The Heat Equation + Special Announcement! | Infinite Series
Summary
TLDRIn this final episode of 'Infinite Series,' the host reflects on the journey of exploring complex mathematical topics such as infinite chess, quantum algorithms, and more. The episode focuses on the heat equation, explaining its importance and its real-world applications. The heat equation is a differential equation describing heat diffusion, and the host illustrates it through a model of heat spreading from a point in a grid. The host bids farewell to the audience, introducing two new hosts, Gabe Pere-Giz and Tai-Danae Bradley, who will continue the show with fresh perspectives. The episode wraps up with an invitation to explore further mathematical ideas.
Takeaways
- 😀 The heat equation is a fundamental differential equation that's widely applicable and visually interesting.
- 😀 The video marks the final episode of the original writer and host of 'Infinite Series' as they shift focus to completing their dissertation.
- 😀 The heat equation is used to model heat diffusion and can be visualized as heat spreading from an initial source point.
- 😀 A key visualization involves imagining a match creating infinite heat at a point on an infinite metal sheet, with the heat diffusing outward over time.
- 😀 The heat distribution can be graphed as a bell-shaped curve, similar to the normal distribution, with the graph being radially symmetric.
- 😀 The heat equation is a differential equation that involves functions of space and time, with the goal of describing heat distribution at various times.
- 😀 Differential equations, like the heat equation, have functions as unknowns, unlike algebraic equations where numbers are solved for.
- 😀 The heat equation involves the Laplacian operator, which describes the difference between a function value at a point and its neighboring points.
- 😀 The right side of the heat equation is the time derivative, which shows how the function is changing at a given point over time.
- 😀 The heat equation models the diffusion of heat, where heat moves from warmer areas to cooler areas, flattening out temperature differences over time.
- 😀 The video concludes with an introduction to the new hosts of 'Infinite Series', Gabe Pere-Giz and Tai-Danae Bradley, who bring fresh perspectives to the show.
Q & A
What is the heat equation and why is it important?
-The heat equation is a differential equation that models heat diffusion across a surface. It is fundamental because it describes how heat spreads over time, which has applications in physics, engineering, and other sciences. The equation helps predict how temperature changes in a given system.
How does the heat equation apply to real-world scenarios?
-In real-world applications, the heat equation is used to model heat flow in materials, but it must be adapted to account for material properties, shapes, and external conditions. These adjustments are necessary for practical use in fields like engineering and material science.
What does the Laplacian in the heat equation represent?
-The Laplacian in the heat equation represents how the value of a function (in this case, the heat distribution) changes at a point relative to its neighboring points. It indicates whether the point is hotter or cooler compared to its surroundings, which is key to understanding how heat diffuses.
What is the role of the time derivative in the heat equation?
-The time derivative in the heat equation tells us how the temperature at a specific point changes over time. It shows whether the temperature is increasing, decreasing, or staying constant at that point.
What is the significance of the bell-shaped graph mentioned in the script?
-The bell-shaped graph represents the heat distribution at a specific time, showing how heat spreads out from a point of origin. It is an example of a solution to the heat equation, where heat initially concentrated at the origin diffuses over time, creating a bell curve, similar to the normal distribution.
How does the heat equation ensure heat flows from hot to cold regions?
-The heat equation ensures that heat flows from warmer regions to cooler ones by balancing the Laplacian (which describes the difference in heat between a point and its neighbors) with the time derivative (which describes the rate of change of temperature). This process naturally drives heat to spread out and equalize across a surface.
What does the term 'fundamental solution' refer to in the context of the heat equation?
-The fundamental solution to the heat equation refers to the basic, idealized case where heat begins as a concentrated spike at a point and spreads out to form a bell-shaped distribution. This solution serves as a building block for more complex solutions, where heat might start from different distributions.
Why is it said that the heat equation is an idealized model?
-The heat equation is considered an idealized model because it assumes perfect conditions for heat diffusion, such as an infinite and homogeneous surface with no other influencing factors. In real-world applications, additional physical constraints, such as material type and geometry, must be taken into account.
How is the heat equation related to differential equations?
-The heat equation is a type of differential equation because it involves derivatives, specifically partial derivatives with respect to both spatial coordinates and time. It describes how a function (in this case, temperature) evolves over time and space, which is a hallmark of differential equations.
What are the new hosts of 'Infinite Series' introduced in the script, and what is their background?
-The new hosts of 'Infinite Series' are Gabe Pere-Giz, a physicist and former host of PBS 'Space Time,' and Tai-Danae Bradley, a mathematician and creator of the blog 'Math3ma.' They bring fresh perspectives to the show, with Gabe focusing on physics and Tai-Danae on mathematics.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Donald no País da Matemágica e O Número de Ouro - [Dublado 720p HD]
An infinite number of $1 bills and an infinite number of $20 bills would be worth the same

