Scheikunde Havo 4 Hoofdstuk 4§4: Rekenen aan zoutoplossingen
Summary
TLDRThis video covers the topic of calculations with salt solutions in chemistry. It explains how to use molar ratios and dilution formulas to determine concentrations and perform calculations related to salts dissolved in water. Examples include calculating the concentration of hydroxide ions in barium hydroxide and identifying the precipitate that forms when different salt solutions are mixed. The video also discusses how to write precipitation reactions and ensure the neutrality of salts, focusing on the practical application of chemistry concepts in solving problems with salt solutions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Concentration and molarity describe the amount of substance in a solution, measured in mol per liter.
- 😀 Molarity (M) is the amount of solute (in moles) per liter of solution, for example, 0.20 molar means 0.20 mol per liter.
- 😀 When salts dissolve in water, they dissociate into ions, and the ion concentrations are determined based on the salt's molar ratio.
- 😀 For example, iron(III) sulfate dissociates into Fe3+ and SO4^2- ions in a 2:3 molar ratio, meaning twice as many Fe3+ ions as SO4^2- ions.
- 😀 To calculate the concentration of ions in solution, you can use molar ratios and known concentrations to find the final concentration.
- 😀 The concentration of OH- ions from barium hydroxide can be calculated using the formula n = m / M, where n is the amount in moles, m is mass, and M is molar mass.
- 😀 Molar mass of barium hydroxide is calculated as 171.3 g/mol, and this helps in determining the amount of substance (n) dissolved in the solution.
- 😀 The concentration of barium hydroxide in mol per liter (molarity) is calculated using n (moles) and volume (in liters).
- 😀 Barium hydroxide dissociates in water in a 1:1:2 ratio, where for each barium ion (Ba2+), two OH- ions are produced.
- 😀 Precipitation reactions occur when insoluble salts form in a solution. An example of this is the reaction between aluminum chloride and barium hydroxide, which forms aluminum hydroxide as a precipitate.
Q & A
What does the concentration of a solution indicate?
-The concentration of a solution indicates how many moles of a substance (mol) are present per liter of solution. This is also known as molarity and is expressed in mol/L.
What happens when a salt dissolves in water?
-When a salt dissolves in water, it dissociates into its constituent ions. For example, iron sulfate dissociates into Fe3+ and SO4^2- ions.
How do you calculate the concentration of dissolved ions from a salt solution?
