Metabolismo de aminoácidos
Summary
TLDRThis lecture covers the metabolism of amino acids, detailing key processes like protein degradation, nitrogen elimination through the urea cycle, and the recycling of carbon skeletons. It explores how proteins are broken down in the digestive system, highlighting enzymes and pathways involved. The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in protein turnover and its implications for diseases like Parkinson's and cancer are discussed. Additionally, it delves into metabolic disorders such as phenylketonuria, maple syrup urine disease, and alkaptonuria, explaining their biochemical origins and treatments. The session also emphasizes the importance of amino acid metabolism in maintaining bodily functions and health.
Takeaways
- 😀 The protein degradation process starts in the stomach, where pepsin begins digesting proteins at a low pH of 2, allowing other proteins to denature.
- 😀 Proteins are further digested in the intestines by pancreatic enzymes, which break down peptides into oligopeptides and free amino acids.
- 😀 The ubiquitin-proteasome system regulates protein turnover, playing a crucial role in gene transcription, cell cycle progression, immune response, and even circadian rhythms.
- 😀 The ubiquitination process involves three enzymes and requires ATP. A defect in these enzymes can lead to diseases like Parkinson's, Huntington's, or Angelman syndrome.
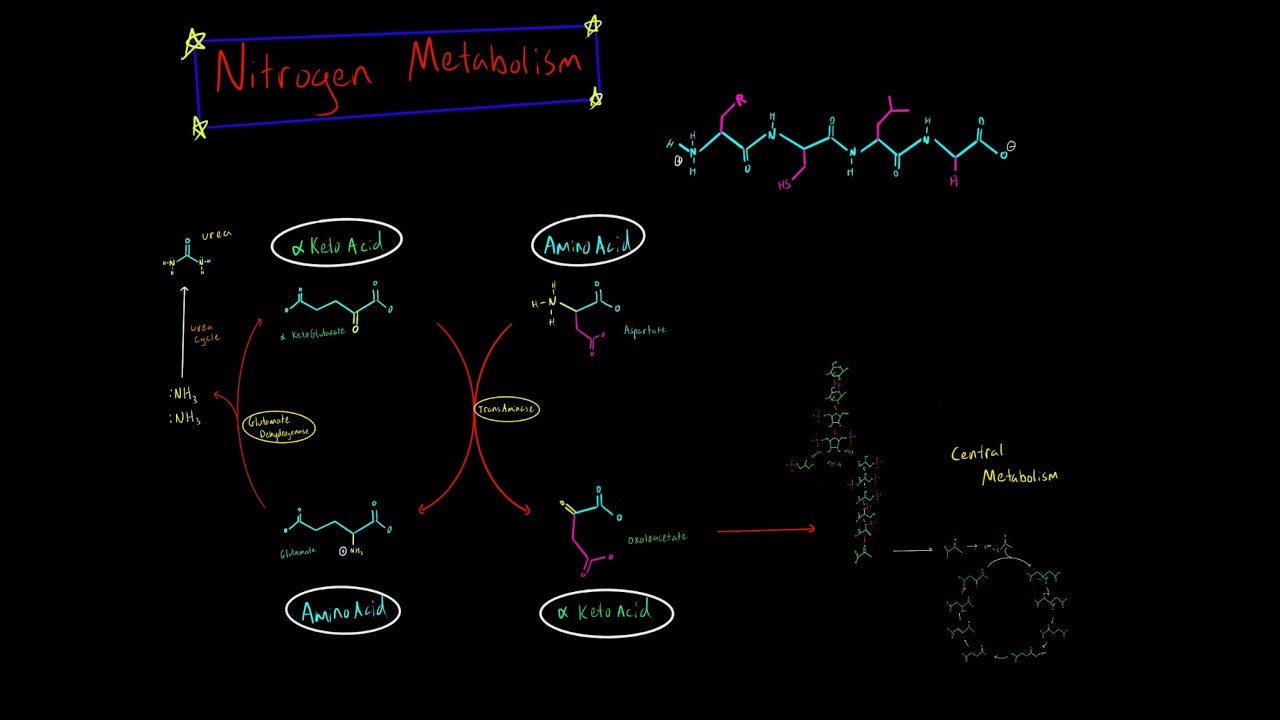
- 😀 The amino acid degradation involves the removal of nitrogen through the urea cycle and recycling of carbon skeletons for energy production or biosynthesis.
- 😀 Glutamate plays a key role in nitrogen elimination by releasing ammonium, which enters the urea cycle. GTP inhibits and GDP stimulates the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase.
- 😀 Aminotransferases use pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), derived from vitamin B6, to transfer amino groups, stabilizing the transition state during amino acid metabolism.
- 😀 The urea cycle eliminates excess nitrogen through a series of steps, involving enzymes like carbamoyl phosphate synthetase and ornithine transcarbamylase.
- 😀 Urea-excreting organisms are classified as ureotelic (e.g., vertebrates), ammonotelic (e.g., fish), and uricotelic (e.g., birds), based on the type of nitrogen waste they excrete.
- 😀 Metabolic diseases like Alkaptonuria, Maple Syrup Urine Disease, and Phenylketonuria arise from defects in amino acid metabolism, leading to symptoms like intellectual disabilities and metabolic disorders.
- 😀 In the case of Phenylketonuria, patients need to avoid phenylalanine-rich foods (like aspartame) to prevent severe neurological damage.
Q & A
What is the main objective of this session?
-The main objectives of the session are to understand the mechanisms of protein degradation, learn about nitrogen elimination in ureotelic organisms, understand the recycling of carbon skeletons from amino acids, and identify major metabolic diseases.
How does the degradation of dietary proteins begin?
-The degradation of dietary proteins begins in the stomach, where the enzyme pepsin starts breaking down large proteins in an acidic environment (pH 2).
