PRÉ HISTÓRIA - RESUMO DESENHADO
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the origins of humanity, delving into the theory of evolution, migration theories, and the development of early human societies. It traces the journey from the first hominids millions of years ago to the rise of agriculture and the domestication of animals in the Neolithic era. The script also challenges linear historical progress narratives, particularly those influenced by 19th-century European positivism, which unjustly ranked societies by their level of 'advancement.' Through this lens, it critiques colonial ideologies and introduces the revolutionary concept of non-linear cultural evolution.
Takeaways
- 😀 The origins of human history date back around 15 million years ago with the emergence of the first hominids, our earliest ancestors, leading up to the appearance of the first human civilizations marked by writing systems, agriculture, and social organization.
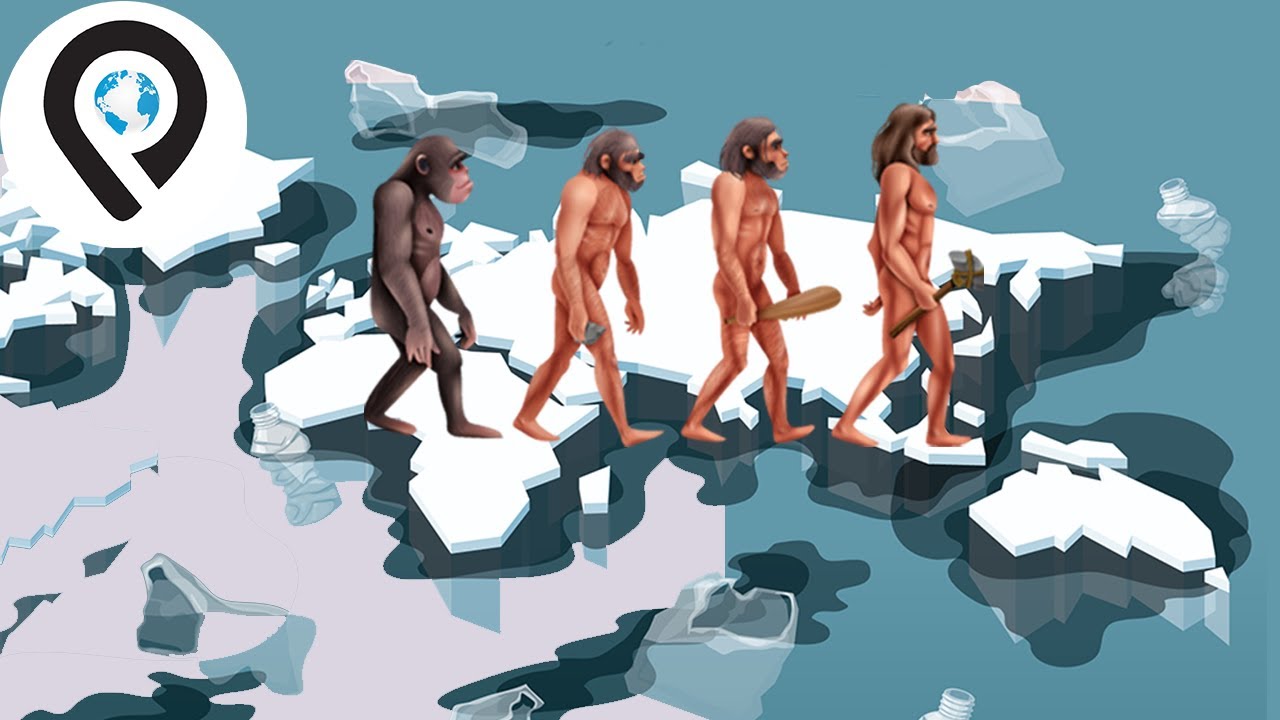
- 😀 Humans did not evolve from monkeys, but share a common ancestor with them, which diverged into two lines millions of years ago. The theory of natural selection explains the survival of the most adapted species.
- 😀 The concept of 'survival of the fittest' suggests that those with beneficial mutations, such as better camouflage or intelligence, have a higher chance of survival and reproduction.
- 😀 Early human societies were hunter-gatherers, living a nomadic lifestyle without fixed territory, relying on nature for food and resources, and living in communal groups.
- 😀 Human evolution is closely tied to environmental changes, such as ice ages, which led to migrations across the globe, including the migration to the Americas through the Bering Strait.
- 😀 The extinction of megafauna in regions like South America and Australia was likely accelerated by human activity, including overhunting and environmental changes caused by early humans.
- 😀 Human intelligence and technological development, such as the use of fire and tools, significantly contributed to their ability to adapt to different environments and increase their chances of survival.
- 😀 The Paleolithic era saw a notable increase in brain size, leading to the development of language and culture, including burial rituals and the creation of more advanced tools.
- 😀 The Neolithic Revolution, around 10,000 years ago, marked the transition from hunting and gathering to settled agricultural societies, leading to the domestication of animals and the establishment of permanent settlements.
- 😀 The development of writing systems around 3,500 years ago in civilizations like Mesopotamia, Egypt, and China marked the transition from prehistory to recorded history.
- 😀 The idea of linear progress in history, popularized by positivists, wrongly suggested that some cultures were more 'advanced' than others, justifying colonialism and racial superiority arguments. This view was used to rationalize European colonial dominance over Africa and other regions.
Q & A
What is the significance of the theory of evolution in understanding human origins?
-The theory of evolution explains that humans did not evolve directly from monkeys but share a common ancestor with them. Over millions of years, natural selection led to the emergence of Homo sapiens, the species most adapted to survival in various environments.
How did natural selection influence human evolution?