-To calculate the concentration of dissolved ions, you need to use the molar ratio from the dissociation equation of the salt. Then, apply the concentration of the salt and the molar ratio to calculate the concentration of each ion.
What is molarity, and how is it expressed?
-Molarity is the concentration of a solution, indicating how many moles of solute are present in one liter of solution. It is expressed in mol/L and is often abbreviated as 'M'.
How do you calculate the number of moles of a substance?
-The number of moles (n) of a substance can be calculated using the formula: n = mass / molar mass, where mass is the mass of the substance and the molar mass is the mass of one mole of the substance.
How can you convert from grams per liter to moles per liter?
-To convert from grams per liter to moles per liter, first calculate the number of moles using the formula n = mass / molar mass, then divide the number of moles by the volume in liters.
What is the molar ratio between barium hydroxide and hydroxide ions in a solution?
-The molar ratio between barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution is 1:2, meaning that for every mole of barium hydroxide, two moles of hydroxide ions are produced.
What is a precipitation reaction, and can you give an example?
-A precipitation reaction occurs when two soluble salts react in solution to form an insoluble salt that precipitates out of the solution. For example, when barium hydroxide and aluminum chloride are mixed, aluminum hydroxide (a poorly soluble salt) precipitates out.
What is the importance of the charge balance in a salt formation?
-In a salt formation, the charge balance is crucial because the overall charge of the salt must be neutral. The positive charges of cations must balance the negative charges of anions.
What happens when aluminum chloride is added to a barium hydroxide solution?
-When aluminum chloride is added to a barium hydroxide solution, a precipitation reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of aluminum hydroxide as a poorly soluble salt.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
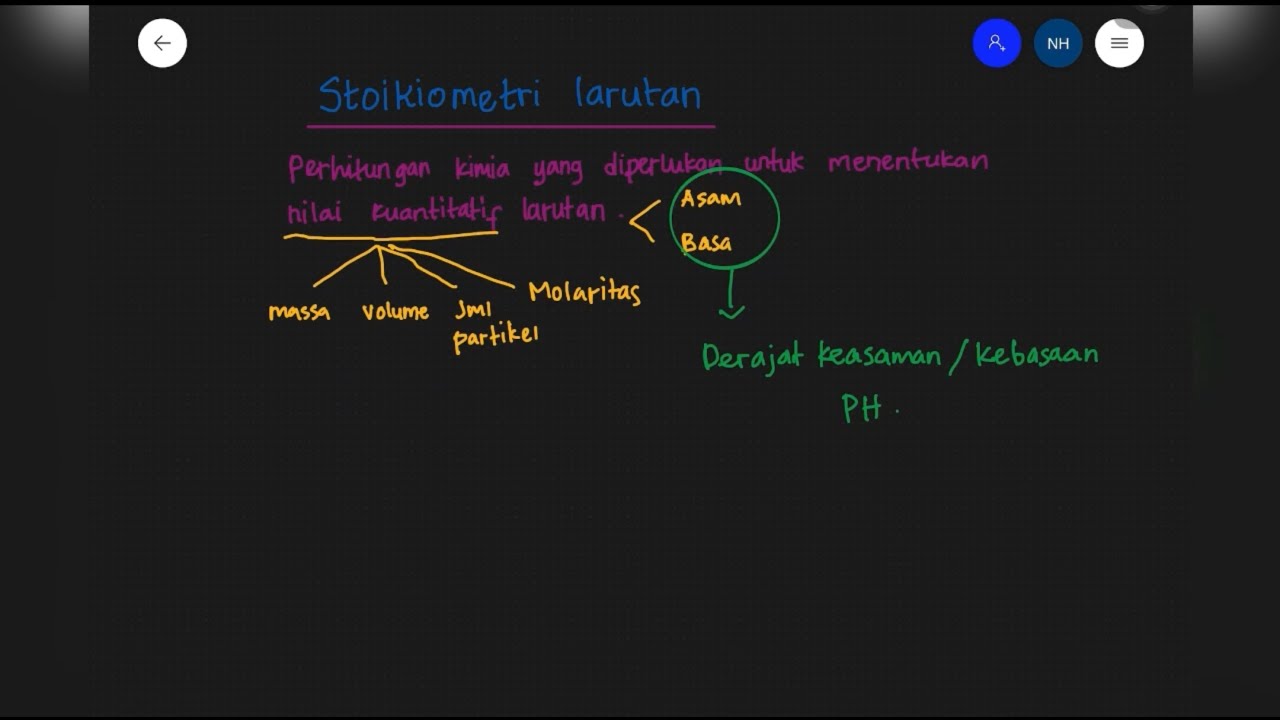
Stoikiometri Larutan || Larutan Asam dan Basa || Materi Kimia SMA Kelas XI || Hikmah nor

Tekanan Uap Larutan Non Elektrolit | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti

Konsep Mol | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti

Hidrolisis Garam By Tetty Afianti
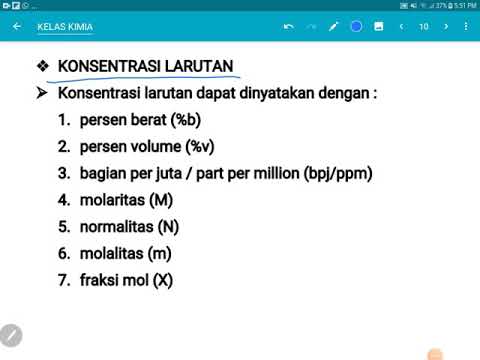
Kelas Kimia : Konsentrasi Larutan (% berat, % volume, ppm / bpj)

Molaridade - Prof. Gabriel Cabral
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
