EVERY ENGINE SENSOR EXPLAINED - MAF, MAP, IAT, TPS, 02, NOx, EGT - How it works, location, OBD2 code
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of essential engine sensors, including oxygen, exhaust gas temperature (EGT), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and knock sensors. It explains their functions, placements, and significance in maintaining optimal engine performance and emissions control. The presenter highlights how these sensors work with the ECU to adjust fuel injection and timing, ensuring the engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Viewers learn about the consequences of sensor failures, including poor performance and emissions test failures. The video encourages engagement by inviting viewers to discuss any overlooked sensors and request deeper dives into specific topics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Oxygen sensors are critical for monitoring engine performance and emissions.
- 🔍 There are two types of oxygen sensors: narrowband (indicates rich or lean) and wideband (provides precise air-fuel ratio).
- ⚙️ The voltage produced by oxygen sensors corresponds to the oxygen level at the sensor tip, affecting fuel injection adjustments by the ECU.
- 🚗 Most catalytic converter-equipped vehicles have at least two oxygen sensors: upstream (before the converter) and downstream (after the converter).
- ⚠️ A failing oxygen sensor can lead to noticeable symptoms such as rough engine performance and may cause a vehicle to fail emissions tests.
- 🔥 Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) sensors measure exhaust gas temperature and help monitor the air-fuel ratio.
- 🛠️ EGT probes are typically placed close to the exhaust valves and are crucial in protecting turbochargers and catalytic converters in diesel engines.
- 🌬️ Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) sensors measure NOx levels in exhaust gases, primarily in diesel vehicles, ensuring SCR systems operate correctly.
- 🛑 Knock sensors detect abnormal combustion (knock) in the engine and relay information to the ECU to adjust ignition timing or fuel injection.
- ⚙️ The number of sensors in modern engines is increasing, highlighting the importance of staying informed about engine monitoring technologies.
Q & A
What is the primary role of oxygen sensors in an engine?
-Oxygen sensors monitor the air-fuel ratio in an engine, which is crucial for both performance and emissions control.
What is the difference between narrowband and wideband oxygen sensors?
-Narrowband sensors can indicate if the engine is running rich or lean but do not provide precise measurements. In contrast, wideband sensors cover a wider range of air-fuel ratios and can provide exact readings to the ECU.
How does the ECU respond to oxygen sensor readings?
-The ECU adjusts the amount of fuel injected into the engine based on the oxygen sensor readings to maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio.
Why are there two oxygen sensors in most catalytic converter-equipped vehicles?
-One sensor is located upstream of the catalytic converter to measure the air-fuel ratio, while the downstream sensor verifies the effectiveness of the catalytic converter.
What are the potential symptoms of a failing oxygen sensor?
-Symptoms can range from a rough-running engine to failing emissions tests. In modern vehicles, a failed oxygen sensor may prevent the engine from starting.
What is the function of an exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensor?
-The EGT sensor measures the temperature of exhaust gases, which helps infer the air-fuel ratio and protects components like turbos and catalytic converters from overheating.
In which types of engines are EGT sensors typically used, and why?
-EGT sensors are commonly found in turbo diesel and diesel engines to monitor exhaust temperatures for DPF regeneration and to protect the SCR system.
What do nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensors measure, and where are they commonly found?
-NOx sensors measure the levels of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases and are typically found in diesel vehicles, as they monitor the operation of the SCR system.
What happens if a NOx sensor fails in a diesel vehicle?
-A failure of a NOx sensor can trigger limp home mode in modern diesel vehicles, potentially resulting in poor fuel mileage and erratic idling.
How does a knock sensor work, and why is it important?
-A knock sensor detects abnormal combustion (knock) within the engine and relays this information to the ECU, which can adjust ignition timing or fuel injection to prevent engine damage.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
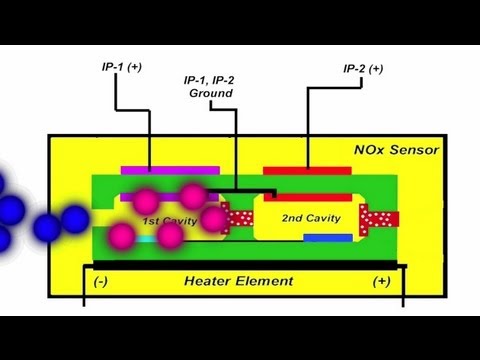
GDI NOx Sensor Operation

