UAD - Kuliah Online 1475530 Karakterisasi Material Lanjut (Lecture 2a - part 1)
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into material characterization techniques, specifically focusing on spectroscopy methods like UV-Vis and Infrared spectroscopy. The script explains how electromagnetic waves interact with matter, covering concepts of absorbance, transmittance, and reflectance. It highlights the importance of the Beer-Lambert Law in determining concentrations and provides practical examples of its use, such as measuring chlorophyll concentrations. The video also explores the mathematical relationships behind spectroscopy, offering valuable insights for applications in chemistry, biology, and material science.
Takeaways
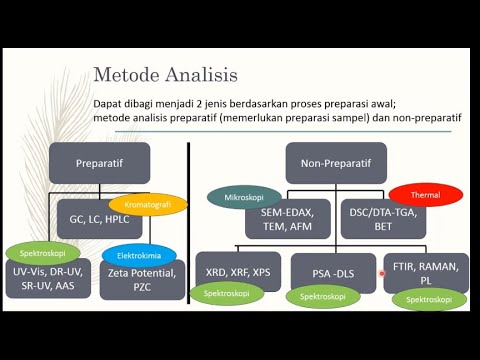
- 😀 Spectroscopy studies the interaction between electromagnetic waves and matter, focusing on electronic, vibrational, and rotational interactions.
- 😀 The electromagnetic spectrum includes various types of radiation, with spectroscopy mainly utilizing UV-visible and infrared radiation.
- 😀 Spectroscopic techniques measure how light interacts with materials through reflection, absorption, and transmission.
- 😀 Transmittance refers to the percentage of light that passes through a material, while absorbance quantifies the amount of light absorbed by it.
- 😀 The Beer-Lambert Law relates absorbance to concentration and path length, helping to determine the concentration of substances in solutions.
- 😀 UV-Vis spectroscopy can detect specific absorption peaks of substances like chlorophyll, which absorbs light at wavelengths of 430 nm and 665 nm.
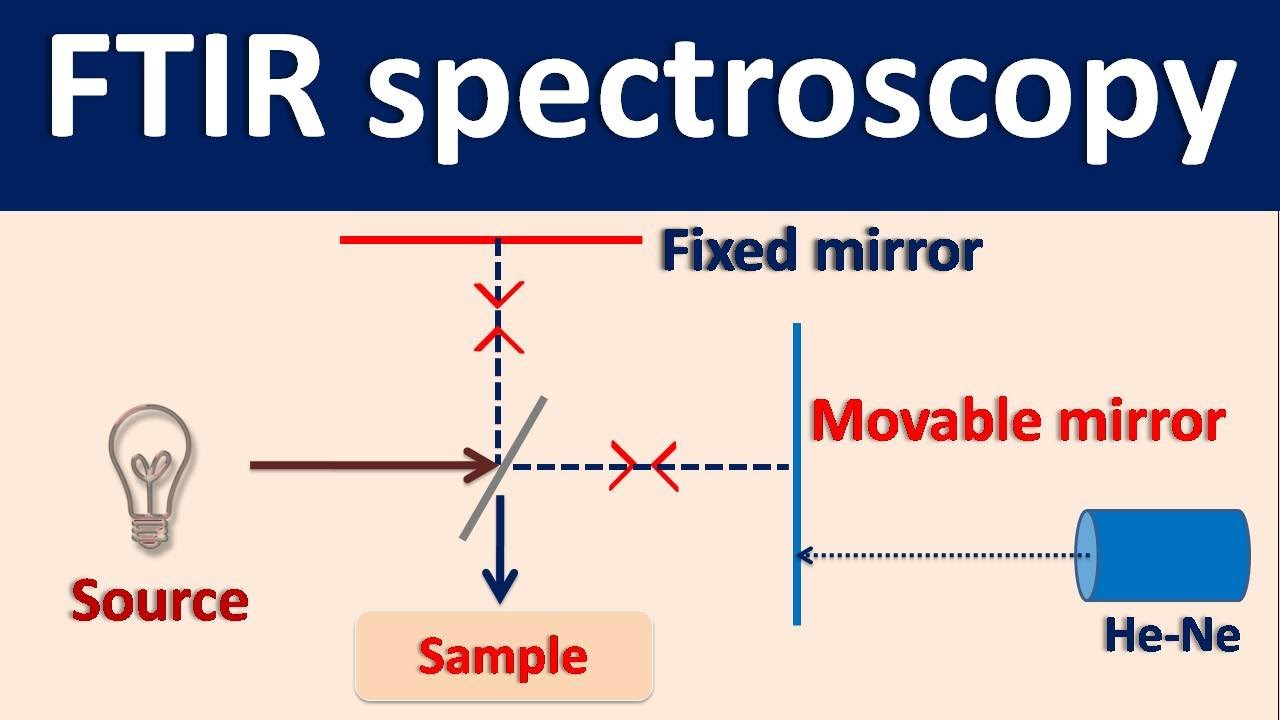
- 😀 Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is used to study the vibrational modes of molecules, helping to analyze material properties.
