5 Essential Steps in Plant Tissue Culture || A beginners guide
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of plant tissue culture, which involves growing plants from their tissues or cells in a controlled environment. It begins with the selection of a disease-free mother plant and the sterilization of the explant. The explant is then inoculated into a medium to promote cell division and form a callus. By manipulating hormones, shoots and roots are induced, and once the plantlets are developed, they undergo a hardening process to adapt from lab conditions to field conditions. The video outlines five key steps: explant selection, sterilization, inoculation, shooting/ rooting, and hardening.
Takeaways
- 😀 Plant tissue culture is easier than animal tissue culture because plant cells have totipotency, meaning any plant cell can potentially form a complete plant.
- 😀 Animal tissue culture is more complex as only the zygote is totipotent, limiting the scope for cloning or regeneration.
- 😀 Plant tissue culture involves growing plant tissues, organs, or cells in a controlled lab environment, providing external nutrients and suitable conditions for growth.
- 😀 The goal of plant tissue culture is often to produce genetically identical plants (clones) or plants with specific desirable traits.
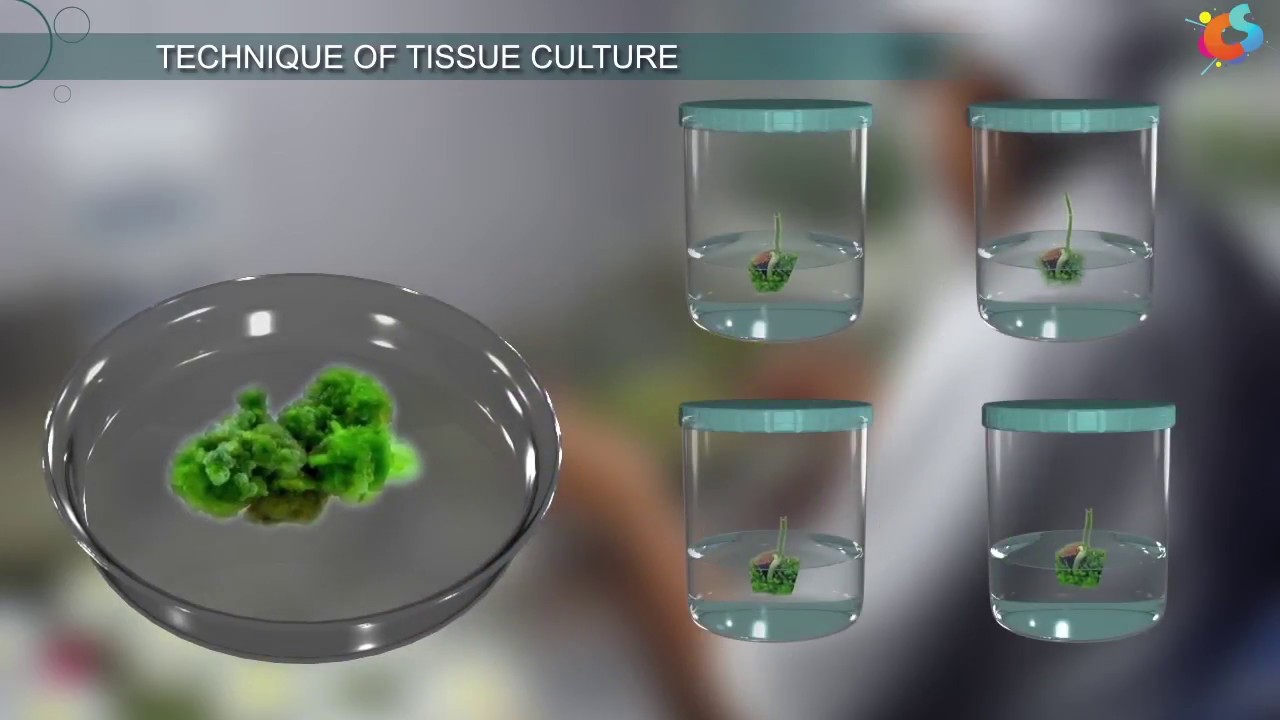
- 😀 The first step in plant tissue culture is selecting an explant, which can be a leaf, root, or even a protoplast, from a disease-free mother plant.
- 😀 Surface sterilization of the explant is crucial to prevent microbial contamination, involving washing with water, detergent, alcohol, and sterilizing agents like Mercury chloride.
- 😀 The sterilized explant is then inoculated into a suitable medium (e.g., MS medium or White's medium) for growth and development.
- 😀 Hormonal combinations (such as high auxin and low cytokinin for rooting, or low auxin and high cytokinin for shooting) are used to induce rooting and shooting from the explant.
- 😀 Once the explant forms a callus, subculturing may be needed if there’s nutrient depletion to continue growth.
- 😀 The final step is hardening, where the cultured plant is gradually acclimatized to outdoor conditions before being transferred to a field or greenhouse for full growth.
- 😀 The entire process of plant tissue culture involves careful attention to sterilization, nutrient management, hormonal control,andgradualacclimatizationforoptimalplantdevelopment.
Q & A
Why is plant tissue culture considered easier than animal tissue culture?
-Plant tissue culture is easier than animal tissue culture because, theoretically, any plant cell has the potential to give rise to a complete plant, a property called totipotency. In animals, only the zygote has this totipotent ability.
What is meant by the term 'totipotency' in plant tissue culture?
-Totipotency refers to the ability of a single plant cell to develop into a complete plant. This property is fundamental to plant tissue culture, as it allows any plant cell or tissue to regenerate into a full plant.
