The Urinary System
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the urinary system, focusing on the kidneys' role in filtering waste and regulating water and solute concentrations. It covers the structure and function of the kidneys, the process of urine formation through glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and secretion, and the roles of the ureters, bladder, and urethra in transporting and expelling urine.
Takeaways
- 🧐 The urinary system is responsible for filtering out waste and unwanted substances from the bloodstream and expelling them from the body.
- 🌟 The kidneys are the chief organ of the urinary system, performing various tasks including regulation of water volume, solute concentration, blood pH, and erythropoietin production.
- 🔍 The kidneys filter the bloodstream by removing toxins and waste while returning necessary components back to the blood.
- 📍 The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra, each with specific functions.
- 🏗️ Kidneys are located in the lumbar region, protected by the ribcage, and have a complex internal structure including the renal cortex, medulla, and pelvis.
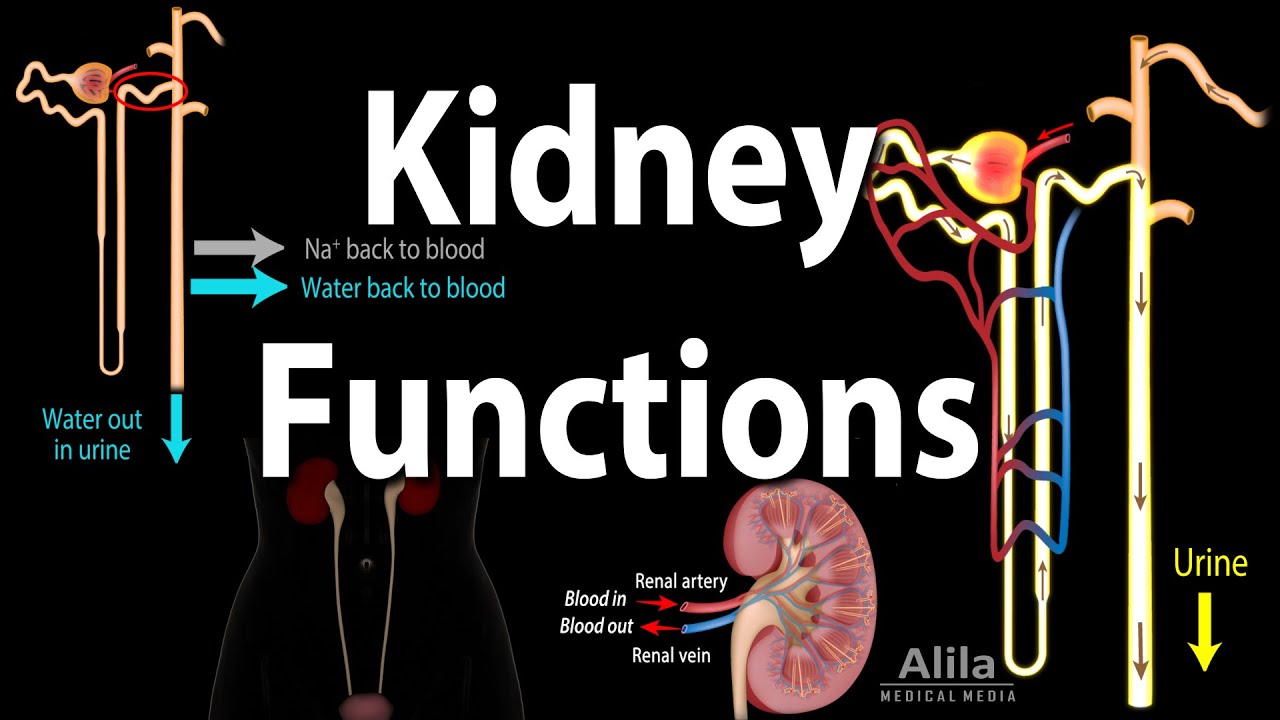
- 💧 The filtration process in the kidneys occurs in nephrons, which consist of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.
- 🌀 The renal corpuscle contains a glomerulus, a porous capillary network, which filters blood into the renal tubule.
- 🔄 Tubular reabsorption is a key process where most of the filtrate, including glucose, amino acids, and water, is returned to the bloodstream.
- 🚰 Tubular secretion is the process where certain substances from the blood are secreted into the filtrate, contributing to urine composition.
- 💦 Urine is primarily composed of water, urea, and other nitrogenous wastes, along with ionic solutes like sodium, potassium, phosphate, and sulfate.
- 🚰 Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder, which stores it until it is expelled through the urethra.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the urinary system?
-The primary function of the urinary system is to filter out waste and unwanted substances from the bloodstream and expel them from the body.
What are the main components of the urinary system?
-The main components of the urinary system are the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
What is the role of the kidneys in the urinary system?
-The kidneys are the chief organs in the urinary system, responsible for filtering the bloodstream, removing toxins and waste, and returning necessary components back to the blood.
How are the kidneys protected within the body?
-The kidneys are protected by being located in the lumbar region and receiving some protection from the ribcage.
What is the structure of the renal hilum and its significance?
-The renal hilum is a vertical cleft that leads to a renal sinus within the kidney, where the ureter, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves join.
What is the function of the adrenal gland located on top of each kidney?
-The adrenal gland is present on top of each kidney, but its function is not directly related to the urinary system; it is part of the endocrine system.
What are the three layers of supportive tissue surrounding each kidney?
-The three layers of supportive tissue surrounding each kidney are the outermost renal fascia, the perirenal fat capsule, and the innermost fibrous capsule.
How does the filtration process in the kidneys occur?
-The filtration process in the kidneys occurs in tiny units called nephrons, where blood is filtered through a filtration membrane into the glomerular capsule, allowing water and small solutes to pass through.
What is the purpose of the tubular reabsorption in the urinary system?
-Tubular reabsorption is the process by which most of the filtrate, including glucose, amino acids, and most of the water, is returned back to the bloodstream, leaving behind substances that will become urine.
What substances are typically found in urine?
-Urine typically contains water, urea (resulting from the breakdown of amino acids), other nitrogenous wastes like uric acid and creatinine, and ionic solutes such as sodium, potassium, phosphate, and sulfate.
How does the urinary system transport and store urine before it is expelled from the body?
-Urine is transported from the kidneys to the bladder via the ureters, where it is stored until it is released from the body through the urethra.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)