Personality Disorders
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host provides a high-yield overview of personality disorders, specifically tailored for medical exams like the USMLE and COMLEX. He walks through the different clusters—A, B, and C—explaining key disorders such as paranoid, schizoid, schizotypal, borderline, narcissistic, antisocial, and others. Through practical examples from pop culture, like characters from *The Sopranos* and *Waterboy*, the video highlights the symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and distinctions between disorders. The host emphasizes the importance of understanding these disorders to boost exam scores and offers study tips for differentiating similar conditions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Personality disorders are pervasive patterns of maladaptive behaviors, cognitions, moods, and attitudes that impair social, occupational, and functional living.
- 😀 There are three clusters of personality disorders: Cluster A (paranoid, schizoid, schizotypal), Cluster B (borderline, histrionic, narcissistic, antisocial), and Cluster C (obsessive-compulsive, dependent, avoidant).
- 😀 Paranoid personality disorder is characterized by persistent suspicion and untrusting behaviors, but with intact reality testing (e.g., Paulie Walnuts from *The Sopranos*).
- 😀 Schizoid personality disorder involves reclusiveness, lack of motivation for relationships, and emotional indifference (e.g., someone working a solitary job like a night-shift security guard).
- 😀 Schizotypal personality disorder involves eccentric behavior, magical thinking, and bizarre beliefs, with some genetic overlap with schizophrenia (e.g., Doc Brown from *Back to the Future*).
- 😀 Borderline personality disorder is marked by unstable mood, negative self-image, and impulsivity, with symptoms including non-suicidal self-injury (e.g., Olivia Soprano from *The Sopranos*).
- 😀 Histrionic personality disorder is characterized by excessive attention-seeking, outward emotional displays, and sexual promiscuity to gain validation (e.g., reality TV characters like those from *Jersey Shore*).
- 😀 Narcissistic personality disorder involves grandiosity, entitlement, lack of empathy, and excessive reaction to perceived challenges or criticism (e.g., Donald Trump).
- 😀 Antisocial personality disorder is marked by disregard for others' rights and social norms, often leading to criminal behavior (e.g., sociopaths with a history of abuse or violence).
- 😀 Key distinctions in personality disorders include differentiating schizoid vs. avoidant (avoidant desires relationships but fears rejection), narcissistic vs. obsessive-compulsive (OCPD is ego-syntonic vs. OCD), and schizotypal vs. psychotic disorders (schizotypal has a risk of developing into schizophrenia).
Q & A
What is the main challenge with diagnosing personality disorders on exams like USMLE or COMLEX?
-The main challenge is that personality disorders often sound very similar to one another, which can make distinguishing between them difficult. However, with a clear understanding of the symptoms and characteristics of each disorder, they become easy to identify and can provide 'free points' on exams.
What is the difference between personality disorders and other mental health disorders like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder?
-Personality disorders are ingrained patterns of behavior, cognition, and emotional responses that persist over time, often starting from childhood. Unlike disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, they manifest through maladaptive behaviors and attitudes but are not associated with psychosis.
What are the three clusters of personality disorders and how are they categorized?
-Personality disorders are grouped into three clusters: Cluster A (paranoid, schizoid, and schizotypal), Cluster B (borderline, histrionic, narcissistic, and antisocial), and Cluster C (obsessive-compulsive, dependent, and avoidant). These clusters are based on the nature of the disorders, with Cluster B being considered the most severe.
Why is schizotypal personality disorder considered the most closely related to schizophrenia?
-Schizotypal personality disorder shares genetic and symptomatic overlap with schizophrenia, making it the most likely personality disorder to evolve into schizophrenia later in life. The eccentric, bizarre behaviors and magical thinking seen in schizotypal individuals are key characteristics linking it to schizophrenia.
How can you differentiate between schizoid and avoidant personality disorders?
-The key difference is that individuals with schizoid personality disorder have no desire for social or romantic relationships, while those with avoidant personality disorder desperately want relationships but fear rejection and avoid social interaction due to low self-esteem.
