Fenomena Geosfer: Litosfer | Geografi Kelas 10 - KHATULISTIWA MENGAJAR
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the Earth’s lithosphere, the outermost layer made up of rocks and minerals. It explains how geological phenomena like earthquakes, volcanoes, and soil fertility variations occur due to the lithosphere. The script covers the different types of rocks—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—and breaks down the structure of the Earth, including the core, mantle, and crust. The lithosphere’s significance for life on Earth is emphasized, showcasing its role in supporting ecosystems and human activities. The video ultimately stresses the importance of preserving the lithosphere for the future of all living beings.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lithosphere is the Earth's outermost layer, composed of rocks and minerals.
- 😀 The word 'lithosphere' comes from the Greek words 'lithos' (rock) and 'sphaira' (layer).
- 😀 The lithosphere includes three types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
- 😀 Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma.
- 😀 Sedimentary rocks are formed by the accumulation and compression of minerals over time.
- 😀 Metamorphic rocks are formed when rocks undergo changes due to high pressure or temperature.
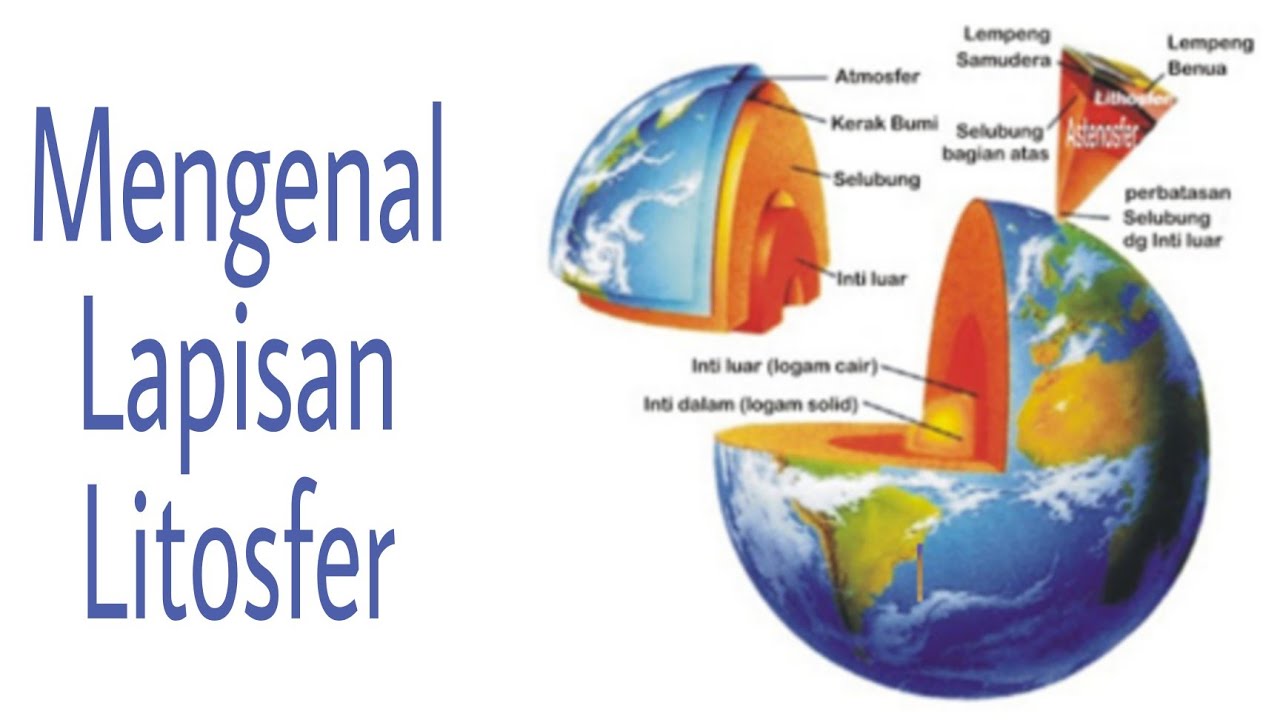
- 😀 The Earth has three main layers: the core, the mantle, and the crust.
- 😀 The core is the innermost layer, made up of molten iron and nickel, with temperatures around 6000°C.
- 😀 The mantle is a thick layer that makes up 80% of the Earth's mass and consists of hot, semi-solid materials.
- 😀 The crust is the thinnest layer, ranging from 5 to 70 km thick, and is where life on Earth exists.
- 😀 The lithosphere plays a crucial role in supporting life by providing the foundation for human, animal, and plant habitation.
- 😀 The lithosphere is also essential for activities like agriculture, mining, and the extraction of materials such as nitrogen and phosphate.
Q & A
What is the lithosphere, and what is it composed of?
-The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth, composed primarily of rocks and minerals. It consists of both igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that form the Earth's crust.
How do igneous rocks form?
-Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma. When magma cools and solidifies, it crystallizes into solid rock.
What happens to igneous rocks after they are formed?
-After igneous rocks form, they undergo weathering and erosion, being broken down and transported by water, air, or ice. Eventually, they accumulate and can form sedimentary rocks.
What are metamorphic rocks, and how do they form?
-Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks (igneous, sedimentary, or other metamorphic rocks) are subjected to high pressure and temperature, causing them to change in structure and composition.
What are the three main layers of the Earth?
-The Earth's three main layers are the core, the mantle, and the crust. The core is divided into an inner solid part and a liquid outer part, the mantle is a thick layer of semi-solid rock, and the crust is the thin outer layer composed of rocks and minerals.
What materials make up the Earth's core?
-The Earth's core is primarily composed of liquid iron and nickel in the outer core, and solid iron and nickel in the inner core.
What is the temperature like at the Earth's core?
-The temperature at the Earth's core reaches around 6000°C, which is comparable to the surface temperature of the Sun.
What is the mantle, and what does it contain?
-The mantle is the thickest layer of the Earth, making up about 80% of the Earth's mass. It contains mostly semi-solid rock and lava, with temperatures that can reach up to 3000°C.
What is the role of the lithosphere in sustaining life on Earth?
-The lithosphere plays a vital role in supporting life on Earth by providing a habitat for humans, animals, and plants. It also protects the inner layers of the Earth and enables various human activities, such as agriculture, construction, and the extraction of minerals.
How does the lithosphere benefit human life?
-The lithosphere benefits humans by providing essential resources such as minerals, fertile soil, and materials for construction. It also protects the planet's inner layers and supports ecosystems.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

IPS (Geografi) Kelas 10 - Litosfer | GIA Academy

Litosfer 🔴 Materi Geografi Kelas X Semester 2 #geografi #gurugeografi #belajar #sekolah #ips
GEOGRAFI - MENGENAL LAPISAN LITOSFER

Litosfer dalam Kehidupan Manusia (Geografi untuk SBMPTN): Litosfer dan Batuan Penyusunnya (Part 1)

Fenomena Geosfer #kurikulum merdeka

#1 #Kelas10 #Geografi #smstr2 | Lapisan Bumi dan Karakteristiknya
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
