Aula 97 FISIOLOGIA ANIMAL Digestão parte 2 - Aulas ENEM
Summary
TLDRIn this informative video, the speaker, Marta, delves into the concept of digestion, explaining how organisms, both animals and humans, process food for energy. She outlines the critical role of enzymes and water in breaking down macromolecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules such as glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids. The speaker compares intracellular and extracellular digestion, highlighting how different organisms, including protozoa and animals, adapt to their environments to perform these processes. The video offers insights into the complexities of digestion, tailored to a diverse range of species.
Takeaways
- 😀 Digestive processes are essential for transforming large food molecules into smaller, usable ones that our cells can absorb.
- 😀 Digestion involves enzymatic hydrolysis, where water and enzymes break down macromolecules into simpler units.
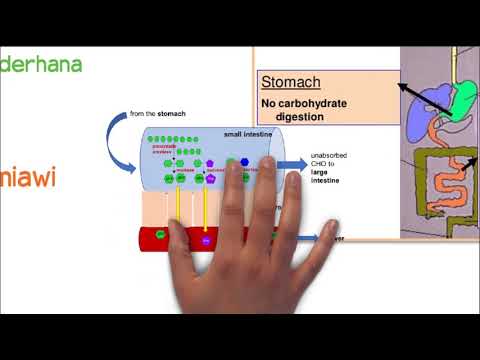
- 😀 Enzymes like amylase break down carbohydrates (e.g., starch) into smaller sugars, such as glucose, which cells can utilize for energy.
- 😀 Proteins need to be broken down into amino acids for cells to absorb and use them.
- 😀 Lipids (fats) are broken down into fatty acids to be absorbed by cells for energy production.
- 😀 Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are also broken down into nucleotides for cellular use.
- 😀 Cells use proteins called transporters to help move small molecules like glucose and amino acids into the cell.
- 😀 Digestive processes can be either extracellular (outside the cell) or intracellular (within the cell).
- 😀 Some organisms, like protozoans, perform intracellular digestion, where food particles are engulfed by the cell and digested inside.
- 😀 Animals with extracellular digestion, such as cnidarians (e.g., jellyfish), have digestive cavities where enzymes break down food before absorption.
- 😀 More advanced animals, like mammals, have a complete digestive system with both a mouth and an anus, allowing for efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Q & A
What is the main process explained in the transcript?
-The main process explained in the transcript is digestion, specifically the breakdown of complex macromolecules into smaller molecules that cells can use for energy and regeneration. This process occurs through enzymatic hydrolysis and is essential for life.
What is the definition of digestion according to the speaker?
-According to the speaker, digestion is the enzymatic hydrolysis of macromolecules, where large molecules are broken down by water and enzymes into smaller molecules that cells can use.
Why can't large molecules like carbohydrates enter cells directly?
-Large molecules like carbohydrates cannot enter cells directly because cells have selective membranes that only allow smaller molecules to pass through. This is why digestion breaks them down into smaller components like glucose.
What role do enzymes play in digestion?
-Enzymes, which are proteins, catalyze the breakdown of complex macromolecules into smaller, usable molecules. For example, amylase breaks down starch into glucose.
What is the significance of glucose in the process of digestion?
-Glucose is a simple sugar and the end product of carbohydrate digestion. It is the main molecule that cells use for energy production.
How does digestion differ between intracellular and extracellular processes?
-In intracellular digestion, organisms like protozoa break down food inside their cells. In extracellular digestion, as seen in more complex animals, food is broken down outside the cells in a digestive cavity before being absorbed.
Can you give an example of an organism that performs intracellular digestion?
-Protozoa, such as amoebas, perform intracellular digestion. They engulf food particles, which are then broken down inside the cell.
What happens in the digestive process when we consume complex proteins and fats?
-Complex proteins are broken down into amino acids, while fats are broken down into fatty acids and alcohols. These smaller molecules are then absorbed into the cells for energy production and other cellular functions.
How does the digestive process differ among various animal species?
-Different animal species have evolved distinct digestive systems. Some, like protozoa, perform intracellular digestion, while others, such as mammals, have complex extracellular digestive systems. Some animals also have incomplete digestive systems, such as certain flatworms, with only a mouth but no anus.
What are the main types of digestion described in the transcript?
-The main types of digestion described are intracellular digestion, where food is broken down inside cells, and extracellular digestion, where food is broken down outside cells in a digestive cavity.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Interaksi Makhluk Hidup dengan Lingkungan (Part 3) Aliran Energi Dalam Ekosistem

Termites Digest Wood Thanks To Microbes | I Contain Multitudes

Grade 7 | Science | Nutrition in animals | Free Tutorial | CBSE | ICSE | State Board
Sistem Pencernaan Makanan (karbohidrat, protein, lemak)

Ecosystem | Science | Grade-4,5 | TutWay |

You are What You Eat
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