What are the main components of plant tissue culture?
-Plant tissue culture involves culturing tissues, organs, or cells of plants under controlled laboratory conditions, with sufficient nutrients, often aiming to produce genetically identical plants with desirable traits.
What is an explant in the context of plant tissue culture?
-An explant is any part of a plant used for tissue culture. It can be a leaf, root, stem, or even a protoplast. The explant is selected from a mother plant, which is usually grown in a controlled environment to ensure it's disease-free.
Why is surface sterilization important in plant tissue culture?
-Surface sterilization is crucial to prevent microbial contamination in plant tissue culture. Contaminants can harm the growing plant culture, so sterilizing the explant surfaces with water, alcohol, and toxic agents like mercury chloride helps maintain a sterile environment.
What is the purpose of using a laminar air flow in plant tissue culture?
-A laminar air flow provides a sterile environment for working with explants. It helps prevent contamination by circulating clean, filtered air during the tissue culture process.
How is inoculation done in plant tissue culture?
-Inoculation involves placing the sterilized explant into a suitable growth medium, such as MS medium or White's medium. This step provides the necessary nutrients for the explant to start growing and developing into a plant.
What is the role of hormones in the shooting and rooting process?
-Hormones play a key role in inducing shooting and rooting. A common method is adjusting the auxin-cytokinin ratio, with high auxin and low cytokinin promoting rooting, and low auxin and high cytokinin promoting shooting.
What happens during the hardening step of plant tissue culture?
-Hardening is the process of gradually acclimatizing the cultured plant from controlled laboratory conditions to normal field conditions. The plant is first kept in a shaded environment, then gradually moved to a greenhouse and eventually out to the field.
What are the five main steps involved in plant tissue culture?
-The five main steps are: 1) Selection of explant, 2) Surface sterilization, 3) Inoculation into a suitable medium, 4) Induction of shooting and rooting through hormonal manipulation, and 5) Hardening, which is the gradual transfer of the plant to field conditions.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Tissue Culture

Plant tissue culture (पादप ऊतक संवर्धन) & पूर्णशक्तता (totipotency) In Hindi @botanyadda

Plant Tissue Culture in SEAMEO BIOTROP - Kultur Jaringan Tanaman di SEAMEO BIOTROP

Jaringan Pada Tumbuhan Kelas 11 | Sifat Totipotensi Pada Tumbuhan Dan Kultur Jaringan

#bioteknologi #kulturjaringantumbuhan #biologisma BIOTEKNOLOGI MODERN | KULTUR JARINGAN TUMBUHAN

Kultur Jaringan, Apa Faedahnya?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
