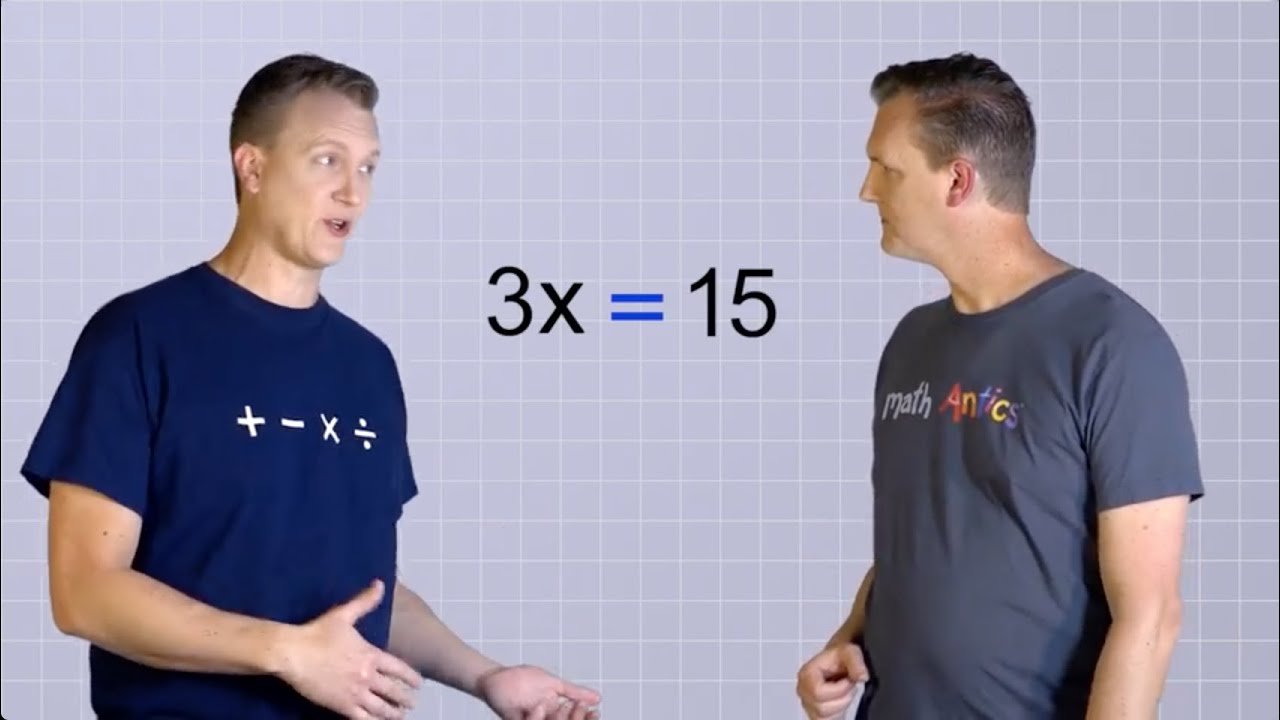Algebra Basics: What Is Algebra? - Math Antics
Summary
TLDRIn this Math Antics video, Rob introduces the basics of Algebra, explaining how it is similar to arithmetic but involves unknown values, represented by symbols like 'x'. He demonstrates how to solve simple equations and emphasizes that multiplication is often implied in algebraic expressions. Rob also highlights the importance of Algebra in real-world applications, such as science, engineering, and economics, where it helps describe and predict various phenomena. The video aims to make Algebra understandable and show its practical value beyond schoolwork.
Takeaways
- 📚 Algebra is similar to arithmetic, following the same basic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- 🔍 Algebra introduces the concept of the unknown, represented by symbols like 'x', which stand in place of numbers that are not yet known.
