¿CÓMO dibujar estructuras de LEWIS? 1º parte.
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script teaches viewers how to draw Lewis structures for both ionic and covalent compounds. It begins with a refresher on valence electrons and their representation in Lewis structures. The script then guides through creating Lewis structures for ionic compounds like potassium iodide and lithium oxide, emphasizing the transfer of electrons to achieve a full octet. For covalent compounds, examples like chlorine diatomic and bromine monoxide illustrate how atoms share electrons to complete their octets. The script simplifies complex concepts, making it accessible for learners to grasp the basics of chemical bonding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lewis structures represent the valence electrons of an atom, which are the electrons in the outermost energy level.
- 🔬 Elements from Group 1 in the periodic table have one valence electron, while Group 2 elements have two, and so on, increasing by one electron per group.
- 🌐 Noble gases, except for helium, have a full octet of eight valence electrons and typically do not form bonds.
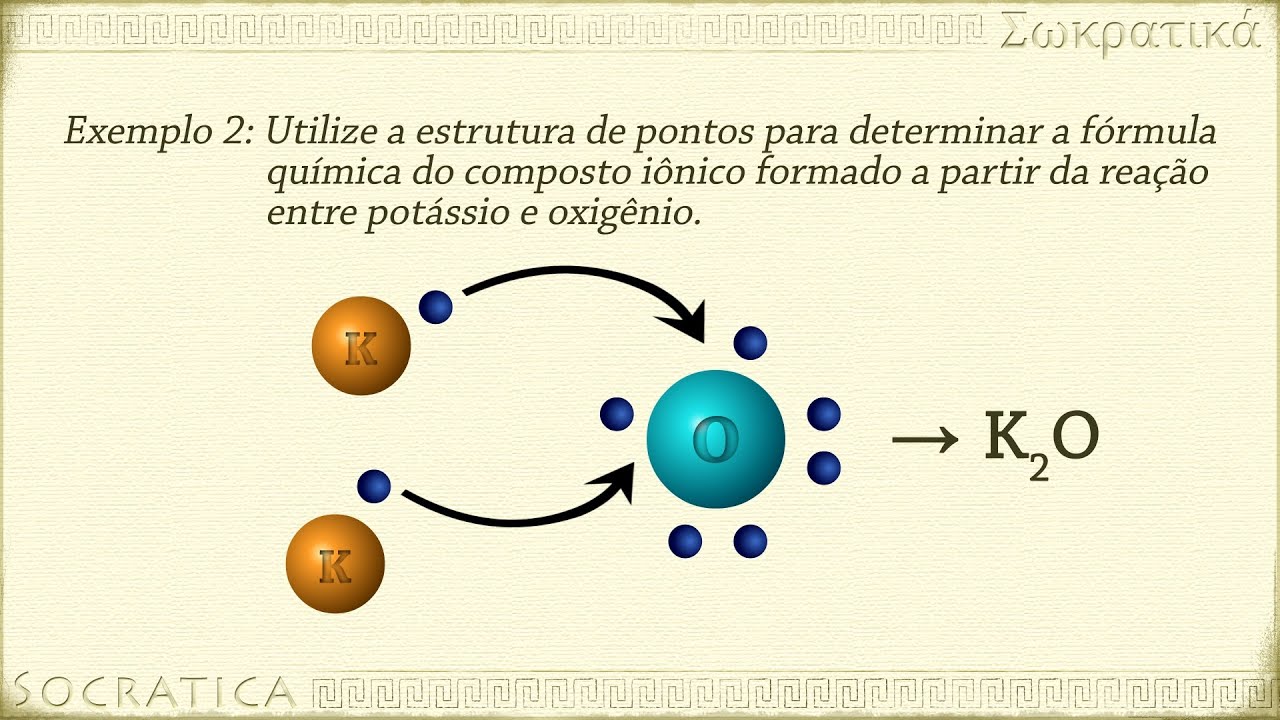
- ⚛️ In ionic compounds, like potassium iodide, the metal (potassium) transfers its valence electron to the non-metal (iodine) to complete its octet.
- 🔋 The charge of ions is indicated by a positive sign for the metal that loses an electron and a negative sign for the non-metal that gains an electron.
- 🧠 For covalent compounds, atoms share electrons to complete their octet, as seen in the diatomic chlorine molecule where each chlorine atom shares one electron to form a single bond.
- 🔬 The central atom in a Lewis structure is often the one that is not repeated in the compound, such as oxygen in lithium oxide.
- 🔗 In covalent bonding, the number of bonds an atom forms is equal to the number of electrons it needs to complete its octet.
- 🔍 To verify a Lewis structure, ensure that all atoms have a complete octet, which means they have eight electrons in their valence shell.
- 📚 The process of creating Lewis structures is likened to solving a puzzle, where the central atom is found first, and then other atoms are added to complete the structure.
Q & A
What is the purpose of a Lewis structure?
-The purpose of a Lewis structure is to represent the valence electrons of an atom, showing how they are arranged around the atom and how they participate in the formation of chemical bonds.
How many valence electrons does sodium have and how is it represented in a Lewis structure?
-Sodium has one valence electron, which is represented by its symbol with a single dot in a Lewis structure.
What is the significance of an octet in Lewis structures?
-An octet refers to having eight electrons in the valence shell, which is a stable electron configuration. Elements tend to form bonds to achieve this stable configuration.
