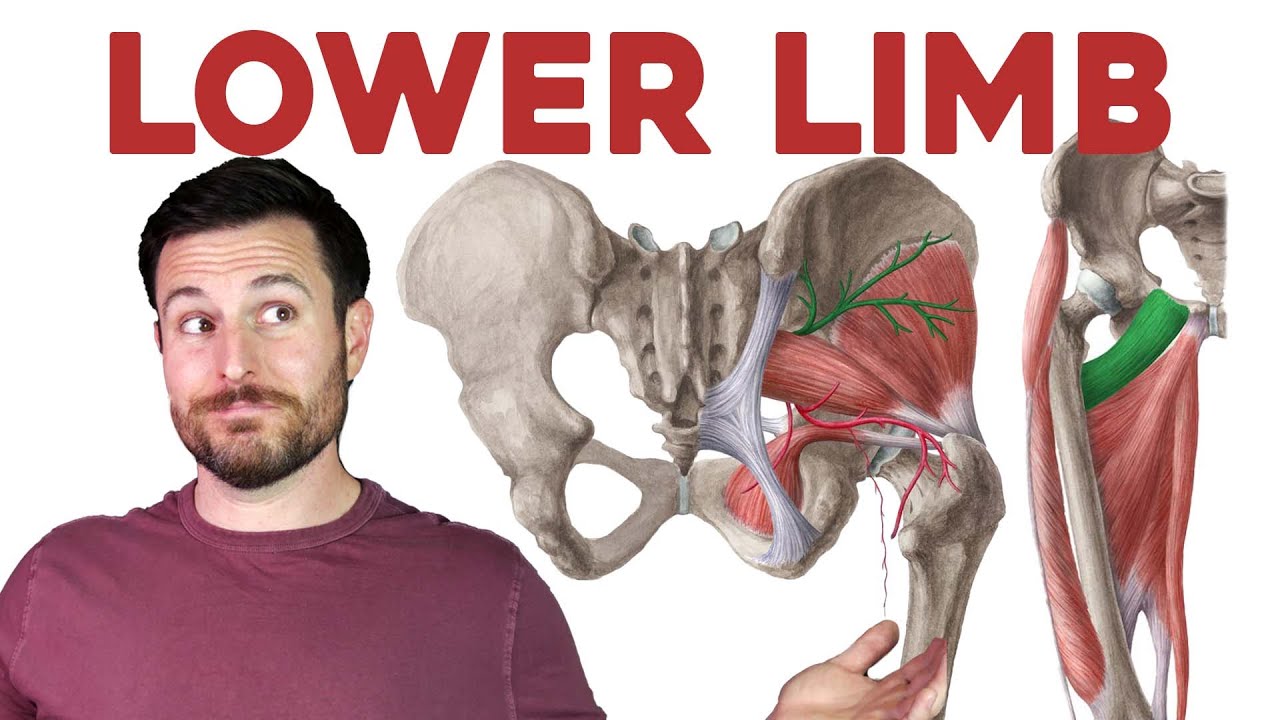
Extract from my course From blocks figures to muscles: a Figure Drawing Foundation course
Summary
TLDRThe transcript details a tutorial on human anatomy for artists, focusing on the muscular structure of the torso and limbs. It discusses the sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis major, and abdominal muscles, emphasizing their interplay and visual representation during movement. The instructor guides through blocking in muscles, considering body proportions, and creating harmony in the figure's structure. The session also covers the impact of arm movement on muscle appearance and the importance of understanding muscle interdigitation for accurate depiction.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The script discusses the anatomy and drawing of the human body, focusing on the sternocleidomastoid muscle and its relation to the ear and mastoid process.
- 🎨 It emphasizes the importance of understanding the body's structure and creating harmony in the drawing, which involves both knowledge of proportions and an aesthetic sense.
- 🤔 The process of blocking in the rectus abdominis and external oblique muscles is described, highlighting the need to consider the body's solidity and the effects of movement.
