Magnetic effect of electric current in one shot (Animation) | CLASS 10 CBSE boards | NCERT Science
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the magnetic effects of electric current, beginning with Hans Christian Oersted's discovery of electromagnetism in 1820. It covers topics such as the formation and behavior of magnetic fields in bar magnets, straight and coiled current-carrying conductors, and solenoids. The video demonstrates how electric currents generate magnetic fields, explains the right-hand thumb rule, and introduces devices that use electromagnetism, like motors and generators. It also touches on the safety aspects of domestic electric circuits, including the role of fuses and earth wires in preventing overloading and electrical shocks.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Hans Christian Oersted discovered in 1820 that electric current affects magnetic fields, laying the foundation for electromagnetism.
- 🧲 The unit of magnetic field strength is named after Oersted in recognition of his contributions.
- 🌍 Magnetic fields exist around magnets, and they influence materials like iron filings to form patterns.
- 🧭 A compass near a magnet deflects due to the magnetic field, showing that like poles repel and opposite poles attract.
- 📐 Magnetic field lines form closed loops, starting from the North Pole of a magnet and merging at the South Pole.
- 🔄 A straight current-carrying conductor produces concentric magnetic field lines, with direction determined by the current flow.
- 👍 The right-hand thumb rule helps determine the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor.
- 🔄 When a straight conductor is bent into a loop, its magnetic field lines appear as straight lines at the loop's center.
- 🔧 Solenoids, tightly wound coils of wire, produce strong magnetic fields similar to bar magnets when current passes through them.
- ⚙️ Devices like motors, generators, and speakers utilize the force generated by interactions between electric currents and magnetic fields.
Q & A
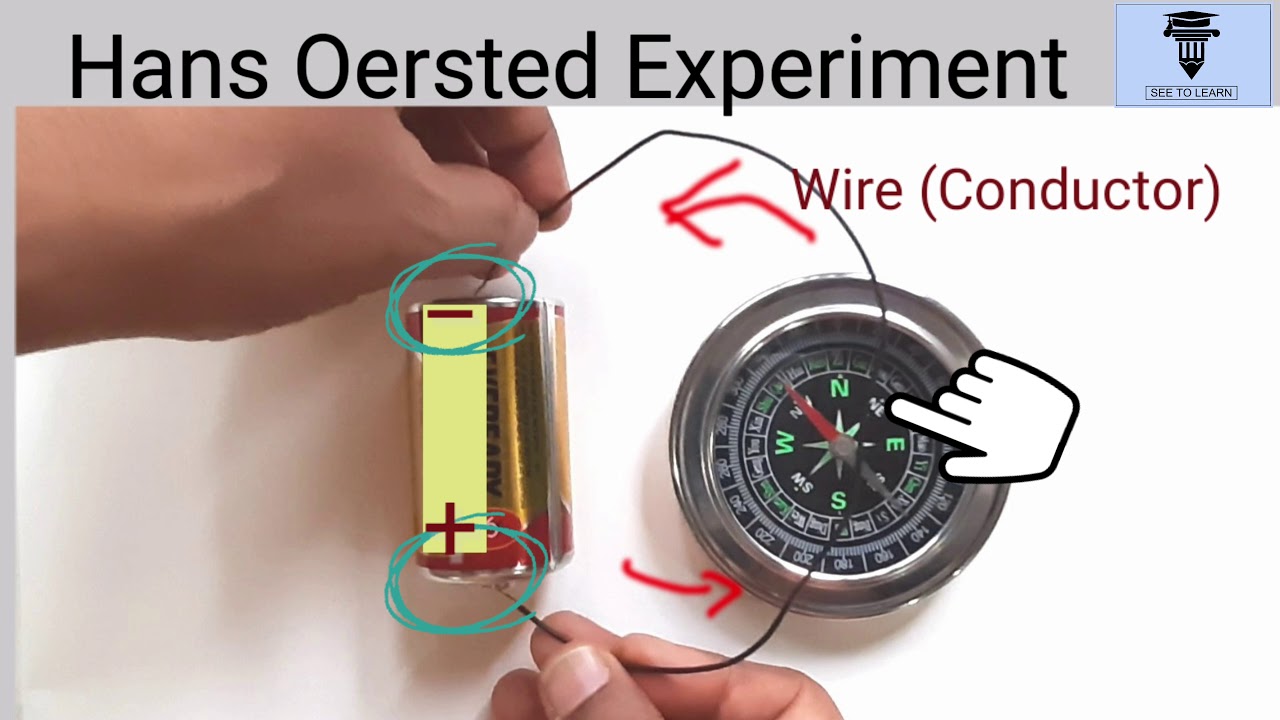
Who discovered the relationship between electricity and magnetism, and how?
-Hans Christian Oersted discovered the relationship between electricity and magnetism in 1820 when he observed that a compass needle deflected near a current-carrying conductor.
What is a magnetic field, and how can it be visualized with a bar magnet?
-A magnetic field is the area around a magnet where magnetic forces can be detected. It can be visualized by sprinkling iron filings around a bar magnet on a surface like cardboard. The filings arrange in a pattern that shows the magnetic field lines.
What happens when two magnets with the same poles are placed near each other?
-When two magnets with the same poles (e.g., both North or both South) are placed near each other, they repel or push apart.
How can we draw magnetic field lines of a bar magnet using a compass?
-To draw magnetic field lines, place a compass near the North Pole of the magnet and mark the direction the needle points. Move the compass along the field line, marking each position. Then, connect the marks with a smooth curve to represent the magnetic field line.
What is the Right-Hand Thumb Rule, and how is it applied?
-The Right-Hand Thumb Rule helps determine the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor. Point your right thumb in the direction of the current, and the curl of your fingers represents the direction of the magnetic field lines.
What is the shape of the magnetic field around a straight current-carrying conductor?
-The magnetic field around a straight current-carrying conductor forms concentric circles, as observed by sprinkling iron filings around the conductor and tapping the surface.
What happens to the magnetic field when the current in a conductor increases?
-As the current flowing through the conductor increases, the strength of the magnetic field increases as well, which is indicated by the increased deflection of a compass needle.
How does the direction of the magnetic field change when the direction of current flow is reversed?
-When the direction of current flow is reversed, the direction of the magnetic field also changes. For example, if the current flows from North to South, the magnetic field deflects eastward, but if reversed, it deflects westward.
What is a solenoid, and how does its magnetic field compare to a bar magnet?
-A solenoid is a coil made of numerous circular turns of insulated wire, which creates a magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet. One end behaves like a North Pole and the other as a South Pole, with uniform field lines inside the solenoid.
What is the role of the Earth wire in domestic electric circuits?
-The Earth wire provides a low-resistance path for excess electrical current, protecting against electric shock and preventing damage to appliances by safely dissipating excess current into the ground.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)