The Human Reproductive System
Summary
TLDRProfessor Dave explores the human reproductive system, highlighting the primary sex organs—testes in males and ovaries in females—which produce sex hormones and gametes through meiosis. He details the male reproductive process, from sperm production in the testes to ejaculation, and the role of accessory glands. The female reproductive system is more complex, involving ovulation, the fallopian tubes, and the uterus for nurturing a fertilized egg. The video also touches on external genitalia and the mammary glands, setting the stage for deeper discussions on the menstrual cycle and hormonal regulation.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The human reproductive system is essential for the continuation of the species and is anatomically distinct between males and females.
- 👨⚕️ The male reproductive system includes the testes, which are responsible for producing testosterone and sperm cells, and accessory glands like the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands.
- 🌡️ The testes are housed in the scrotum, which maintains a lower temperature optimal for sperm production.
- 🧬 Sperm cells are produced through a process called spermatogenesis within the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
- 💧 Semen, produced by the seminal vesicles, enhances sperm motility and fertilizing ability by providing a mixture of hormones and compounds.
- 🤺 The penis serves as the male copulatory organ, facilitating the delivery of sperm into the female reproductive tract.
- 👩⚕️ The female reproductive system includes the ovaries, which produce egg cells (ova) and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
- 🌀 Oogenesis is the process of mature egg cell production, culminating in ovulation where the egg is released from the ovary.
- 🤰 The uterus, or womb, is the site of fetal development, with a thick wall composed of the perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium.
- 🍼 The mammary glands in the breasts produce milk during pregnancy, which is then transferred to the lactiferous ducts for nursing.
- 🔄 The reproductive system's function is regulated by complex hormonal cycles, including the menstrual cycle and the ovarian cycle.
Q & A
What are the primary sex organs in the human body?
-The primary sex organs, also known as gonads, are the testes in males and the ovaries in females. These organs are responsible for producing sex hormones and gametes.
What is the difference between gametes and other cells in the body?
-Gametes are haploid cells produced through meiosis, while the majority of the body's cells are diploid, produced through mitosis.
How does the process of fertilization lead to the development of a new human being?
-Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell from the male meets an egg cell from the female, resulting in a zygote. This zygote undergoes embryonic development, leading to the birth of a new human being.
What is the role of the scrotum in the male reproductive system?
-The scrotum houses the testes and provides a cooler environment outside the body, which is ideal for sperm production.
Describe the process of spermatogenesis and where it occurs.
-Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm production from spermatogenic cells and occurs in the seminiferous tubules within the testes.
What are the accessory glands in the male reproductive system and their functions?
-The accessory glands include the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands. The seminal vesicles produce semen to mix with sperm, the prostate contributes prostatic secretions to activate sperm, and the bulbourethral glands produce mucus for lubrication during sexual arousal.
How does the female reproductive system differ structurally from the male?
-The female reproductive system includes internal gonads (ovaries), accessory ducts (uterine tubes and uterus), and external genitalia (vulva), and is more complex due to the involvement in menstrual cycles, fertilization, and fetal development.
What is the function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
-The ovaries produce female gametes (egg cells or ova) and secrete sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. They also undergo ovulation, where an oocyte is released.
Can you explain the process of ovulation and its significance?
-Ovulation is the process where a mature egg (oocyte) is released from the ovary, typically once per menstrual cycle. It is significant as it allows for the potential of fertilization to occur if the egg meets a sperm.
What is the role of the uterus in the female reproductive system?
-The uterus receives the fertilized egg, retains it in the uterine wall, and nourishes it through fetal development until birth.
How does the structure of the breast relate to its function in lactation?
-The breast contains mammary glands with lobules and alveoli that produce milk. This milk is transferred to lactiferous ducts, which lead to lactiferous sinuses where it collects for nursing.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Sistem Reproduksi: Regulasi Reproduksi Pria | Alternatifa