- 👀 The script explains how to visualize and draw the serratus anterior muscle, which covers the side of the ribcage and adds to the figure's profile.
- 📏 The importance of considering the body's three-dimensionality and how it affects the tonal characteristics of the drawing is discussed.
- 💡 The approach to drawing is described as one that considers the body as a series of volumes rather than flat shapes, which aids in understanding the form's interaction with light and shadow.
- 👕 The script describes how the pectoralis major muscle changes shape as the arm moves, affecting its appearance in the drawing.
- 🤲 The interplay between the serratus anterior and the external oblique muscles is highlighted, showing how they interdigitate and affect each other's visibility.
- 👉 The process of drawing involves considering the body's movement and how it impacts the muscle's appearance, such as the stretching of the pectoralis major when the arm is abducted.
- ✍️ The script provides a detailed step-by-step guide on how to block in and refine the muscles of the torso, emphasizing the need for accuracy and attention to detail.
Q & A
What is the significance of the sternocleidomastoid muscle in the context of the provided script?
-The sternocleidomastoid muscle is significant as it is discussed in terms of its external portion and its development towards the clavicle. It is used to illustrate the connection and fluidity between different parts of the body, emphasizing the importance of understanding the structural aspects of the body in movement.
How does the script describe the relationship between the earlobe and the mastoid process?
-The script describes the earlobe as being in a specific location relative to the mastoid process, which is felt under the ear. This description is used to provide a tactile understanding of the anatomy being discussed.
What is the purpose of blocking the muscle in the script?
-Blocking the muscle serves to observe the flow and connection between different parts of the body. It is a method to understand the harmonies inherent to the body's structure and movement.
How does the script suggest measuring the aesthetic sense in relation to body proportions?
-The script implies that the aesthetic sense in relation to body proportions is not something that can be directly measured. Instead, it is a result of the knowledge of proportions combined with an individual's aesthetic sensibility, which is reflected in how they put the elements together.
What is the significance of the rectus abdominis and external oblique muscles in the script?
-The rectus abdominis and external oblique muscles are significant as they are used to demonstrate how to block in the abdominal structure and understand the body's form and movement. The script describes their origin and insertion points, and how they change with the movement of the arms.
How does the script discuss the concept of 'interdigitation' in relation to the serratus and external oblique muscles?
-The script discusses 'interdigitation' as the process where the serratus and external oblique muscles interlace with each other. This concept is used to explain how the flat profile of the muscles becomes more complex and bumpy as they interact with each other.
What role does the pectoralis major muscle play according to the script?
-The pectoralis major muscle plays a role in changing shape as the arms move. The script describes its origin from the clavicle, sternum, and ribs, and how its fibers intermingle with the rectus abdominis. It also explains how the muscle's appearance changes with the rotation of the arm.
How does the script describe the process of drawing the figure considering the three-dimensionality of the body?
-The script describes the process of drawing the figure by considering the body as a series of volumes and forms rather than flat shapes. This approach helps in understanding the tonal characteristics of the subject and the interaction between different body parts.
What is the importance of understanding the structural aspect of the body in the script?
-Understanding the structural aspect of the body is important because it allows for the creation of harmonies that are inherent to the body's parts and movements. This understanding is crucial for accurately representing the body in various poses and actions.
How does the script guide the reader to visualize the positioning of the iliac crest and the navel?
-The script guides the reader to visualize the positioning of the iliac crest and the navel by suggesting that the navel is located roughly halfway between the top of the iliac crest and the sternum, providing a reference point for the abdominal region.
What is the significance of the serratus anterior muscle's digitations in the script?
-The serratus anterior muscle's digitations are significant as they contribute to the profile of the figure and interact with the external oblique muscle. The script describes how these digitations should be oriented properly and how they change the muscle's profile as they interdigitate with the external oblique.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)