What is the significance of 'splitting' in borderline personality disorder?
-In borderline personality disorder, 'splitting' is a defense mechanism where individuals see people as either all good or all bad, with no middle ground. This can lead to unstable relationships, as the person may idealize someone one moment and devalue them the next.
What distinguishes obsessive-compulsive personality disorder (OCPD) from obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)?
-The key distinction is that in OCPD, individuals are perfectionistic and rigid about their need for order and control, and they do not typically find their behavior distressing (ego-syntonic). In contrast, OCD involves intrusive, unwanted thoughts or compulsions that cause significant distress (ego-dystonic).
Why are borderline personality disorder and histrionic personality disorder often confused?
-Both disorders involve emotional instability and attention-seeking behaviors. However, borderline personality disorder is characterized by intense mood swings, self-harm tendencies, and unstable relationships, while histrionic personality disorder is primarily about seeking attention and being overly emotional, often through promiscuity or inappropriate behavior.
What are some common traits of narcissistic personality disorder?
-Individuals with narcissistic personality disorder exhibit grandiosity, a lack of empathy, and a constant need for admiration. They are often highly sensitive to any form of criticism and may react with rage or defensiveness when challenged.
What is the impact of personality disorders on social, occupational, and functional life?
-Personality disorders significantly impair an individual's ability to function in various areas of life. This can lead to difficulties in maintaining relationships, holding a job, or functioning effectively in society, causing distress both for the individual and those around them.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Schizophrenia vs. Schizophreniform vs. Schizoaffective vs. Schizoid vs. Schizotypal
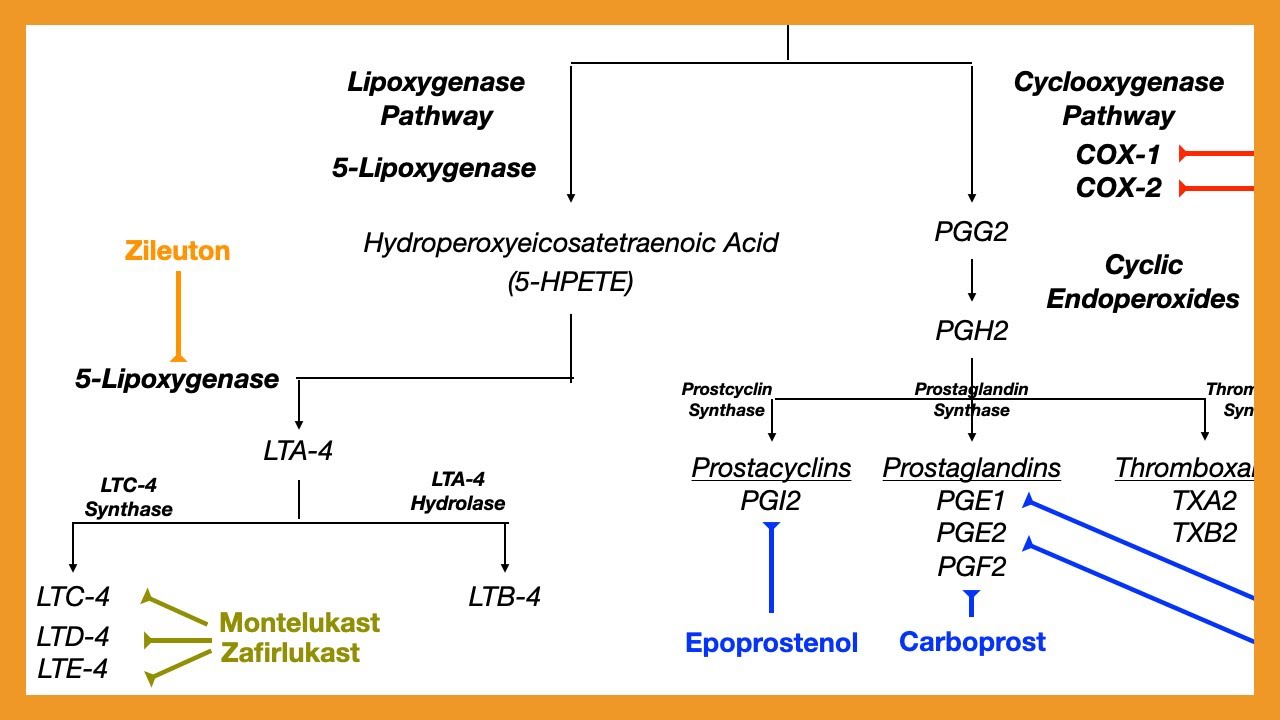
Arachidonic Acid Pathway (Prostaglandins, Prostacyclins, Thromboxanes, & Leukotrienes)

Consent vs. Assent
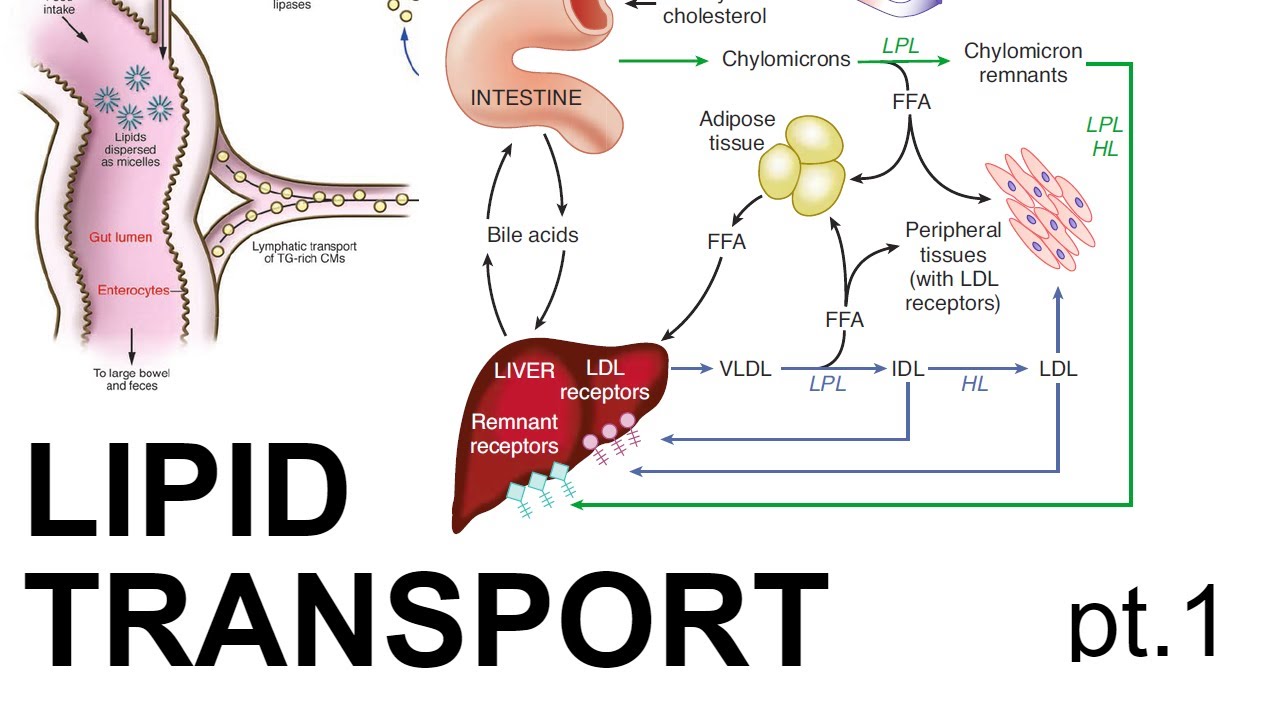
Lipid Transport (pt. 1)

Lipid Transport (pt. 1)

How to start early on your USMLE /US goal - must watch for 1st/2nd year year MBBS #USMLE #US
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
