Aula 8 - Circuito em série e paralelo
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the behavior of light bulbs in series and parallel circuits. It demonstrates how in a series circuit, the current remains constant but voltage is divided, causing bulbs to shine dimly. If one bulb is removed, the entire circuit is broken. In contrast, parallel circuits provide the same voltage to each bulb, allowing them to shine brightly even if one bulb is removed. The key concepts of electric potential, current, and resistance are explored, with a focus on how the arrangement affects bulb brightness and circuit functionality.
Takeaways
- 😀 A circuit can be connected in two ways: in series or in parallel. Each configuration behaves differently in terms of voltage and current.
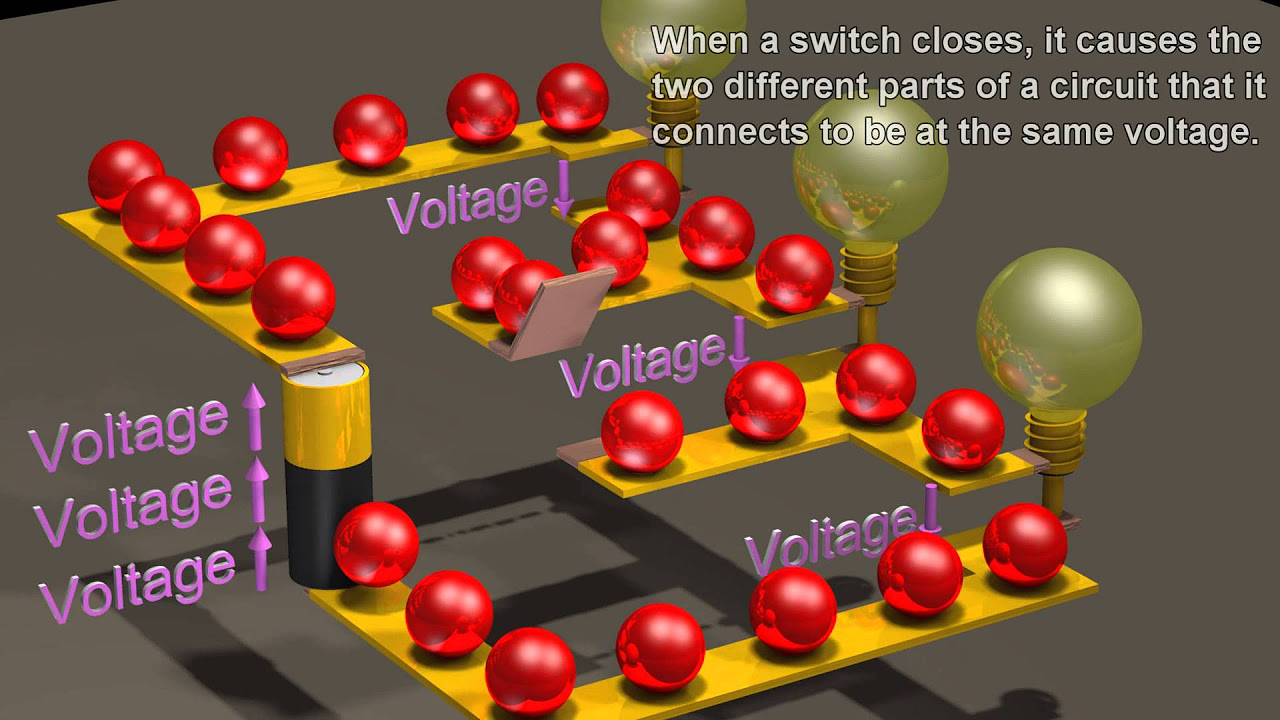
- 😀 In a series circuit, the current is constant throughout the entire circuit, but the voltage is divided among the components.
- 😀 In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each component remains the same, but the current is divided between the branches.
- 😀 When bulbs are connected in series, they shine with a dimmer light because the voltage is split between them.
- 😀 When bulbs are connected in parallel, each bulb receives the full voltage, so they shine brighter compared to those in series.
- 😀 If a bulb is removed from a series circuit, all other bulbs stop working because the circuit is broken (open circuit).
- 😀 In a parallel circuit, if one bulb is removed, the others still work because the current can flow through the other paths.
- 😀 The potential difference (voltage) is a key factor in determining how brightly bulbs shine. Higher voltage results in brighter bulbs.
- 😀 In a series circuit, the current flows through each resistor (or bulb) sequentially, and the voltage drop across each is proportional to its resistance.
- 😀 In a parallel circuit, the total current is the sum of the currents through each branch, and the voltage across each component remains constant.
- 😀 The power of a bulb is related to its voltage and current. In series, the lower voltage across each bulb reduces its brightness, whereas in parallel, each bulb gets the full voltage, maintaining its brightness.
Q & A
What is the main difference between a series and parallel circuit?
-In a series circuit, components are connected in a single path, and the current is the same across all components. In a parallel circuit, components are connected in multiple paths, and the current divides among the paths, with each component receiving the same voltage.
Why do the bulbs shine differently in series and parallel circuits?
-In a series circuit, the voltage is divided among the bulbs, which causes them to shine less brightly. In a parallel circuit, each bulb receives the full voltage, so they shine more brightly.
What happens when you remove a bulb from a series circuit?
-When a bulb is removed from a series circuit, the circuit is broken, and none of the other bulbs will work because the current can no longer flow through the circuit.
What happens when you remove a bulb from a parallel circuit?
-When a bulb is removed from a parallel circuit, the other bulbs continue to work because the current has other paths to flow through, and the circuit remains complete.
How does current flow in a series circuit?
-In a series circuit, the current flows through each resistor (or bulb) in sequence, meaning the same current flows through all components without splitting.
What happens to the total resistance in a series circuit when more resistors are added?
-In a series circuit, the total resistance increases as more resistors are added because the resistances are summed together.
What is the difference between the voltage in a series circuit and a parallel circuit?
-In a series circuit, the voltage is divided among all components, while in a parallel circuit, each component receives the full voltage from the source.
What is the role of the voltage (or potential difference) in a circuit?
-Voltage (or potential difference) is the driving force that pushes electric current through the circuit. It causes the electrons to flow, creating current and allowing components like light bulbs to work.
How does the current behave in a parallel circuit compared to a series circuit?
-In a parallel circuit, the current splits and flows through multiple paths, while in a series circuit, the current flows through a single path, remaining constant throughout the circuit.
Why do the bulbs in a parallel circuit shine brighter than in a series circuit?
-The bulbs in a parallel circuit shine brighter because each bulb gets the full voltage from the source, while in a series circuit, the voltage is shared, resulting in lower brightness for each bulb.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

DC Resistors & Batteries: Crash Course Physics #29

Electric Circuits: Series and Parallel

Cara membuat rangkaian seri dan paralel sederhana / tugas kelas 6 tema 3

Video Pembelajaran IPA Rangkaian Listrik Seri dan Paralel menggunakan KIT

Cara Membuat Rangkaian Listrik Seri Dengan Cara Yang Mudah
Electric Circuits: Basics of the voltage and current laws.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