Gamet Structure part 1

PRESENTASI SISTEM REPRODUKSI MANUSIA OLEH SUCHIANA

DUNIA REMAJA: Sistem Reproduksi Manusia
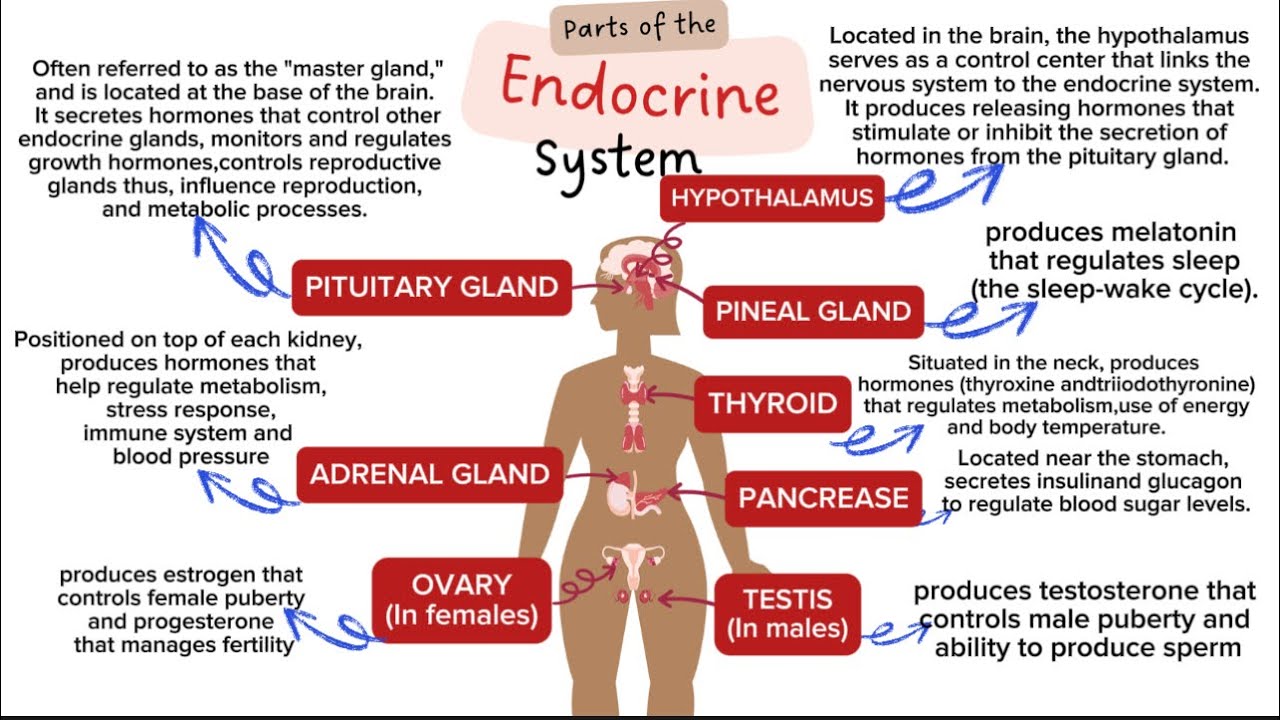
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM : What It Is, Parts and Functions of the Endocrine System.
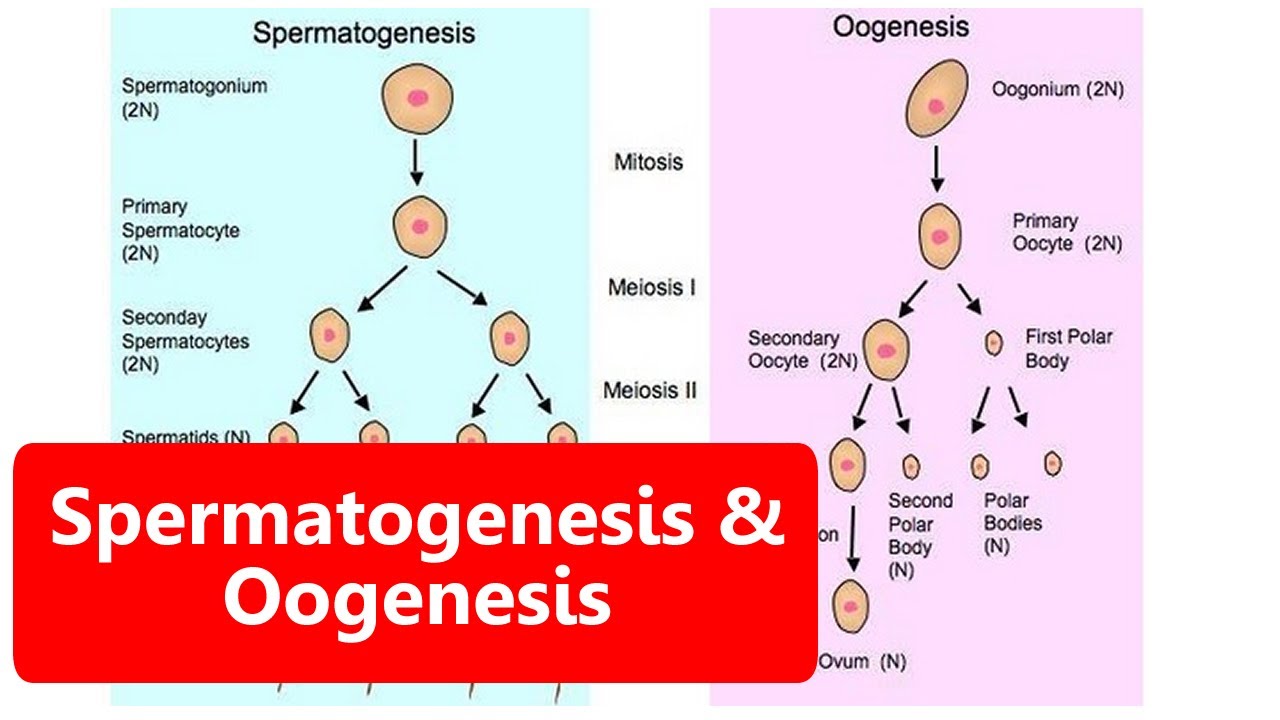
SPERMATOGENESIS DAN OOGENESIS - Sistem Reproduksi Pada Manusia | Belajar IPA Kelas 9 SMP/ MTS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