- 😀 By measuring the absorption or transmission of light across different wavelengths, we can obtain spectra that provide detailed information about the material.
- 😀 In practical applications, UV-Vis and IR spectroscopy can be used to determine material concentrations, such as chlorophyll in plants or chemicals in solutions.
- 😀 The principle of greenhouse effects is linked to transmission and absorption properties of materials, where visible light can pass through glass, but infrared radiation is absorbed.
- 😀 Spectroscopic analysis plays a crucial role in various fields like chemistry, biology, and materials science, providing essential insights into molecular and atomic structures.
Q & A
What is the basic concept behind spectroscopy?
-Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between electromagnetic waves (such as light) and matter, specifically atoms and molecules. It helps in understanding material properties by analyzing how materials absorb, transmit, or reflect electromagnetic radiation.
What are the two main types of spectroscopy discussed in the script?
-The two main types of spectroscopy discussed are UV-Vis (Ultraviolet-Visible) spectroscopy and Infrared (IR) spectroscopy. Both techniques analyze how materials absorb light in different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
How is transmittance defined in the context of spectroscopy?
-Transmittance refers to the fraction of light that passes through a material. It is the ratio of transmitted light intensity to the initial light intensity, and it is expressed as a percentage.
What is absorbance, and how is it calculated?
-Absorbance is the measure of how much light a material absorbs. It is calculated using the formula: A = -log(T), where 'A' is absorbance, and 'T' is transmittance. High absorbance indicates that less light is transmitted through the material.
What is the Beer-Lambert Law, and what does it describe?
-The Beer-Lambert Law describes the relationship between absorbance, concentration, and path length. It states that absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing substance and the length of the path the light travels through the sample. The equation is: A = εcl, where A is absorbance, ε is molar absorptivity, c is concentration, and l is path length.
How can spectroscopy be used to measure the concentration of a substance?
-Spectroscopy can determine the concentration of a substance by measuring its absorbance at specific wavelengths. Using the Beer-Lambert Law, absorbance is related to concentration, allowing scientists to calculate the concentration of the substance in a solution.
Why is transmittance not always directly measurable in certain situations?
-Transmittance can be difficult to measure directly because it requires precise determination of the amount of light that passes through a material. However, it can be inferred from absorbance, as they are mathematically related through the Beer-Lambert Law.
What is the significance of molar absorptivity (ε) in the Beer-Lambert Law?
-Molar absorptivity (ε) is a constant that represents how strongly a substance absorbs light at a specific wavelength. It depends on the nature of the substance and the wavelength of light being used. This value is essential in determining absorbance and consequently calculating the concentration of a substance.
What is the relationship between the thickness of a sample and absorbance?
-Absorbance is directly proportional to the thickness of the sample. The thicker the sample (greater path length), the more light it absorbs. This relationship allows spectroscopy to be used to analyze materials of varying thicknesses.
What practical applications can UV-Vis and IR spectroscopy have in different industries?
-UV-Vis and IR spectroscopy are widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and material science. They help in analyzing the composition of materials, determining the concentration of chemicals in solutions, identifying unknown compounds, and monitoring environmental pollutants.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)