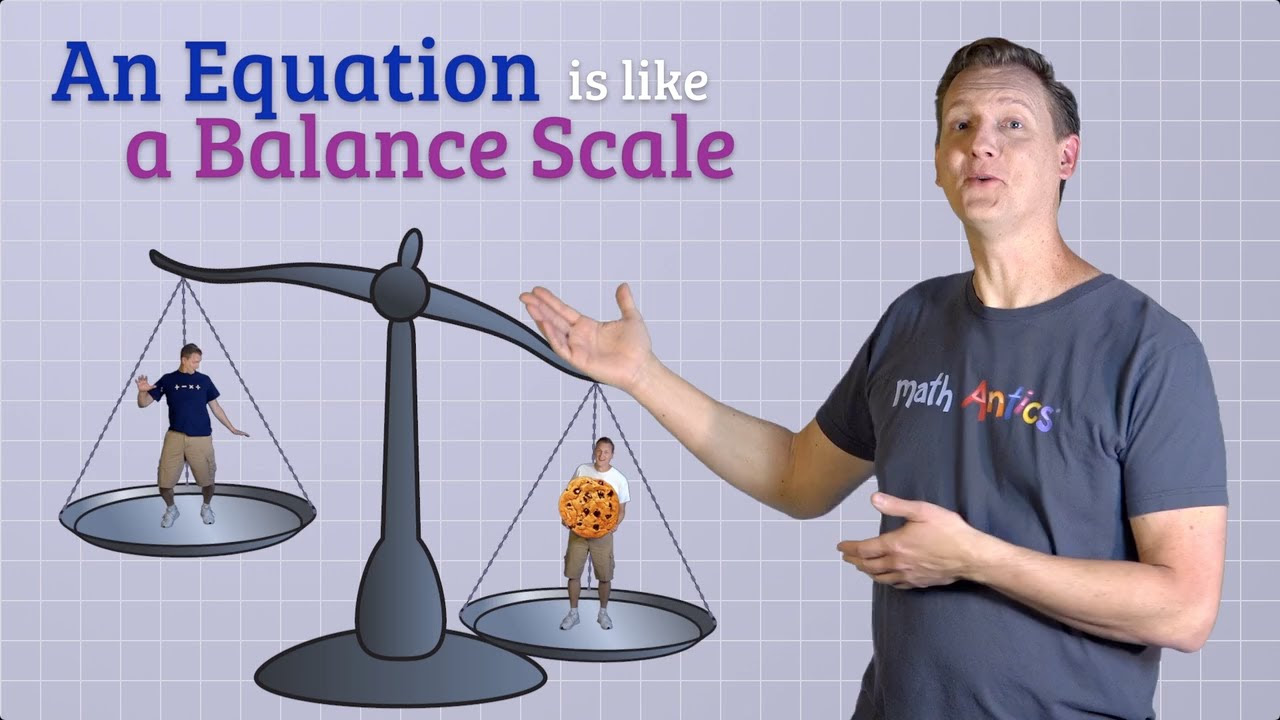
- 🧩 An equation in algebra is a statement that two expressions are equal, and solving an equation involves determining the unknown values.
- 🔑 The symbol 'x' can represent different values in different problems, but within the same problem, it must represent the same value consistently.
- 🚫 Using the same symbol to represent different values in the same problem is not allowed, whereas using different symbols to represent the same value is permissible.
- 🔄 Variables in algebra can change their values depending on the context or the values of other variables in the equation.
- 🤔 Multiplication in algebra is often implied and does not require a multiplication symbol when two variables are written next to each other.
- 💡 However, a multiplication symbol or parentheses must be used when multiplying known numbers to avoid confusion with two-digit numbers.
- 📈 Algebraic equations can be graphed to visually represent and predict real-world phenomena, such as linear equations for slopes and quadratic equations for population growth.
- 🌐 Algebra is widely applicable in various fields including science, engineering, economics, and computer programming, making it a crucial tool for modeling and understanding the world.
Q & A
What is Algebra and how is it similar to arithmetic?
-Algebra is a branch of mathematics that introduces the concept of the unknown, using symbols to represent unknown values. It is similar to arithmetic in that it follows the same rules and uses the four main operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
What is the purpose of using symbols in Algebra?
-Symbols in Algebra are used to represent unknown values. They allow us to create equations that we can solve to find the value of the unknown.
What is an equation in Algebra?
-An equation in Algebra is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions, indicating that the values on both sides of the equal sign are the same.
Why is the letter 'x' commonly used in Algebra?
-The letter 'x' is a popular choice for representing an unknown value in Algebra because it is easily recognizable and commonly associated with variables.
What is the main goal when solving equations in Algebra?
-The main goal when solving equations in Algebra is to determine the value of the unknowns, which is achieved by simplifying and rearranging the equation until the unknown value can be easily identified.
Can the same symbol represent different values in different algebra problems?
-Yes, the same symbol can represent different unknown values in different algebra problems. For example, 'x' could represent the number 3 in one problem and the number 5 in another.
Why is it not allowed for a symbol to represent different values in the same problem?
-It is not allowed because it would create confusion and inconsistency within the problem. Each symbol must represent the same unknown value throughout a single equation to maintain logical consistency.
What is the special treatment of multiplication in Algebra?
-In Algebra, multiplication is the 'default' operation. When no other operation is shown between two symbols, they are assumed to be multiplied. This means the multiplication sign is often omitted for simplicity.
When is it necessary to use a multiplication symbol in Algebra?
-A multiplication symbol is necessary when multiplying two known numbers to avoid confusion with a single number, or when the multiplication needs to be explicitly shown for clarity.
How can parentheses be used to imply multiplication in Algebra?
-Parentheses can be used to group expressions, and when two groups are placed next to each other without an operation shown, multiplication is implied.
Why is Algebra useful in the real world?
-Algebra is useful in the real world because it allows us to model and describe various phenomena and situations. It is applied in fields such as science, engineering, economics, and computer programming to solve problems and make predictions.
What are some examples of how Algebra is applied in different fields?
-Algebra is used to describe the slope of a roof, calculate travel times, design telescope lenses, analyze the trajectory of a ball in flight, and predict population growth, among other applications.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)