Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Explained
Summary
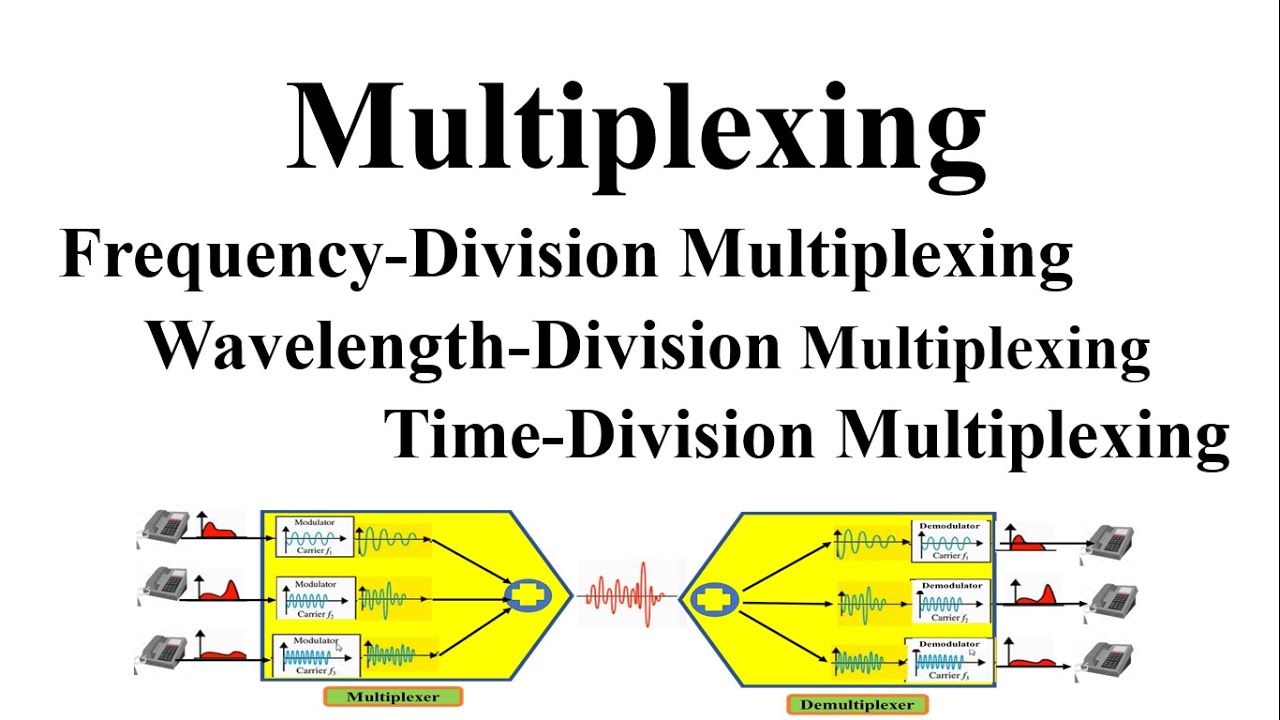
TLDRIn this video, the concept of Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) is explained, highlighting its role in efficiently utilizing channel bandwidth by allowing multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over a single channel. The process involves modulating message signals at different carrier frequencies, which are then combined into a composite signal. At the receiver end, signals are separated using bandpass filters and demodulated. FDM is widely used in applications like radio, television broadcasting, telephony, and cellular networks. The video also discusses the importance of avoiding interference and the use of guard bands to ensure clear transmission.
Takeaways
- 😀 Multiplexing allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over a single communication channel.
- 😀 Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) involves modulating message signals at different carrier frequencies and combining them into a single composite signal.
- 😀 FDM helps improve the efficiency of bandwidth usage by sharing the channel with multiple users.
- 😀 The composite signal in FDM is separated at the receiver using band-pass filters tuned to each message signal’s carrier frequency.
- 😀 Guard bands are added between signals in FDM to avoid interference and ensure smooth signal separation due to filter roll-off.
- 😀 FDM is used in various applications like radio and television broadcasting, telecommunications, and early cellular networks.
- 😀 In radio and TV broadcasting, multiplexing is achieved without physical multiplexing, as each station uses a different carrier frequency.
- 😀 In telephony systems, voice signals are single sideband modulated and multiplexed, with multiple levels of grouping to accommodate many users.
- 😀 In telephony, 12 voice signals form a 'group,' 5 groups form a 'super group,' and 10 super groups form a 'master group,' each occupying specific bandwidths.
- 😀 The bandwidth required for the master group in telephony is 2.52 MHz, accounting for guard bands and signal separation.
- 😀 The FDM technique is essential for systems like analog telephony, where multiple voice signals need to be transmitted efficiently over a limited bandwidth.
Q & A
What is multiplexing in communication systems?
-Multiplexing is a technique that allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously through a single communication channel. It helps in efficiently utilizing the channel bandwidth by combining several signals into a single composite signal.
Why is multiplexing important in communication systems?
-Multiplexing maximizes the use of available bandwidth, enabling multiple users or signals to share the same channel. This makes communication more efficient and cost-effective, allowing more data to be transmitted simultaneously.
What are the three main types of multiplexing techniques?
-The three main types of multiplexing are Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM), Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), and Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM).
How does Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) work?
-In FDM, multiple message signals are modulated onto different carrier frequencies. These modulated signals are then combined into a single composite signal and transmitted over the same channel. The signals are separated at the receiver using band-pass filters.
What is the role of a band-pass filter in FDM?
-A band-pass filter at the receiver is tuned to each specific carrier frequency. It separates the multiplexed signals by filtering out unwanted frequencies, ensuring that each message signal is retrieved correctly.
Why is a guard band used in FDM?
-A guard band is a small frequency gap placed between signals in FDM to prevent interference and signal overlap, particularly to account for the gradual roll-off of filters, ensuring clear separation between the signals.
What happens to the modulated signal after it passes through the band-pass filter in FDM?
-After passing through the band-pass filter, the modulated signal is demodulated. The demodulated signal is then passed through a low-pass filter to eliminate higher frequency components, leaving only the baseband signal.
In which applications is Frequency Division Multiplexing commonly used?
-FDM is used in radio and television broadcasting, telemetry, telephony systems, and early-generation cellular networks.
What is the difference in carrier frequency separation between AM and single sideband modulated signals in FDM?
-In AM and double sideband modulation, the minimum carrier frequency separation required is 2B, where B is the bandwidth of the message signal. In single sideband modulation, the separation is B, which allows for more efficient use of the available bandwidth.
How is Frequency Division Multiplexing used in telephony systems?
-In telephony systems, FDM is used to combine multiple voice signals into a single composite signal. For example, 12 voice signals might be multiplexed into a group, which can then be further multiplexed into super groups and master groups, allowing for efficient use of the available bandwidth.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Frequency division multiplexing|Time division multiplexing|FDM|WDM| TDM| computer networks in detail

Multiplexing Tutorial - TDM, STDM, FDM Explained

TDM, Statistical TDM & FDM

Types of Multiplexing | FDM TDM WDM | Analog Digital | Computer Networks

CO3 Introduction Communication Systems videolecture

CS601_Topic116
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
