What is a Transistor | Working Principles
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore the vital role of transistors in modern electronics, explaining how they amplify or switch signals and power. From your phone to industrial automation systems, transistors are everywhere. The video breaks down how transistors are made from semiconductor materials like silicon and germanium, and introduces the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) with its types: NPN and PNP. We also delve into real-world applications, such as transistor radios and proximity sensors, showcasing their impact on technology. Whether in audio amplification or switching in PLCs, transistors are essential components in today’s tech-driven world.
Takeaways
- 😀 Transistors are essential electronic components found in various devices, including phones and computers.
- 🔍 The term 'transistor' is derived from 'transfer' and 'resistor', indicating its function in electronic circuits.
- ⚡ A transistor can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power.
- 🌐 Silicon is the most common material used to make transistors, while germanium is another semiconductor material.
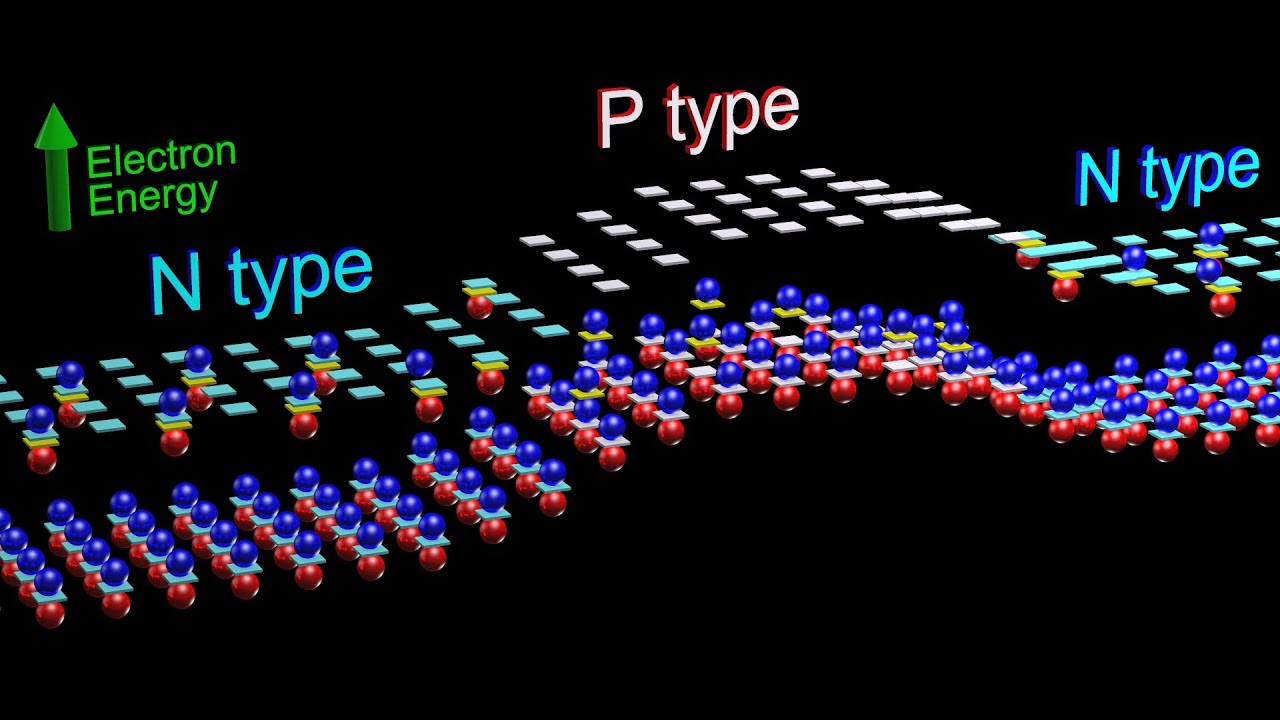
- 🧪 The process of doping introduces impurities into a semiconductor, creating 'N' (negative) and 'P' (positive) regions.
- 🔄 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is the most common type, available in two configurations: NPN and PNP.
- ⚙️ Transistors act as switches by controlling voltage between the Collector and the Emitter.
- 📻 The invention of the transistor revolutionized technology, leading to the development of the portable transistor radio.
- 🔧 In industry, transistors are used in active proximity sensors and PLC output modules for improved reliability and speed.
- 📚 For further learning, related topics include limit switches and proximity sensors, with additional resources available.
Q & A
What is a transistor?
-A transistor is an electronic component used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power.
What does the name 'transistor' signify?
-The name 'transistor' is derived from merging the words 'transfer' and 'resistor', indicating its function in transferring resistance.
What is a semiconductor?
-A semiconductor is a material that is neither a good conductor nor a good insulator, positioned between the two in terms of conductivity.
Which materials are commonly used to make transistors?
-The majority of transistors are made from silicon, while a small percentage are made from germanium.
What are the main types of transistors mentioned in the video?
-The main types of transistors mentioned are the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), Field Effect Transistor (FET), and Unijunction Transistor (UJT).
What is the structure of a Bipolar Junction Transistor?
-A Bipolar Junction Transistor consists of three layers of semiconductor material (sandwiched) that are doped to create N (negative) and P (positive) regions.
What is the function of the terminals Emitter, Base, and Collector in a transistor?
-The Emitter, Base, and Collector are the three terminals of a transistor, where the Emitter emits charge carriers, the Base controls the transistor, and the Collector collects the charge carriers.
How does a transistor amplify voltage?
-A transistor amplifies voltage by controlling a large current or voltage with a small input voltage applied at the Base, which influences the current flow between the Collector and Emitter.
What are the two types of Bipolar Junction Transistors?
-The two types of Bipolar Junction Transistors are NPN and PNP, named based on the arrangement of the N and P layers.
How do transistors operate as switches?
-Transistors operate as switches by controlling the voltage between the Base and Emitter, which determines whether the switch is open or closed, affecting the output voltage.
What impact did transistors have on radio technology?
-Transistors revolutionized radio technology by making radios smaller and portable, replacing large vacuum tube radios with compact transistor radios.
What are some industrial applications of transistors?
-In industry, transistors are used in active proximity sensors, replacing traditional limit switches, and in PLC output modules for enhanced reliability and speed.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)