Which group in the periodic table has one valence electron?
-Group 1 elements in the periodic table have one valence electron.
Why are noble gases not typically involved in bond formation according to the script?
-Noble gases are not typically involved in bond formation because they already have a full valence shell with eight electrons, making them chemically stable and less likely to react.
What is the chemical formula for potassium iodide and how does it form an ionic bond?
-The chemical formula for potassium iodide is KI. It forms an ionic bond through the transfer of one electron from potassium (a group 1 element) to iodine (a group 7 element), resulting in potassium having a +1 charge and iodine having a -1 charge.
How do you determine the central atom in a Lewis structure?
-The central atom in a Lewis structure is typically the least electronegative atom or the one that is not repeated in the compound. In the case of lithium oxide, oxygen is chosen as the central atom because it is not repeated.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds in the context of Lewis structures?
-In ionic bonds, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, while in covalent bonds, electrons are shared between atoms. Ionic bonds often involve metals and nonmetals, whereas covalent bonds typically involve nonmetals.
How does aluminum chloride form its Lewis structure?
-In aluminum chloride, aluminum (with 3 valence electrons) forms covalent bonds with three chlorine atoms (each with 7 valence electrons). Each chlorine atom shares one electron with aluminum to complete its octet, resulting in a -1 charge for each chlorine and a +3 charge for aluminum.
What is the process to ensure that all atoms in a Lewis structure satisfy the octet rule?
-To ensure that all atoms satisfy the octet rule, count the total number of electrons around each atom, including those in bonds. Each bond counts as two electrons, and the goal is for each atom to have eight electrons in its valence shell.
How do you verify the correctness of a Lewis structure for a covalent compound?
-You verify the correctness of a Lewis structure for a covalent compound by ensuring that all atoms have a complete octet (eight electrons in their valence shell) and that the total number of electrons used in the structure matches the sum of the valence electrons of the atoms in the compound.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Video 6b/17- Lewis Dot Diagrams, the BVICS method- Chemistry, Regents360

Gambarkan struktur Lewis pembentukan senyawa ion berikut! a. BeF2 b. Al2O3 c. Li2O

Soal-soal Ikatan Kimia Kelas 10 dan 11 SMA/MA Pilihan

How to Name Chemicals Made Easy

Naming Ionic and Molecular Compounds | How to Pass Chemistry
Química: Ligações Iônicas
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
