Permanent Maxillary Central Incisor
Summary
TLDRThe transcript explains the anatomy and key features of the maxillary central incisor, emphasizing its prominence in a person's smile, termed 'Incisal dominance.' It describes the tooth's development from four lobes, its role in cutting, and details its shape, measurements, and morphology. The script also covers clinical aspects, such as the occurrence of Mamelons, curvature differences between mesial and distal sides, and anomalies like Hutchinson's incisors seen in patients with congenital syphilis. It concludes with the tooth's structural details from various aspects including labial, palatal, proximal, and incisal views.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Maxillary Central Incisor is the first tooth from the midline and plays a crucial role in a person's smile, known as 'Incisal dominance.'
- 📏 In the FDI system, the permanent maxillary central incisors are numbered 11 and 21, in the Universal system, they are 8 and 9, and in the Zsygmondy Palmar system, they are 1 with different brackets according to the quadrant.
- ✂️ The primary function of the maxillary central incisor is cutting.
- 🦷 The tooth develops from 4 developmental lobes: mesial, labial, distal, and lingual.
- 👶 Newly erupted incisors show three protuberances known as Mamelons, which wear off with use and are not present in adult teeth.
- 📅 The maxillary central incisor erupts between the ages of 7 and 8 years.
- 📏 The crown length of the tooth is 10.5 millimeters, and the root length is 13 millimeters.
- 🔍 The labial aspect of the crown is trapezoidal, with the incisal ridge featuring a sharp mesio-incisal angle and a rounded disto-incisal angle.
- 🔄 From the lingual aspect, the tooth has three ridges: incisal ridge, mesial marginal ridge, and distal marginal ridge, with a prominent cingulum.
- 👥 Maxillary central incisors are prone to developmental anomalies such as talon cusp, fusion, gemination, and dens invaginatus, and are frequently involved in trauma cases.
Q & A
What is the significance of the maxillary central incisor in a person's smile?
-The maxillary central incisor has the most prominent effect on a person's smile due to its central position, a concept known as 'Incisal dominance.'
What are the tooth numbers for the maxillary central incisor in different dental numbering systems?
-In the FDI system, the tooth numbers are 11 and 21. In the Universal system, the tooth numbers are 8 and 9, and in the Zsigmondy-Palmer system, they are labeled as 1, with different brackets based on the quadrant.
What is the primary function of the maxillary central incisor?
-The primary function of the maxillary central incisor is cutting.
What are Mamelons, and are they present in adult or deciduous incisors?
-Mamelons are protuberances seen on the incisal ridge of a newly erupted incisor. They wear off with continuous use and are not seen in adults or in deciduous incisors.
At what age does the maxillary central incisor typically erupt?
-The maxillary central incisor typically erupts at the age of 7 to 8 years.
What are the four developmental lobes of the maxillary central incisor?
-The four developmental lobes are the mesial, labial, distal, and lingual lobes. The mesial, labial, and distal lobes form the labial aspect of the crown and incisal ridge, while the lingual lobe forms the cingulum.
How does the maxillary central incisor appear from the labial aspect?
-From the labial aspect, the crown has a trapezoidal outline with a smooth and convex surface. The mesio-incisal angle is sharp, while the disto-incisal angle is rounded.
What are the three ridges present on the lingual surface of the maxillary central incisor?
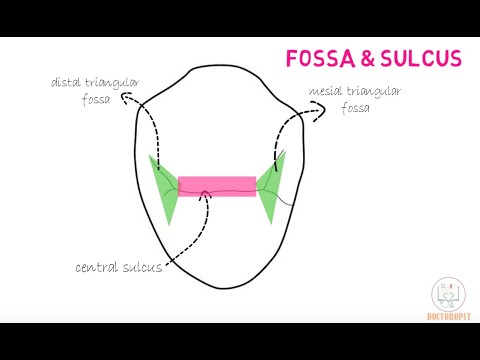
-The three ridges on the lingual surface are the incisal ridge, mesial marginal ridge, and distal marginal ridge. The cingulum is present in the cervical third, and a concavity called the lingual fossa, often w-shaped, is located in the middle.
What is a shovel-shaped incisor, and in which race is it more common?
-A shovel-shaped incisor has prominent marginal ridges, making the lingual surface concave. It is more commonly seen in the Mongoloid race.
What are some developmental anomalies associated with the maxillary central incisor?
-Developmental anomalies associated with the maxillary central incisor include talon cusp, fusion, gemination, and dens invaginatus. Additionally, screw-driver shaped incisors (Hutchinson's incisors) are a clinical feature in patients with congenital syphilis.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Permanent Maxillary Central Incisor | Tooth Morphology Made Easy

Anatomi Gigi Incisivus dan Caninus Maxilla

What are the Surfaces of a Tooth? Learn the 5 Dental Surfaces Every Future Dentist Needs to Know

Embryology of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses

Skull Anatomy - Older Version
Permanent Maxillary 1st Premolar
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
