The Contemporary World - Sustainable Development
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture, Professor Tripp Anthony Aramis discusses sustainable development, differentiating stability from sustainability. He explains that sustainability ensures the balance between economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity without compromising future resources. The lecture highlights the alarming state of the planet, with land degradation and increasing global warming, driven by human activities. Key sustainable development actions led by the United Nations include poverty eradication, clean energy, climate action, and quality education. Professor Aramis encourages individual contributions to sustainability by reducing carbon footprints, minimizing plastic use, and promoting eco-friendly practices.
Takeaways
- 🌍 The session focuses on sustainable development and its importance in balancing human activities with environmental preservation.
- 📊 75% of the world’s land area is already degraded due to human activity, contributing to global warming by 1°C since 2017.
- 🌡️ The risk of reaching the 2°C global temperature increase is growing, with the demand for energy rising as the population doubles.
- ⚖️ The difference between stability and sustainability is crucial: stability means resistance to change, while sustainability refers to maintaining resources for future generations.
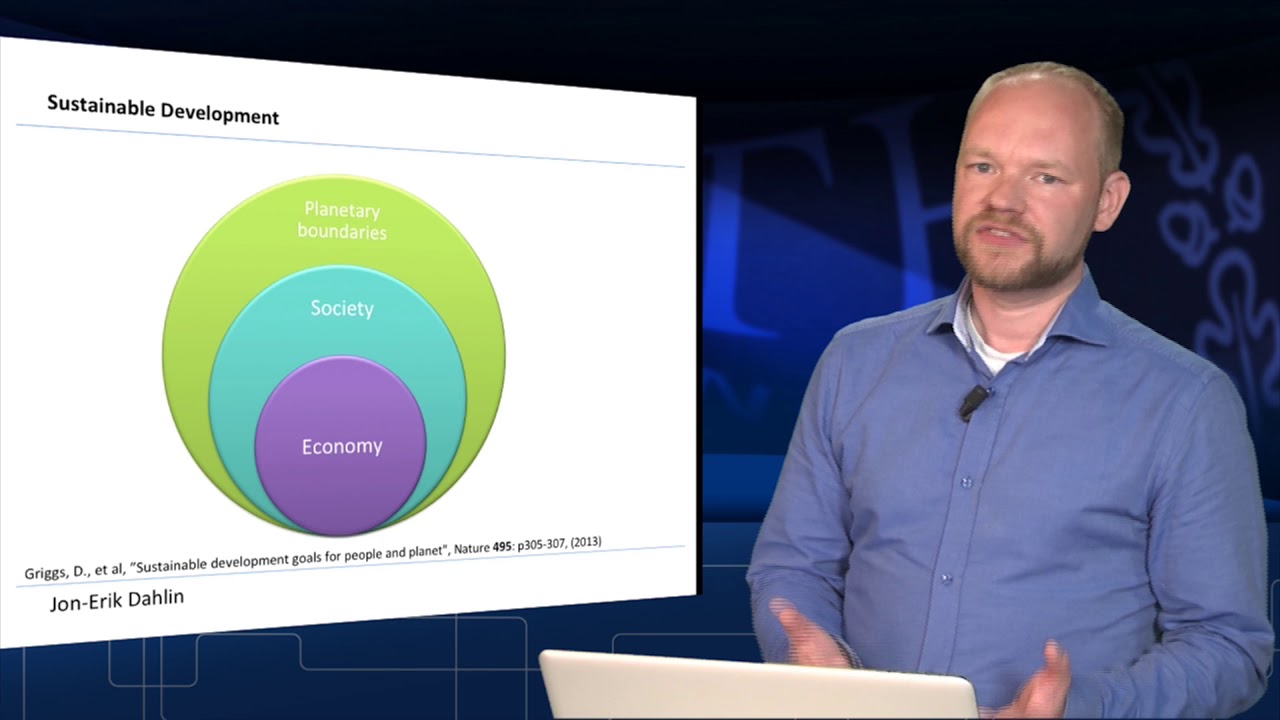
- 🏗️ Sustainable development ensures society can progress without harming future resource availability, focusing on economic, environmental, and social balance.
- 💰 Economic sustainability emphasizes production and consumption that meet present needs without compromising future resources.
- 👥 Social sustainability includes equity, empowerment, participation, and accessibility, helping individuals and communities meet their needs.
- 🌱 Environmental sustainability focuses on maintaining a productive and resilient natural environment to support human life.
- 📈 The United Nations is addressing sustainable development through efforts like poverty eradication, quality education, clean water, and reducing inequality.
- 🚶 Individuals can contribute to sustainability by reducing their carbon footprint, consuming responsibly, reducing plastic use, and advocating for environmentally friendly policies.
Q & A
What is the primary topic of this lecture session?
-The primary topic of this lecture session is sustainable development.
What does the professor ask students to reflect on at the beginning of the session?
-The professor asks students to share how they are feeling and reflect on their current emotions.
What is the difference between stability and sustainability according to the lecture?
-Stability is the condition of being in equilibrium and resistant to change, often recovering from disruptions. Sustainability is the ability to maintain certain conditions or resources over time without compromising future needs.
What does the International Science Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) report about land degradation?
-According to IPBES, 75% of the world’s land area is already degraded due to human activities and resource overuse.
Why is sustainable development necessary?
-Sustainable development is necessary to ensure that society can continue to grow and interact with the environment without depleting resources for future generations.
What are the three main pillars of sustainable development?
-The three main pillars of sustainable development are economic sustainability, social sustainability, and environmental sustainability.
How does the professor define economic sustainability?
-Economic sustainability is defined as a system of production that satisfies current consumption levels without compromising the ability to meet future needs.
What are some key aspects of social sustainability?
-Social sustainability includes equity, empowerment, accessibility, participation, cultural identity, and institutional stability.
What role does the United Nations play in promoting sustainable development?
-The United Nations promotes sustainable development through initiatives aimed at eradicating poverty, ensuring quality education, providing clean water and sanitation, and other efforts to improve global well-being.
What are some actions individuals can take to contribute to sustainability?
-Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint, consume only necessary goods, reduce plastic use, support sustainably produced products, and advocate for environmentally friendly practices.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

UCSP: Cultural, Social, and Political Change

Lesson 6:Towards a Sustainable World//Section 1: Sustainable Development
Economic, environmental and social sustainability: Sustainable Development - Jon Erik Dahlin

Recursos naturais e desenvolvimento sustentável - Geografia - Ensino Médio

The Contemporary World: Global Food Security

MPA 5305: Urban Sustainability - Global Policy Frameworks: SDGs NUA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
