Stoikiometri 1 (mol adalah jumlah)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Heru explains the concept of stoichiometry for 10th-grade chemistry students, focusing on the mole (mol) as a unit of measurement for particles like atoms, molecules, and ions. He clarifies the difference between moles and molecules, emphasizing that a mole refers to a quantity while a molecule is the smallest particle of a substance. The video covers key stoichiometric calculations, such as converting between mass and moles using molar mass and provides practical examples like H₂SO₄ and H₂O. Understanding moles and mass relationships is essential for mastering stoichiometry in chemistry.
Takeaways
- 😀 Stoichiometry is a crucial topic in chemistry, and it must be understood thoroughly, especially the concept of the mole (mol).
- 😀 The term 'mol' refers to a quantity or amount, not to be confused with molecules, which are the smallest particles of a substance.
- 😀 A mole is not the same as a molecule; a molecule refers to a particle made up of atoms, while a mole represents a number of particles.
- 😀 Atoms, molecules, and ions are all types of particles, with molecules being formed from atoms (either of the same or different elements) and ions being charged particles.
- 😀 Chemical bonding (covalent vs ionic bonds) helps determine whether a substance is a molecule or an ion.
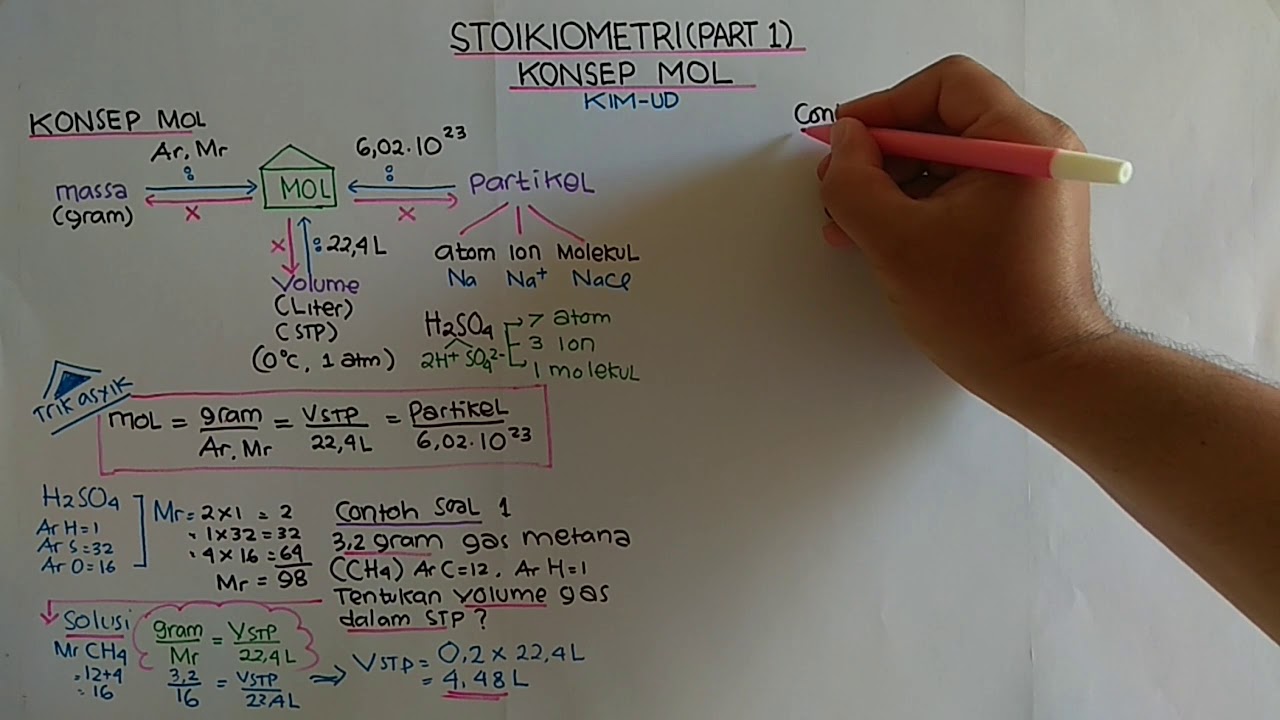
- 😀 The concept of 'mal' (mole) is similar to terms like 'million' or 'dozen,' which represent quantities or counts (e.g., 1 mole = 6.02 × 10^23 particles).
- 😀 In a chemical compound like H₂SO₄, the mole count can be used to determine the number of individual atoms (e.g., 2 hydrogen atoms per H₂SO₄ molecule).
- 😀 For 0.2 mol of H₂SO₄, you can calculate the number of hydrogen, sulfur, and oxygen atoms by multiplying by the appropriate coefficients.
- 😀 A mole of a substance is not equivalent to its mass; it's a count of particles. For instance, 6 molecules of H₂O have the same count, but their masses vary greatly compared to 6 elephants.
- 😀 To calculate the mass of a given number of moles, you use the molecular weight (relative atomic mass), for example, H₂O has a molar mass of 18 g/mol.
Q & A
What is the definition of stoichiometry?
-Stoichiometry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions, focusing on the quantitative relationships between substances involved.
How does the concept of a mole differ from a molecule?
-A mole is a unit of quantity representing 6.02 x 10^23 particles, whereas a molecule refers to the smallest unit of a substance that retains its chemical properties. Molecules are the particles counted in moles.
What does the term 'mol' represent in chemistry?
-The term 'mol' refers to a quantity used to count particles in chemistry. One mole contains 6.02 x 10^23 particles, known as Avogadro's number.
What is the relationship between a mole and the number of particles?
-A mole represents 6.02 x 10^23 particles, whether they are atoms, molecules, or ions. This number is fixed, so 1 mole of any substance contains the same number of particles.
Why is it important to understand the concept of the mole in stoichiometry?
-Understanding the mole is crucial in stoichiometry because it allows us to calculate and balance the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions, using a consistent unit of measurement for particles.
What is Avogadro's number and how is it used?
-Avogadro's number is 6.02 x 10^23, and it represents the number of particles in one mole of any substance. It is used to convert between moles and the number of particles.
How can we calculate the number of hydrogen atoms in 0.2 moles of H2SO4?
-In one molecule of H2SO4, there are 2 hydrogen atoms. To calculate the number of hydrogen atoms in 0.2 moles of H2SO4, multiply 0.2 moles by 2 (the number of hydrogen atoms per molecule), resulting in 0.4 moles of hydrogen atoms.
How do atomic and molecular masses relate to stoichiometric calculations?
-Atomic and molecular masses (measured in grams per mole) are used to convert between moles and mass. For example, the molecular mass of H2O is 18 g/mol, so 1 mole of H2O weighs 18 grams.
What is the molecular mass (Mr) of H2O and how is it calculated?
-The molecular mass of H2O (water) is calculated by adding the atomic masses of hydrogen (1 g/mol) and oxygen (16 g/mol). Since H2O has 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom, its molecular mass is 18 g/mol.
What is the key difference between mass and number in stoichiometry?
-In stoichiometry, mass refers to the weight of a substance, while number refers to the quantity of particles (atoms, molecules, ions). For example, 6 molecules of H2O do not have the same mass as 6 elephants, even though their count is the same.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)