Finite Vs Infinite Games || Game Theory

Why I Left Quantum Computing Research

Assisted Reading: Sloterdijk's 'Infinite Mobilization' - Asian Renaissance (p.25-28) #1
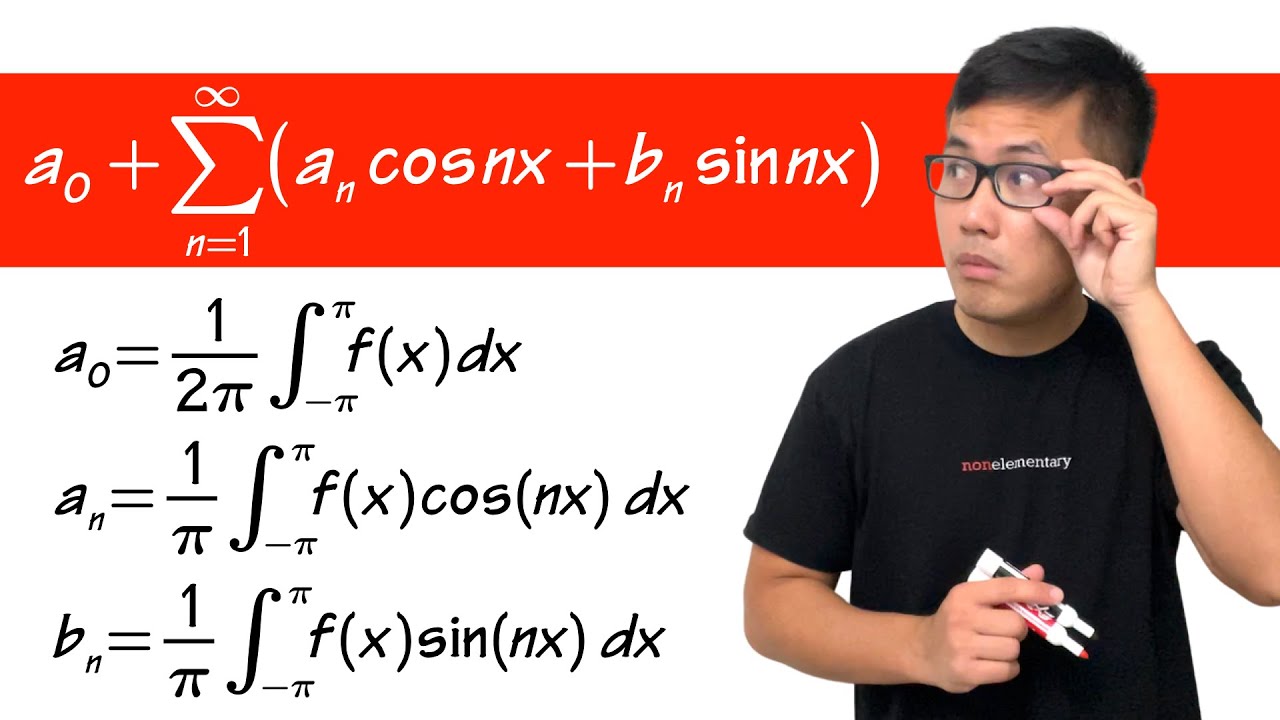
how to get the Fourier series coefficients (fourier series engineering mathematics)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
