FUNÇÕES BIOLÓGICAS - MAPA CONCEITUAL
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the concepts of Cytology and Genetics are explored in depth. Cytology is defined as the study of cell structure and function, emphasizing the importance of understanding cellular components and their interactions, as well as historical breakthroughs such as the invention of the microscope. Genetics focuses on heredity, genes, and DNA, with key insights from Gregor Mendel's work on inheritance patterns. The video also highlights the distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, providing a foundation for understanding biological functions and the connection between these two vital fields of biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cytology is the branch of biology focused on the study of cell morphology, including the structure and function of cells and their components.
- 😀 The nucleus of a cell plays a crucial role in cellular functions, and understanding cell interactions is essential for grasping the complexity of biological systems.
- 😀 The study of cytology helps us understand the functions of cells in humans and microorganisms, some of which may be pathogenic.
- 😀 Robert Hooke was the first to observe cells in cork, and his discovery led to the naming of 'cells' based on their appearance.
- 😀 The invention of the microscope enabled the discovery of microorganisms like protozoa and bacteria, allowing for further exploration of cell biology.
- 😀 The classification of cells into prokaryotes and eukaryotes distinguishes between simpler organisms like bacteria and more complex organisms like plants and animals.
- 😀 Genetics is the study of heredity, which focuses on how traits are passed from parents to offspring, as well as how genes influence these traits.
- 😀 Mendel's work with pea plants led to the discovery of dominant and recessive genes, which are key to understanding inheritance patterns.
- 😀 The genetic material inside cells, particularly within the nucleus, determines the transmission of genetic traits across generations.
- 😀 Cytology and genetics are interconnected fields, with cytology providing the framework for understanding cellular structure, and genetics explaining how traits are inherited and expressed within those cells.
Q & A
What is cytology?
-Cytology is the branch of biology that studies the structure and function of cells, including the morphology of cell components such as the nucleus.
Why is cytology important in the study of biology?
-Cytology is important because it helps us understand the various cellular structures and their interactions, which is crucial for comprehending how cells function in the human body and in microorganisms.
Who is credited with the discovery of cells?
-Robert Hooke is credited with the first observation of cells. He examined cork cells under a microscope and coined the term 'cell' to describe the structures he saw.
What major discovery was made with the invention of the microscope?
-The invention of the microscope led to the discovery of bacteria and protozoa, expanding our understanding of microorganisms and their role in biology.
What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells lack a defined nucleus and include bacteria, while eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and are found in animals, plants, and other organisms like protozoa.
What is the role of genetics in biology?
-Genetics is the study of heredity and the structure and function of genes. It helps explain how traits are passed from one generation to the next and is key to understanding biological processes in medicine, agriculture, and the environment.
Who is considered the father of genetics and why?
-Gregor Mendel is considered the father of genetics due to his pioneering work with pea plants, where he discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance, including dominant and recessive genes.
What are dominant and recessive genes?
-Dominant genes are those that express their traits even when only one copy is present, while recessive genes require two copies (one from each parent) to express their traits.
How do cytology and genetics connect in the study of biology?
-Cytology and genetics are connected because both focus on understanding cells. Cytology studies the structure and function of cells, while genetics focuses on the genes within the cell's nucleus, which control hereditary traits.
What historical figures contributed to the development of cytology and genetics?
-Robert Hooke contributed to cytology by discovering cells, while Gregor Mendel contributed to genetics with his experiments on heredity and the inheritance of traits in pea plants.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

BIOLOGIA - Lezione 11 - Genetica: Le Leggi di Mendel

LESSON ON CHROMOSOMES, DNA AND GENES | IN FILIPINO

MATERI GENETIKA: BIOLOGI KELAS 12 SMA

Introdução à Genética [Conceitos] - Aula 01 - Mód. 2 - Genética | Prof. Guilherme
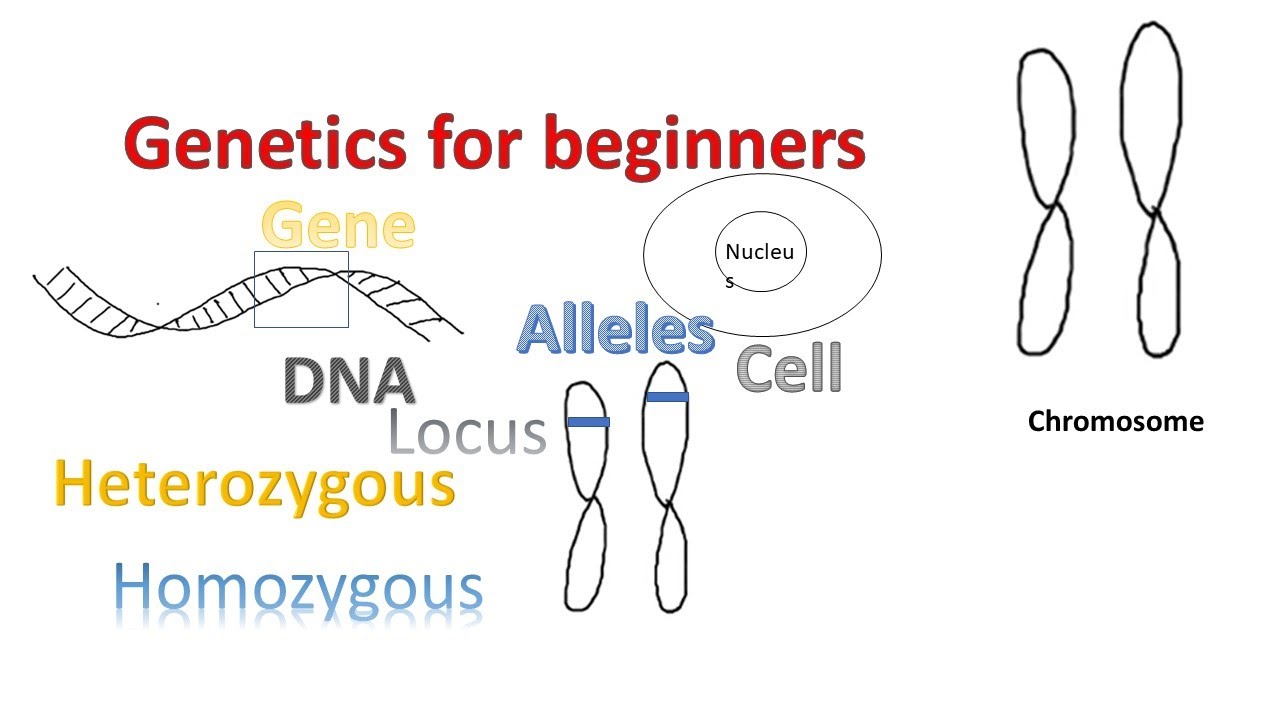
Genetics for beginners | Genes Alleles Loci on Chromosomes |

KA1-7-01Bab 7 Metode Analisis Volumetri - Pengantar
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
