Intro to electric potential | Electric potential and capacitance | Physics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of electric potential is explained using the analogy of gravitational potential energy. It starts with the example of a bowling ball held at a certain height, where its potential energy is calculated based on its mass. This is then compared to electric potential, using charged objects and explaining how electric potential is the amount of potential energy per unit charge. The video clarifies the difference between electric potential and electric potential energy and introduces the concept of volts (joules per coulomb), with practical implications of how electric potential works in space.
Takeaways
- 😀 Gravitational potential energy refers to the energy stored in an object due to its position relative to the ground, like a bowling ball held at a height.
- 😀 Potential energy is energy that is stored and can be converted into kinetic energy when the object is released or moves.
- 😀 If a 5 kg ball has 55 joules of potential energy at a specific height, a 1 kg ball at the same height would have 1/5 of that potential energy, i.e., 11 joules.
- 😀 The amount of potential energy per unit mass is a measure of potential energy at that point and is referred to as 'potential.'
- 😀 Gravitational potential is similar to a price indicator in a store, where the price per kilogram indicates how much energy an object has based on its mass.
- 😀 Electric potential is analogous to gravitational potential but applies to electric charges, where energy is stored based on the charge's position relative to other charges.
- 😀 Electric potential energy is the energy stored in a charged object, which can be calculated using the same principles as gravitational potential energy.
- 😀 If a charge of 20 coulombs has 100 joules of potential energy, a charge of 1 coulomb at the same point would have 1/20 of that energy, i.e., 5 joules.
- 😀 Electric potential at a point is defined as the potential energy per unit charge (joules per coulomb), also known as 'volts.'
- 😀 A voltage of 20 volts means that if you place 1 coulomb of charge at that point, it would have 20 joules of potential energy.
- 😀 Electric potential is an indicator of the potential energy that any charge would have at a given point in space, not just for one specific charge.
Q & A
What is potential energy in the context of gravity?
-Potential energy in gravity is the stored energy an object has due to its position relative to the ground. For example, a bowling ball held at a height has potential energy that can be converted into kinetic energy when it falls.
How is potential energy related to mass and height?
-Potential energy increases with both the mass of the object and its height above the ground. For example, a heavier object or one held at a greater height will have more potential energy.
If a 5 kg ball has 55 joules of potential energy, how much potential energy would a 1 kg ball have at the same height?
-The potential energy of a 1 kg ball at the same height would be 11 joules, which is one-fifth of the 55 joules of the 5 kg ball, because potential energy is proportional to mass.
What is the difference between potential energy and potential?
-Potential energy is the total energy stored in an object due to its position, while potential is the energy per unit mass or charge. In the example, 11 joules of potential energy per kilogram is the potential at a point in a gravitational field.
How does electric potential compare to gravitational potential?
-Electric potential is similar to gravitational potential in that it represents energy per unit charge rather than per unit mass. Just as gravity acts on mass, electric potential acts on electric charge, indicating how much energy a charge would have at a particular point.
What is the electric potential at a point where a 20 coulomb charge has 100 joules of potential energy?
-The electric potential at that point would be 5 joules per coulomb (100 joules divided by 20 coulombs), meaning each coulomb of charge at that point would have 5 joules of potential energy.
What is the unit of electric potential and why is it called a volt?
-The unit of electric potential is the volt, which is defined as joules per coulomb. It is named after Alessandro Volta, the inventor of the first battery.
How do you calculate electric potential at a point?
-Electric potential at a point is calculated by dividing the potential energy at that point by the amount of charge. The result is the energy per unit charge, expressed in volts (joules per coulomb).
What does it mean when someone says the electric potential at a point is 20 volts?
-It means that a 1-coulomb charge placed at that point would have 20 joules of potential energy. Electric potential is an indicator of the energy per unit charge at a specific point in space.
What is the relationship between electric potential and potential energy?
-Electric potential is the potential energy per unit charge. While potential energy is the total energy stored in a charge at a specific point, electric potential gives the energy per unit charge, helping us understand how electric fields affect charges at various locations.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
AS & A Level Physics (9702) - Chapter 5: Work, Energy, and Power
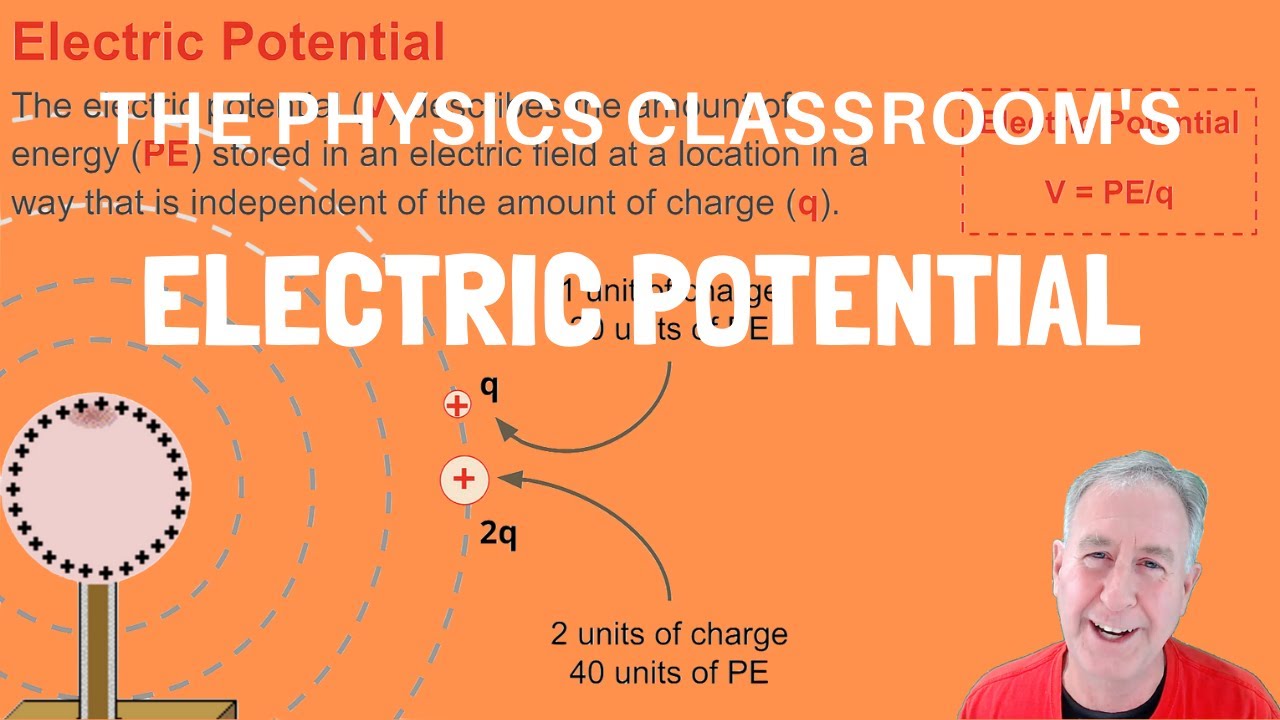
Electric Potential

POTENCIAL ELÉTRICO | AULA 02 | ENERGIA POTENCIAL ELÉTRICA
Energia Cinética, Potencial Gravitacional e Potencial Elástica

Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference

Energy | The Dr. Binocs Show | Educational Videos For Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
