Mekanika Fluida dan Sifat-sifat Fluida #1
Summary
TLDRThe video script is a lecture on fluid mechanics, focusing on the properties of fluids, including liquids and gases. It explains the difference between incompressible liquids and compressible gases, and introduces concepts like fluid statics and dynamics. The lecture also covers topics such as surface tension, capillarity, and the ideal gas law. Practical examples like dams and pipelines are used to illustrate the importance of understanding fluid properties in engineering applications.
Takeaways
- 📚 The course is Fluid Mechanics 1, a 2-credit subject that covers various aspects of fluids including their properties and behavior.
- 🌊 Fluids are classified into liquids and gases. Liquids take the shape of their container and are incompressible, while gases are compressible and can change volume under pressure.
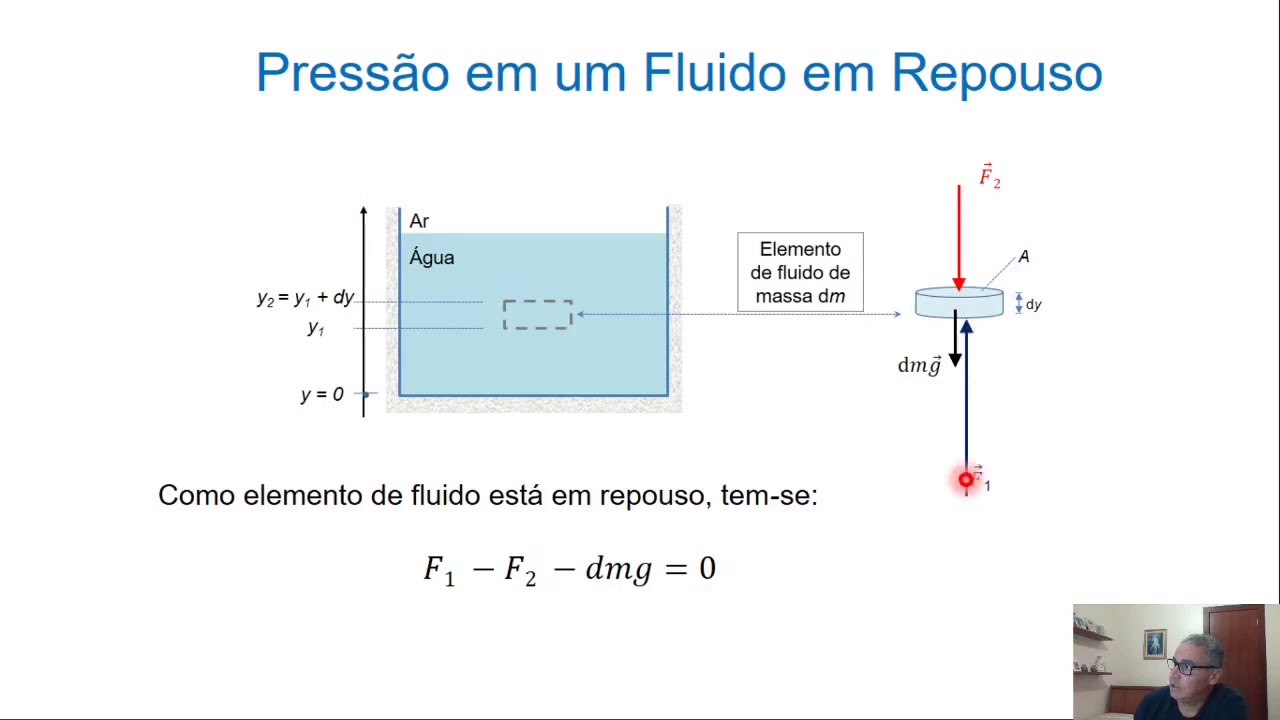
- 🏞️ Static fluid mechanics studies fluids at rest, such as water in a dam, and focuses on pressure and the strength of containment.
- 🚰 Dynamic fluid mechanics explores fluids in motion, like a person drinking juice through a straw, and involves designing efficient piping systems.
- 🧠 Fluid properties like density, mass, volume, temperature, and pressure are key factors in fluid mechanics. Intensive properties remain constant even if the fluid is divided, while extensive properties change.
- ⚖️ Density is the mass of a fluid divided by its volume, with units in kg/m³. It helps differentiate between fluids like oil and water.
- 🔄 Specific volume is the inverse of density, and specific gravity compares the density of a fluid to that of water, where water has a specific gravity of 1.
- 🛠️ The design of pressurized systems, such as dams or hydraulic systems, requires calculating the pressure on container walls to ensure safety and structural integrity.
- 💨 Gases are compressible, meaning their volume can change under pressure, and this plays a crucial role in fluid dynamics, particularly in the behavior of air and other gases.
- 🧪 The ideal gas law, PV = nRT, is important for calculating properties like pressure and density of gases in specific conditions, with temperature always measured in Kelvin.
Q & A
What is the main difference between liquid and gas in terms of compressibility?
-The main difference is that liquids are incompressible, meaning their volume doesn't significantly change under pressure. In contrast, gases are compressible and can be compacted into a smaller volume when pressure is applied.
How does fluid statics differ from fluid dynamics in fluid mechanics?
-Fluid statics deals with fluids at rest and their behavior under pressure, such as water in a dam or container. Fluid dynamics focuses on fluids in motion, like the flow of liquid through pipes, and considers factors like velocity and pressure changes.
What is an example of a real-world application of fluid statics?
-An example of fluid statics is the design of a dam in hydroelectric power plants, where engineers must calculate the pressure exerted by the water on the dam's walls to ensure structural integrity and safety.
What role does pipe material play in fluid dynamics?
-The material of the pipe affects the flow rate and friction within the system. Different materials may cause more or less resistance to fluid flow, impacting the design of piping systems, such as those used in hydrants or other fluid transport systems.
What is density in the context of fluid mechanics?
-Density is the mass of a fluid per unit volume. It is a crucial property in fluid mechanics, as it helps determine how a fluid will behave under different conditions, such as when it's subjected to pressure or temperature changes.
What is specific volume and how is it related to density?
-Specific volume is the reciprocal of density. It represents the volume occupied by a unit mass of a substance. If a fluid has a higher density, it will have a lower specific volume, and vice versa.
How does the specific gravity of a substance differ from its density?
-Specific gravity is a dimensionless quantity that compares the density of a substance to the density of water. It indicates whether a substance is heavier or lighter than water. For example, a specific gravity of 19.3 for gold means gold is 19.3 times denser than water.
What is the ideal gas law and how is it relevant in fluid mechanics?
-The ideal gas law is expressed as PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the amount of substance, R is the gas constant, and T is temperature. It describes the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature for ideal gases and helps predict how gases behave under varying conditions.
Why is it important to consider temperature in fluid mechanics calculations?
-Temperature affects the behavior of fluids, especially gases, as it influences properties like density and pressure. In fluid mechanics, accurate temperature measurements are crucial for predicting fluid flow, pressure changes, and gas behavior.
What are extensive and intensive properties in fluid mechanics?
-Extensive properties, like mass and volume, depend on the amount of substance present and change when the substance is divided. Intensive properties, like temperature and density, do not change when the substance is divided, and are the same regardless of the amount of substance.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)