Apa Itu Massa Jenis Zat
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of mass density (or 'massa jenis') in simple terms. It demonstrates how different objects, despite having the same volume, can have different masses due to varying densities. The video walks through an example with a wooden block, calculating its density by comparing its mass and volume. It also discusses how mass density determines whether an object will float or sink in water, using water's density as a reference. The lesson concludes with a teaser on measuring the density of irregular objects and encourages viewers to subscribe for more educational content.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mass density (massa jenis) refers to the mass of an object divided by its volume, and it varies between different substances.
- 😀 Different materials have different densities, even if their volumes are the same.
- 😀 The density of a material determines whether it will float or sink in water: objects with a density greater than 1 g/cm³ will sink, while those with a density less than 1 g/cm³ will float.
- 😀 A wooden block can be used to demonstrate how to calculate density using the formula: Density = Mass / Volume.
- 😀 In the example, the wooden block has a mass of 82 grams and a volume of 210 cm³, resulting in a density of 0.39 grams/cm³.
- 😀 Objects with a density equal to 1 g/cm³, like water, will neither float nor sink, but will remain suspended in the liquid.
- 😀 Materials with higher density than water will sink, while those with lower density will float.
- 😀 The volume of regular objects like a wooden block can be easily calculated by multiplying length, width, and height.
- 😀 Understanding mass density is essential for predicting the behavior of objects in different fluids.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to like, subscribe, and share the content to support the channel and help make learning easier and more enjoyable.
Q & A
What is mass density?
-Mass density (or density) is the ratio of the mass of a substance to its volume. It indicates how tightly matter is packed within a substance.
How does mass density affect whether an object floats or sinks in water?
-If an object's mass density is greater than 1 gram/cm³, it will sink in water. If its mass density is less than 1 gram/cm³, it will float. If the mass density equals 1 gram/cm³, the object will neither sink nor float but will stay suspended in the water.
Why does the mass of two objects with the same volume differ?
-Two objects with the same volume can have different masses because their mass densities are different. Objects with a higher mass density will have a greater mass for the same volume.
How do you calculate the volume of a rectangular object?
-To calculate the volume of a rectangular object, multiply its length, width, and height. The formula is Volume = Length × Width × Height.
What are some common examples of regular objects whose volume can be calculated easily?
-Common examples of regular objects include cubes, rectangular blocks, cylinders, pyramids, and spheres. These shapes have straightforward formulas for calculating volume.
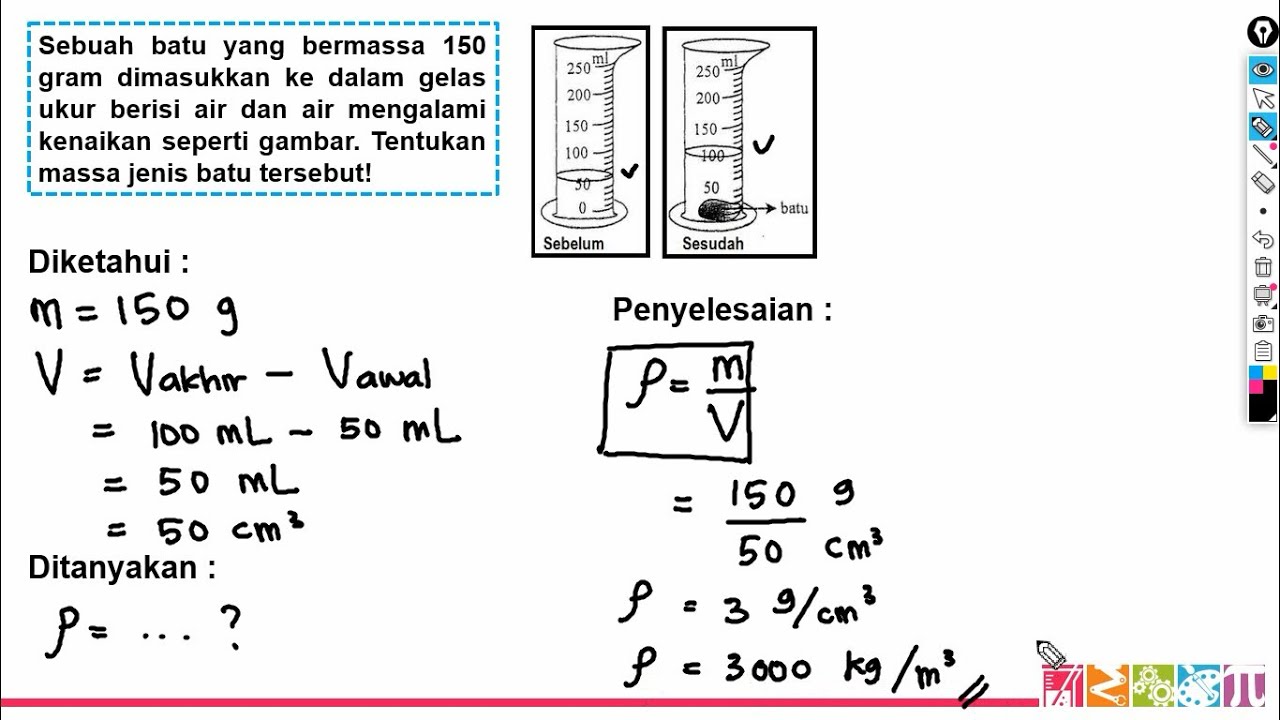
How can you find the mass density of an object like wood?
-To find the mass density of an object like wood, first calculate its volume (e.g., using the dimensions of a rectangular block) and then divide the mass of the object by its volume. The formula is mass density (ρ) = mass/volume.
What is the mass density of water?
-The mass density of water is 1 gram/cm³.
What happens if the mass density of an object is equal to that of water?
-If the mass density of an object is exactly 1 gram/cm³, the object will neither sink nor float but will stay suspended in the water.
Why is mass density important in understanding whether an object will float or sink?
-Mass density helps determine whether an object will float or sink because substances with higher densities than water will sink, while those with lower densities will float.
How does the concept of mass density apply to everyday life?
-Understanding mass density helps in various real-life scenarios, such as designing ships (which must float) or understanding why oil floats on water, as well as in measuring the properties of materials used in construction, manufacturing, and many other industries.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Massa Jenis Benda (IPA SMP)

Kelas XI Bab 3 Fluida Statis Part 1 Massa Jenis

4.3a Density and Composite Mixture (MJ16 P12 Q13) | AS Density | Cambridge A Level Physics

IGCSE Physics [Syllabus 1.4] Density

MASSA JENIS (DENSITAS) - Menentukan Massa Jenis Suatu Zat | IPA Kelas 7

PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS: Different properties of fluids. (Fluid mechanics lesson 2)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
