Cara Kerja Diode – Lengkap Beserta Contoh Rangkaian Diode
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker provides an in-depth explanation of diodes, covering different types such as silicon, germanium, zener, and bridge diodes. The focus is on how diodes work in forward and reverse bias conditions, demonstrating how voltage differences affect current flow. The speaker uses a simple example with a 12V power supply to show the practical implications of diode behavior in circuits. The video concludes with an interactive question about which lamp will light up based on diode orientation, reinforcing the concept of biasing and the practical applications of diodes in electronics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Diodes are fundamental electronic components that allow current to flow in one direction, depending on their bias condition.
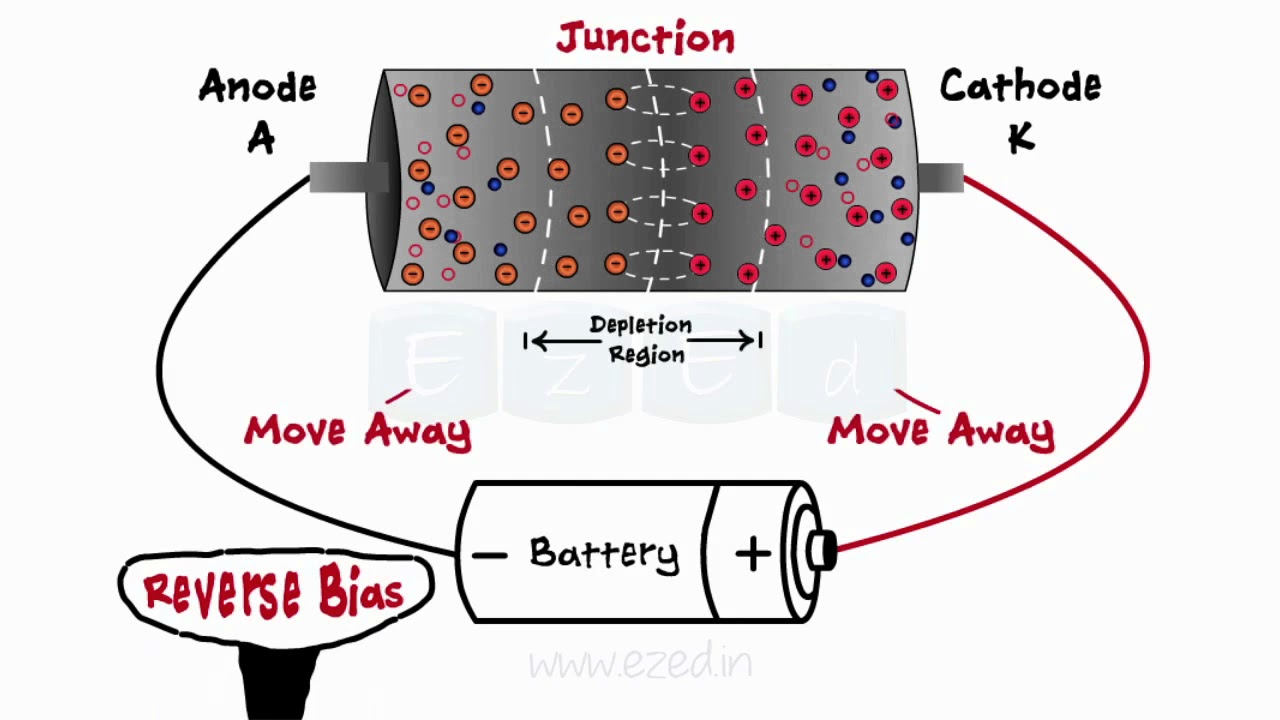
- 😀 A diode has two main terminals: the anode (positive) and the cathode (negative), and their polarity determines the flow of current.
- 😀 Forward bias occurs when the anode is more positive than the cathode, allowing current to flow through the diode.
- 😀 Reverse bias happens when the anode is more negative than the cathode, preventing current from flowing through the diode.
- 😀 Silicon diodes typically require a minimum voltage of 0.6V to allow current to pass, while germanium diodes need at least 0.2V.
- 😀 The video covers different types of diodes, including silicon, germanium, Zener, and bridge diodes, each with specific uses in electronics.
- 😀 A Zener diode is unique in that it is designed to allow current to flow in reverse when a specific voltage is reached, acting as a voltage regulator.
- 😀 Diodes are often used in circuits for applications like power supply regulation and signal rectification.
- 😀 The video demonstrates a simple circuit where a 12V power supply and a diode are used to show the effects of forward and reverse bias on current flow.
- 😀 In a forward bias condition with a sufficient voltage difference, the diode conducts electricity, turning on components like a lamp in the circuit.
- 😀 The tutorial encourages a hands-on approach to learning electronics, stressing the importance of understanding the principles of diode behavior before diving into complex calculations.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of a diode in electronics?
-A diode's main purpose in electronics is to allow current to flow in one direction only, from the anode to the cathode, while blocking current in the reverse direction.
What are the two most common types of diodes discussed in the video?
-The two most common types of diodes discussed in the video are the silicon diode and the germanium diode.
What is the voltage requirement for a silicon diode to conduct current?
-A silicon diode requires a minimum voltage difference of 0.6 volts between the anode and cathode to conduct current.
How does the diode work when the anode is more positive than the cathode?
-When the anode is more positive than the cathode, the diode is in a forward bias condition, allowing current to flow from the anode to the cathode.
What happens when the polarity is reversed, making the anode negative and the cathode positive?
-When the polarity is reversed, the diode enters reverse bias, and no current flows because the diode blocks the current in this configuration.
What is the difference between forward bias and reverse bias in a diode?
-Forward bias occurs when the anode is more positive than the cathode, allowing current to flow. Reverse bias occurs when the anode is more negative than the cathode, preventing current from flowing.
How can you visually identify the anode and cathode on a diode?
-The anode is typically marked with a strip or a white dot, while the cathode is the side without the mark. In diodes like Zener diodes, the cathode side will also have a line.
What does 'bias maju' or forward bias mean in terms of current flow?
-'Bias maju' or forward bias means the diode allows current to flow from the anode to the cathode when the anode is more positive than the cathode, with a voltage difference above the threshold (usually 0.6V for silicon diodes).
What happens if the voltage difference is less than the required threshold (e.g., 0.6V for silicon diodes)?
-If the voltage difference is less than the required threshold, the diode will not conduct any current, effectively blocking the flow of electricity.
Why is it important to understand the basic operation of diodes for learning about other electronic components?
-Understanding the basic operation of diodes is essential because it provides foundational knowledge for studying other electronic components, as diodes are key in controlling current flow in circuits.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Zener Diode (Basics, Symbol, Characteristics, Applications, Pros & Cons) Explained

Diodos: o guia básico para entender de forma fácil

Dioda Bridge (Simbol, Bentuk Fisik, dan Analisis Cara Kerja ) #Part 2
Diodes - What Are Diodes - PN Junction - Forward Bias - Reverse Bias - Zener Diodes

O que é um diodo?

What is a zener diode and how does it work? | Intermediate Electronics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