-Natural selection favored individuals with mutations that enhanced survival. For example, in cold climates, animals like wolves with white fur were better camouflaged in the snow, leading to their survival and reproduction, passing on these traits to future generations.
Why is the theory of migration across the Bering Strait important in human history?
-The theory of migration across the Bering Strait suggests that humans crossed from Siberia to the Americas during the Ice Age when sea levels were lower, connecting Asia and North America via a land bridge. This migration led to the settlement of the Americas and had significant environmental and cultural impacts.
What was the role of the environment in shaping early human societies?
-The environment shaped early human societies by providing resources for survival and driving the development of new tools, hunting techniques, and strategies. As humans adapted to different climates, they developed innovations such as fire and tools to improve survival.
How did the development of agriculture change human society?
-The development of agriculture marked a significant shift from nomadic hunting and gathering to settled farming. It allowed for the production of food surpluses, the domestication of animals, and the growth of social structures centered around land ownership and division of labor.
What is 'primitive communism' and how did it describe early human societies?
-Primitive communism refers to early human societies that operated without private property. People lived communally, sharing resources like food and tools. Social organization was based on family groups, and there was no concept of personal ownership.
What is the connection between the brain's development and the rise of human intelligence?
-The increase in brain size, particularly the telencephalon, enabled early humans to become more intelligent. This development allowed for the creation of complex tools, the use of fire, and the ability to communicate through language, all of which played a crucial role in human survival and cultural development.
What were cave paintings, and what do they tell us about early humans?
-Cave paintings were created by early humans using natural pigments and tools to depict their environment and animals. These paintings are considered one of the earliest forms of communication, reflecting both the creativity and the cultural significance of early humans.
How did the Neolithic Revolution affect the structure of human societies?
-The Neolithic Revolution, marked by the discovery of agriculture, transformed human societies. It led to the establishment of permanent settlements, the development of surplus food, and the emergence of new social hierarchies, where land ownership and labor division became central to social organization.
Why did the positivist view of history lead to problematic ideas in the 19th century?
-The positivist view of history, which assumed that all cultures evolve in a linear fashion towards a European model, justified colonialism and racial inequality. This perspective deemed non-literate societies as 'primitive' and inferior, reinforcing harmful stereotypes and ideologies.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
(8) Who is the first human to arrive in Australia? How to judge the route of human migration?

Asal Usul Melayu

Asal - Usul Nenek Moyang Bangsa Indonesia

TEORI ASAL USUL NENEK MOYANG BANGSA INDONESIA - Materi Sejarah Fase E

CARTA: Childrearing in Human Evolution--Melvin Konner:Hunter-Gatherer Childhood and Human Evolution

Povoamento das Américas | Pré-História
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
