What is the Material Requirement planning (MRP)? | MRP Process
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains Material Requirements Planning (MRP), a computer-based inventory management technique. It outlines the functions, inputs (master production schedule, bill of materials, inventory record), and process of MRP, which includes estimating demand, checking inventory, production scheduling, and monitoring. The script also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of MRP, highlighting its role in inventory management, production scheduling, and customer satisfaction.
Takeaways
- 😀 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a computer-based inventory management technique aimed at improving productivity for businesses.
- 🔍 MRP ensures materials and components are available in the right quantities and on time, often considered a subset of inventory control.
- 🛠️ The primary functions of MRP include controlling inventory levels, assigning priorities for components, and determining capacity requirements at a detailed level.
- 📝 Inputs to MRP include the master production schedule, bill of materials (BOM), and inventory record file, which are essential for planning.
- 📈 The master production schedule is based on demand estimation and production capacity, detailing what products to produce, in what quantities, and when.
- 🏗️ The bill of materials file specifies the components, parts, and sub-assemblies needed for each product, essential for calculating raw material and component requirements.
- 📊 Inventory record file maintains accurate, current data on inventory status, including lead times for raw materials, components, and assemblies.
- 🔄 The MRP process involves estimating demand, checking against inventory, allocating resources, scheduling production, and monitoring the process for issues.
- 📑 MRP generates various outputs, including order release notices, rescheduling or cancellation notices, inventory status reports, and performance reports.
- 🚀 Advantages of MRP include assured material availability, minimized inventory costs, optimized inventory management, reduced customer lead times, increased manufacturing efficiency, labor productivity, capacity utilization, and overall customer satisfaction.
- 🔄 Disadvantages of MRP include the potential for high implementation costs, lack of flexibility in production schedules, and the risk of holding more inventory than necessary, which can increase costs.
Q & A
What is Material Requirements Planning (MRP)?
-Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a computer-based inventory management technique designed to improve productivity for businesses by ensuring that materials and components are available in the right quantities and on time.
Why is MRP considered a subset of inventory control?
-MRP is considered a subset of inventory control because it is an effective tool for minimizing unnecessary inventory investment and optimizing inventory management.
What are the three main functions of MRP?
-The three main functions of MRP are: 1) Control of inventory levels, 2) Assignment of priorities for components based on their delivery dates, and 3) Determination of capacity requirements at a detailed level.
What are the three primary inputs to the MRP system?
-The three primary inputs to the MRP system are the master production schedule, the bill of materials file, and the inventory record file.
Can you explain the role of the master production schedule in MRP?
-The master production schedule is based on an accurate estimation of demand for the firm's product and a realistic assessment of its production capacity. It lists what end products are to be produced, how many of each, and when they are likely to be ready for shipment.
What is the purpose of the bill of materials file in MRP?
-The bill of materials file specifies the product structure by listing the component parts and sub-assemblies that make up each product. It is essential for computing the raw material and component requirements for the end products listed in the master production schedule.
Why is the inventory record file important in the MRP process?
-The inventory record file is important because it provides accurate, current data on inventory status. It is maintained by a computerized inventory system and includes lead time explanations for raw materials, components, and assemblies.
What are the four basic steps in the MRP process?
-The four basic steps in the MRP process are: 1) Estimating demand and the materials required to meet it, 2) Checking demand against inventory and allocating resources, 3) Production scheduling, and 4) Monitoring the process for any issues.
What kind of outputs does MRP generate for plant operations planning and management?
-MRP generates primary outputs like order release notices, rescheduling or cancellation notices, and reports on inventory status. Secondary outputs include performance reports, expectation reports, and inventory forecasts indicating projected inventory levels in future periods.
What are some advantages of using the MRP process?
-Advantages of using MRP include assurance that materials and components will be available when needed, minimized inventory levels and costs, optimized inventory management, reduced customer lead times, increased manufacturing efficiency, increased labor productivity, ensured capacity utilization, and increased overall customer satisfaction.
What are the potential disadvantages of the MRP process?
-Disadvantages of the MRP process include the difficulty and expense of implementation, lack of flexibility in the production schedule due to reliance on accurate information about key inputs, and the temptation to hold more inventory than necessary, which can increase inventory costs.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
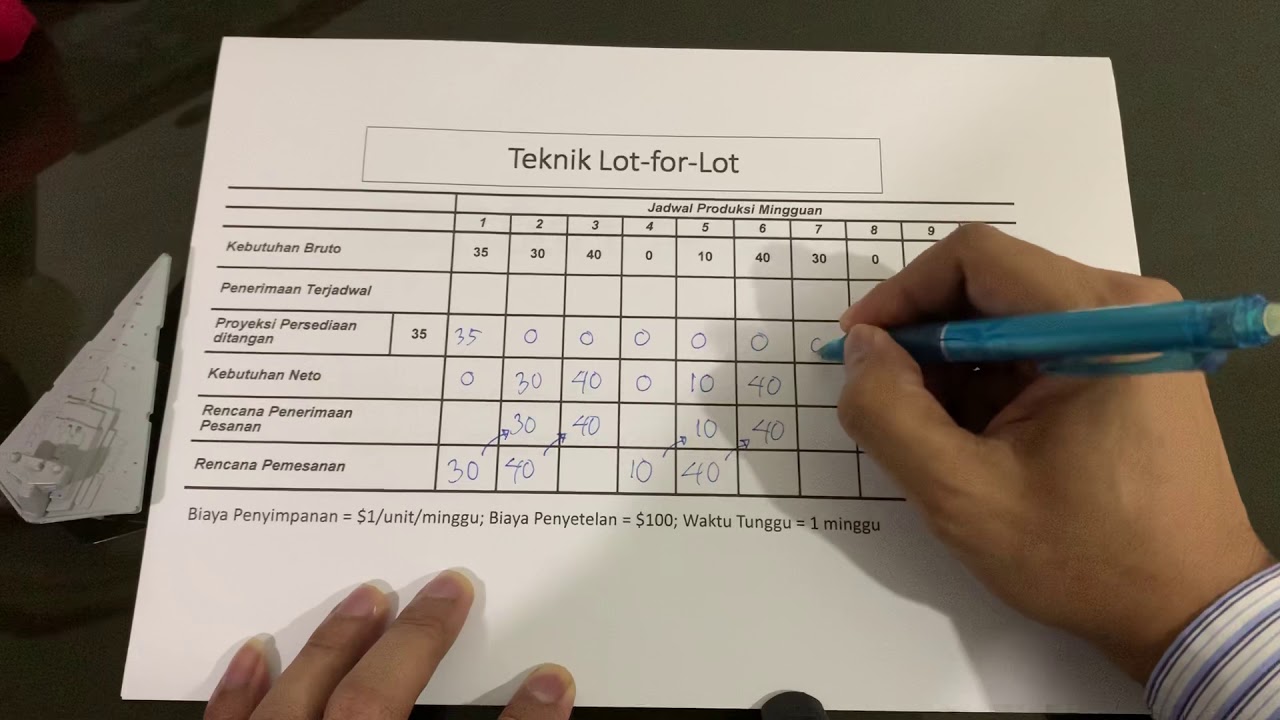
Teknik Lot for Lot pada Lot Sizing (Penentuan Ukuran Lot) dalam Sistem MRP

Planejamento e Controle da Produção # 15 – Implantação do MRP

Memahami Perencanaan Kebutuhan Material untuk proses produksi ...

Chapter 14. Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP - Part 3

Materi kuliah Pengantar Bisnis, Pertemuan Ke-5
Pengantar Bisnis Sesi 11 Produksi dan Manajemen Operasi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