What role do pancreatic enzymes play in protein digestion?
-Pancreatic enzymes, which are initially secreted as inactive zymogens, are activated in the small intestine. These enzymes break down polypeptides into smaller peptides and free amino acids.
What is the protein turnover system in the body?
-The protein turnover system, known as proteostasis, involves the constant degradation and synthesis of proteins. This system is regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, which is important for cellular functions like gene transcription, cell cycle progression, and immune responses.
What is the function of the ubiquitin-proteasome system?
-The ubiquitin-proteasome system tags proteins for degradation by attaching ubiquitin molecules to them. This process requires ATP and is essential for various biological processes, such as regulating cell growth, immune function, and removing damaged proteins.
What are the main diseases associated with defects in the ubiquitin-proteasome system?
-Defects in the ubiquitin-proteasome system can lead to neurodegenerative diseases such as juvenile Parkinson's, Huntington's disease, and Angelman syndrome, as well as certain types of cancer, like cervical cancer, due to improper degradation of tumor suppressor proteins.
What is the role of transamination in nitrogen elimination?
-Transamination is the process where an amino group from an amino acid is transferred to an alpha-keto acid, forming glutamate. This step is crucial for the subsequent removal of nitrogen through the urea cycle.
What happens in the urea cycle to eliminate nitrogen?
-In the urea cycle, ammonia is converted into urea, which is then excreted in the urine. This process involves several enzymes, including carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase, ornithine transcarbamylase, and arginase.
How does an arginine deficiency affect nitrogen metabolism?
-A deficiency in arginine or its enzymes in the urea cycle can lead to hyperammonemia, as the body is unable to efficiently remove excess nitrogen. This condition requires dietary restriction of proteins and supplementation with arginine.
What are the two types of amino acids based on their metabolic fate?
-Amino acids are classified into glucogenic and ketogenic categories. Glucogenic amino acids can be converted into glucose, while ketogenic amino acids are precursors for ketone bodies or fatty acids.
What is phenylketonuria (PKU), and how is it treated?
-Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency in phenylalanine hydroxylase, leading to elevated levels of phenylalanine in the body. It is treated with a diet low in phenylalanine to prevent neurological damage.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Bioquímica - Aula 16 - Catabolismo de Aminoácidos
Nitrogen Metabolism, Transamination and Deamination (EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW BIOCHEMISTRY MCAT)

Biokimia: Metabolisme Protein

BIOKIMIA PDK PROTEIN

AMINO ACID UTILIZATION

2: Overview of Amino Acids Metabolism | Amino Acid Metabolism | Biochemistry |N'JOY Biochemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