p2000-00 Trouble Code, (NOx) Nitrous Oxides Number 1 Trap Efficiency....Engine Oil Level Rising !!
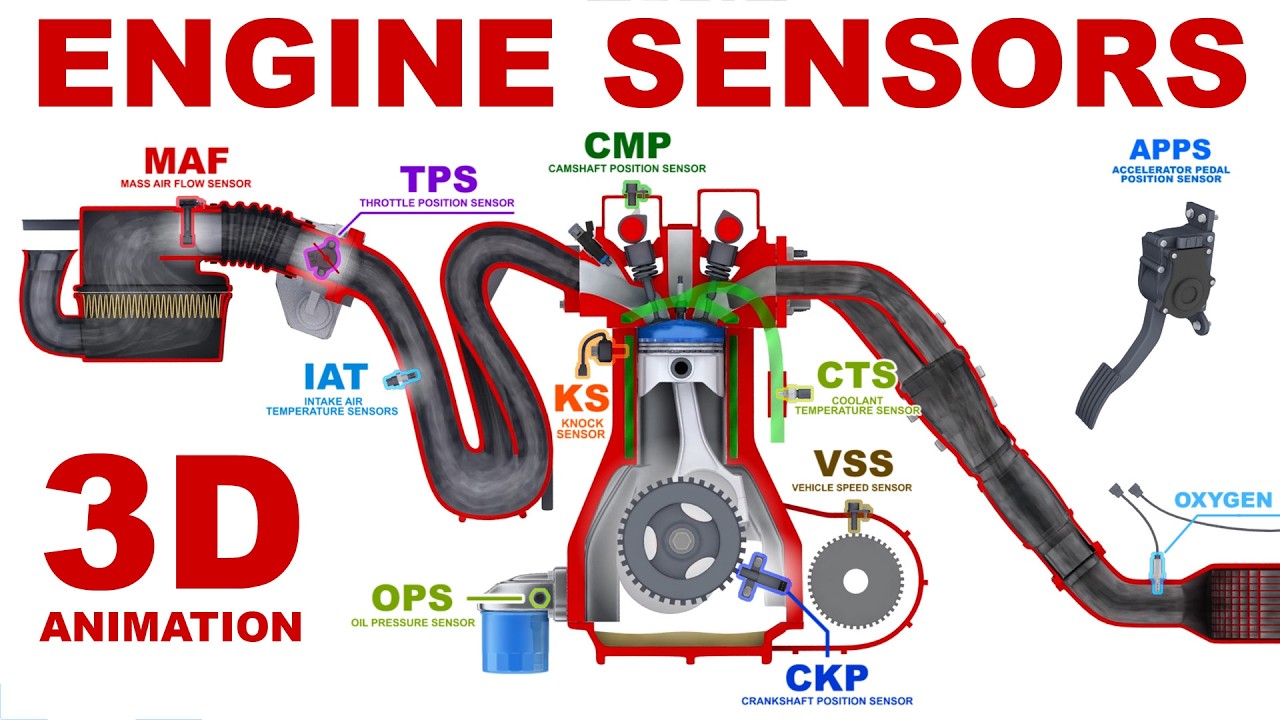
Engine Sensors - Basics. 3D Animation
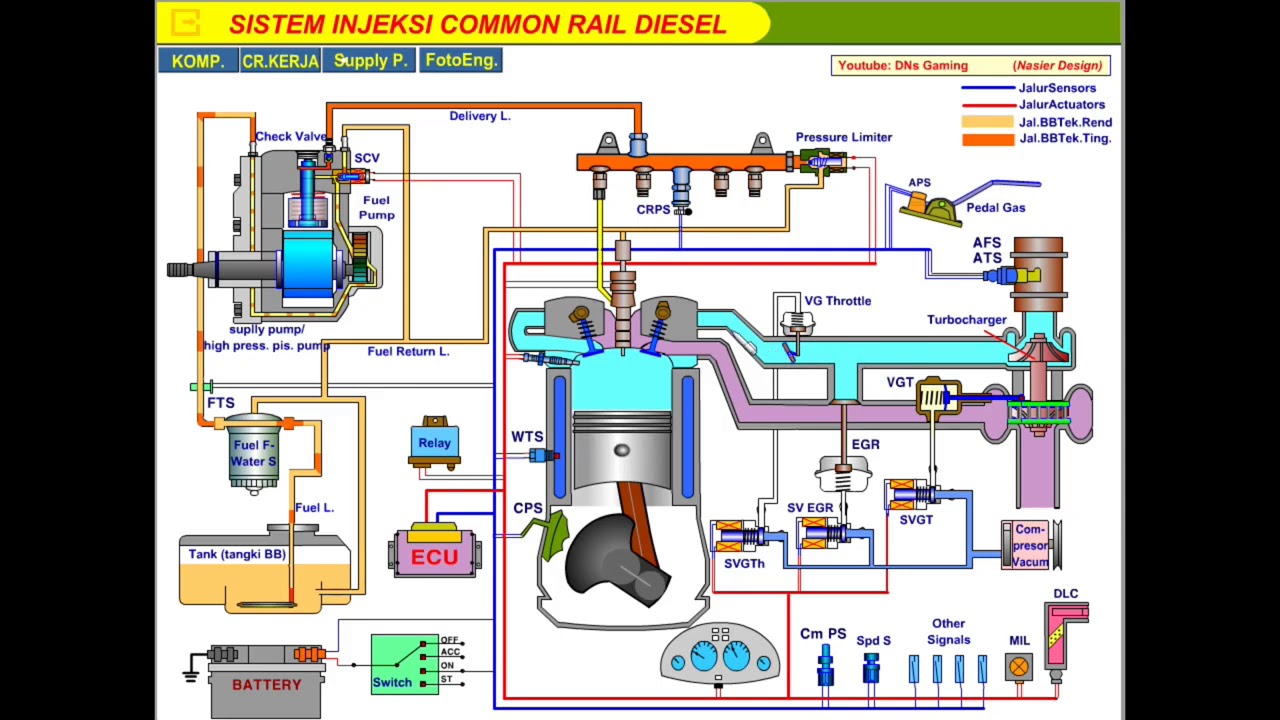
cara kerja bahan bakar diesel (Tipe common rail)

The MOST AMAZING Features of the GE Jenbacher 6000HP V12 Engine

EMS Part 2: Sensor-sensor Mobil I Engine Management System #ems #enginemanagementsystem #sensor
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
