Ocean Currents (Part 5): Ekman Transport & Upwelling / Downwelling
Summary
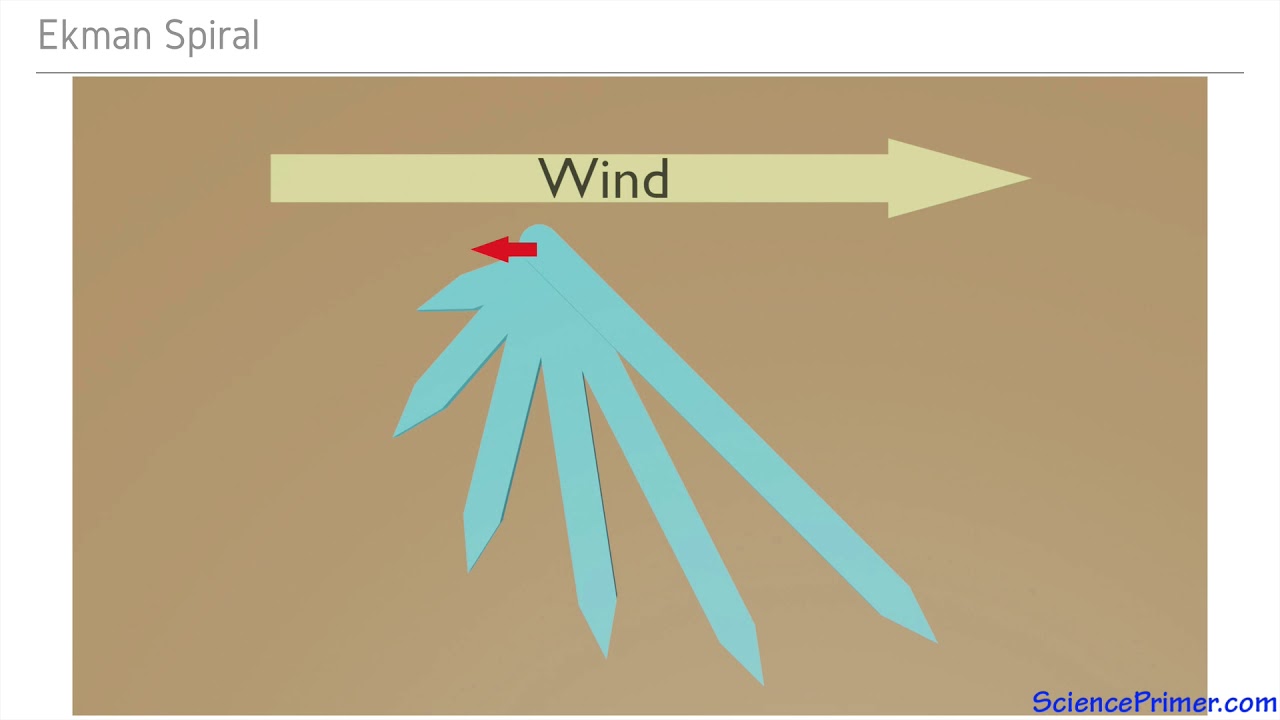
TLDRThis video explains the concept of Ekman transport, a crucial oceanic process driven by wind, the Coriolis effect, and geostrophic currents. It describes how surface winds move water at an angle, creating spiraling motion with depth, known as the Ekman spiral. This movement causes upwelling and downwelling near coasts and in the open ocean, bringing cold, nutrient-rich water to the surface and regulating ocean temperature. The video emphasizes the importance of these processes for recycling nutrients, supporting marine life, and maintaining oceanic ecosystems. Visual examples illustrate how water movement varies between hemispheres and coastal versus open ocean regions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Wind pushes surface water in the ocean, causing the top layer to move while deeper layers are displaced to replace it.
- 😀 The Coriolis effect shifts surface water at a 45-degree angle to the wind direction, creating a clockwise motion in the northern hemisphere and a counterclockwise motion in the southern hemisphere.
- 😀 As wind moves surface water away, deeper water from the ocean's bottom rises (upwelling) to replace it, bringing nutrients and cold water to the surface.
- 😀 The Ekman Spiral describes how water moves in layers at different angles as you go deeper, with the direction of movement changing and weakening with depth.
- 😀 The net movement of water caused by wind and the Coriolis effect is at a 90-degree angle to the direction of the wind.
- 😀 In the northern hemisphere, water moves to the right of the wind direction, while in the southern hemisphere, water moves to the left of the wind.
- 😀 Upwelling occurs when wind pushes surface water away from the continent, bringing nutrient-rich, cold water from the bottom to the surface.
- 😀 Downwelling occurs when surface water moves toward the continent, causing the water to sink and forming a convergence zone.
- 😀 Upwelling supports marine life by providing essential nutrients for phytoplankton, which perform photosynthesis, and oxygenate the water.
- 😀 The movement of ocean currents (upwelling and downwelling) helps recycle both temperature and nutrients in the ocean, supporting life and balancing ecosystem health.
Q & A
What is the main role of the Ean transport system in ocean circulation?
-The Ean transport system plays a crucial role in circulating nutrients and regulating the temperature of ocean water. It drives upwelling, where deep, nutrient-rich water rises to the surface, supporting marine life by providing essential nutrients for photosynthesis.
How does wind influence surface ocean currents?
-Wind pushes the surface layer of ocean water, causing it to move. This displacement forces the water beneath it to rise, replacing the surface water. This process is vital for nutrient circulation and temperature regulation in the ocean.
What is the Coriolis effect, and how does it affect ocean currents?
-The Coriolis effect is caused by the Earth's rotation, which deflects moving fluids like air and water. In the Northern Hemisphere, it causes currents to shift to the right, while in the Southern Hemisphere, currents shift to the left. This shift alters the direction of water movement and contributes to the formation of gyres.
How does the Coriolis effect interact with the wind to create ocean currents?
-The Coriolis effect causes the wind to push water at an angle to its direction. In the Northern Hemisphere, this means water moves to the right of the wind, while in the Southern Hemisphere, water moves to the left. This interaction contributes to the formation of gyres and influences oceanic circulation patterns.
What happens to ocean water as the surface layer is displaced by the wind?
-When wind displaces the surface water, water from deeper layers rises to replace it. This causes a vertical circulation known as upwelling, where deep, nutrient-rich water moves to the surface, supporting marine ecosystems.
Why does deeper ocean water move less compared to surface water?
-Deeper ocean water is less affected by wind because of its depth and density. As a result, it moves slower and at a different angle compared to the surface water. This contributes to the formation of different currents at various depths.
What is the overall effect of the Ean transport system in the ocean?
-The Ean transport system creates a spiraling pattern of water movement, driven by the combined forces of wind and the Coriolis effect. This system results in upwelling of nutrient-rich water, which is crucial for marine life and ocean health.
How does upwelling support marine ecosystems?
-Upwelling brings cold, nutrient-rich water from the ocean's depths to the surface. This water contains essential nutrients like carbon dioxide, which algae use for photosynthesis, supporting the entire marine food chain and boosting ocean productivity.
What happens when ocean currents move water toward a continent?
-When ocean currents move water toward a continent, it creates a downwelling zone, where surface water sinks back into the ocean. This process is the opposite of upwelling and is crucial for maintaining ocean circulation and nutrient distribution.
How does the upwelling and downwelling process impact ocean temperature and nutrient recycling?
-Upwelling and downwelling help regulate ocean temperatures and recycle nutrients. Upwelling brings cool, nutrient-rich water to the surface, while downwelling moves surface water down, creating a cycle that helps maintain the balance of ocean ecosystems.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)