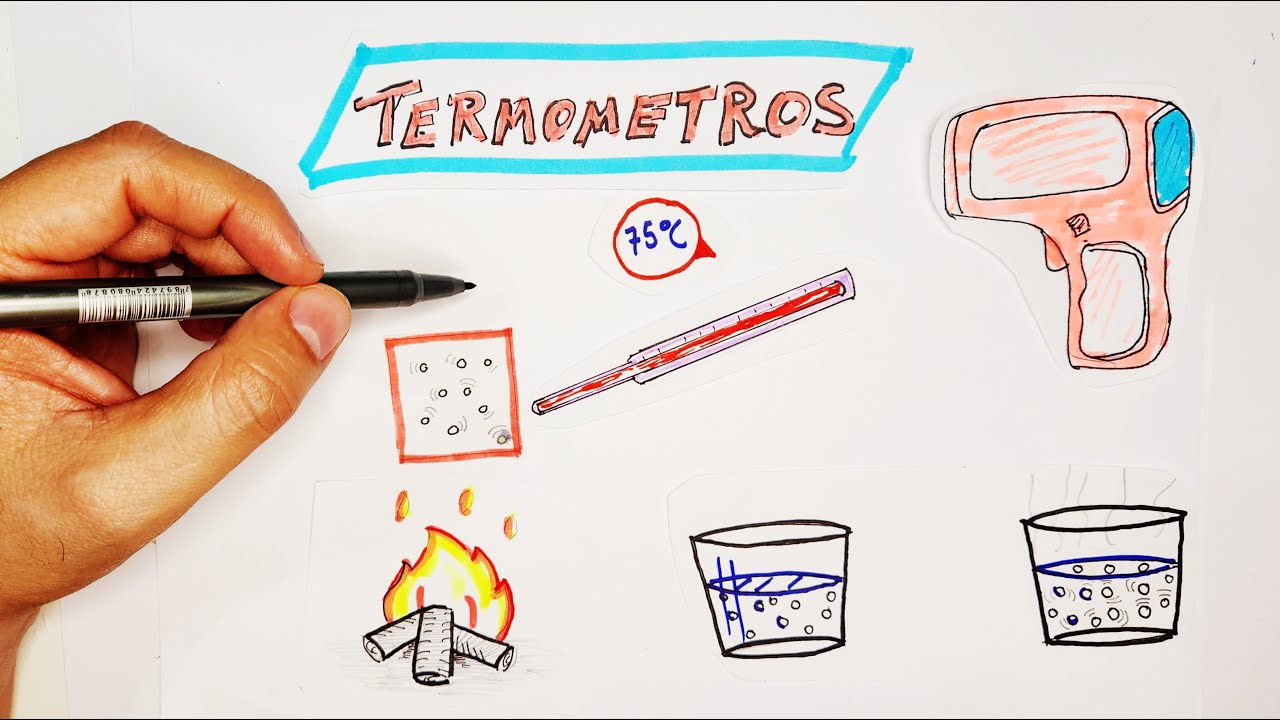
Termologia: Termômetros, aula 1, vídeo 2.
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the instructor introduces the concept of thermometers, explaining their role in measuring temperature, which reflects the average agitation of atoms and molecules in a body. The video covers the working principles of different thermometers, such as mercury thermometers and infrared thermometers, and the concept of thermal radiation emitted by vibrating molecules. The instructor also discusses the relationship between the Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin temperature scales, explaining how to convert between them. The video concludes with a brief mention of upcoming lessons and an invitation for questions and interaction.
Takeaways
- 😀 Temperature measures the average agitation of atoms and molecules, indicating the thermal state of a body.
- 😀 Mercury thermometers use a liquid (mercury) that expands when it comes into contact with a warmer object, indicating the temperature.
- 😀 A thermometer needs to be in contact with a body to measure its temperature, but this doesn't apply to distant objects like the Sun.
- 😀 Infrared thermometers measure the thermal radiation emitted by vibrating atoms and molecules instead of direct contact with the object.
- 😀 Molecules vibrate and release thermal radiation, which can be detected by infrared thermometers.
- 😀 To see the radiation emitted by a body, the temperature must be over 600°C for it to become visible.
- 😀 Water boils at 100°C, which is below the temperature at which thermal radiation becomes visible to the human eye.
- 😀 Common temperature scales include Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin, each with specific conversion formulas.
- 😀 The relationships between the temperature scales are given by the equations: (Celsius - Fahrenheit = 5/9), (Fahrenheit - 32 = 9/5), (Kelvin = Celsius + 273).
- 😀 The next lesson will explain how to derive these conversion formulas and demonstrate example calculations.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a thermometer?
-The primary function of a thermometer is to measure the temperature of a body by detecting the degree of agitation of atoms and molecules within that body.
How is temperature related to the motion of atoms and molecules?
-Temperature is the physical quantity that measures the average kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. The more agitated or vibrated the atoms and molecules are, the higher the temperature of the body.
What happens to the mercury in a thermometer when it is placed in contact with a warm object?
-When the mercury thermometer is placed in contact with a warmer object, heat is transferred from the object to the thermometer, causing the mercury to expand. The thermometer then indicates the temperature of the object when thermal equilibrium is reached.
Why is mercury used in thermometers?
-Mercury is used in thermometers because it has a high coefficient of expansion, which makes it very responsive to temperature changes. It is also liquid at room temperature and can expand or contract uniformly, making it suitable for accurate temperature measurements.
How does an infrared thermometer work?
-An infrared thermometer works by detecting the thermal radiation emitted by an object. As atoms and molecules vibrate, they release thermal radiation. The thermometer reads this radiation to determine the object's temperature.
Can we see the radiation emitted by vibrating atoms and molecules?
-No, we cannot see the radiation emitted by atoms and molecules vibrating at temperatures below 600°C because it is infrared radiation, which is invisible to the human eye.
What temperature must a body reach to emit visible radiation?
-A body must reach a temperature of at least 600°C to emit visible radiation, which can then be observed with the naked eye.
What are the three most common temperature scales mentioned in the script?
-The three most common temperature scales mentioned are Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
How can we convert between different temperature scales?
-To convert between temperature scales, the script provides the following equations: (Celsius - 5/9) = (Fahrenheit - 32)/9, (Fahrenheit - 32)/9 = (Kelvin - 273)/5, and Celsius = Kelvin - 273.
What practical use does knowing how to convert between temperature scales have?
-Knowing how to convert between temperature scales is useful when working with different measurement systems, especially when interpreting temperature data from different regions or scientific fields where different scales may be used.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)