Extraction Using Heat | Environment Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the chemistry of iron production from iron ore, explaining the process through the reactivity series, redox reactions, and the role of carbon in reducing iron oxide. It discusses how early Earth conditions led to the formation of iron oxides and how carbon (in the form of coke) was utilized to extract iron during the Industrial Revolution. The video explains the step-by-step chemical reactions involved, the concept of oxidation and reduction, and why iron extraction is more complex than copper extraction. A clear and engaging explanation of redox processes makes this video both educational and accessible.
Takeaways
- 😀 Iron in its natural state was initially found as an element in the Earth's crust.
- 😀 When plants began releasing oxygen, it reacted with iron to form iron oxides, a process that took millions of years.
- 😀 Iron is primarily found in the ore known as hematite, which contains iron oxide.
- 😀 Carbon is used to displace iron from its oxide due to its higher reactivity, availability, and low cost.
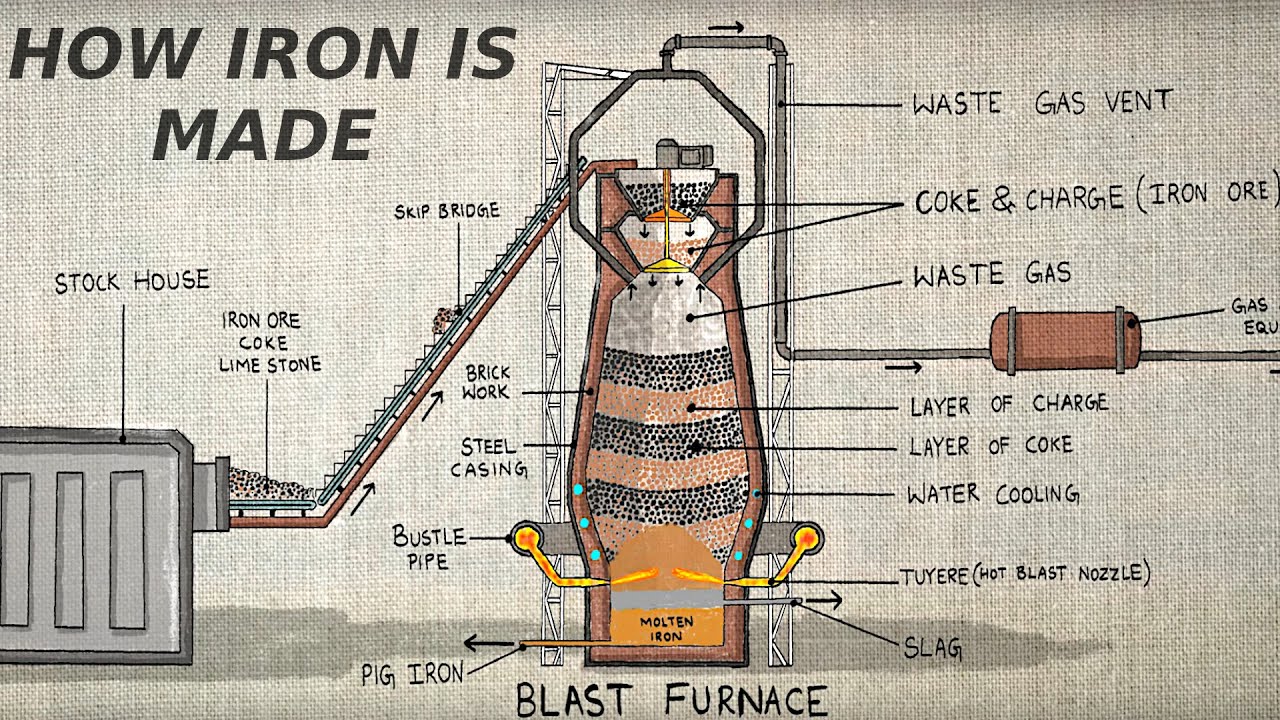
- 😀 Charcoal was historically the source of carbon until the industrial revolution when coke (almost pure carbon from coal) became the preferred material.
- 😀 Carbon serves as both a reducing agent and a fuel in the iron production process, enabling reactions at temperatures exceeding 1500°C.
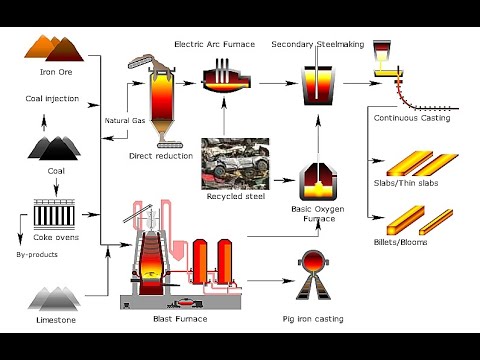
- 😀 The process of iron extraction is a three-step reaction involving carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and iron oxide reduction.
- 😀 The extraction reaction is a redox (reduction-oxidation) process, with carbon being oxidized and iron being reduced.
- 😀 In a redox reaction, oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons (oil rig).
- 😀 Copper, being less reactive than iron, is extracted under milder conditions and was discovered earlier than iron extraction.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to engage with the content, subscribe, and check out related educational apps for further learning.
Q & A
What is the reactivity series of metals?
-The reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in order of their reactivity, from the most reactive to the least reactive. It helps to understand which metals can displace others in chemical reactions, like the reduction of metal oxides.
How did iron combine with oxygen in early Earth history?
-Iron in its elemental form combined with oxygen, which was released by evolving plants. This combination formed iron oxides, a process that took millions of years.
What is hematite and why is it important in iron production?
-Hematite is an ore of iron that contains iron oxide. It is a significant source of iron because it can be processed to extract iron through reduction reactions.
Why is carbon used to displace iron from iron oxide?
-Carbon is more reactive than iron, which makes it capable of displacing iron from its oxide. Additionally, carbon is inexpensive and easily obtainable, making it an ideal material for this process.
What was the role of charcoal in iron production before the industrial revolution?
-Before the industrial revolution, charcoal, which is derived from wood, was used as the source of carbon to reduce iron oxides. However, the widespread use of charcoal led to deforestation in Europe.
What is coke and how did it change the process of iron production?
-Coke is almost pure carbon, produced from coal. Its discovery allowed for a more efficient and sustainable source of carbon compared to charcoal, revolutionizing iron production during the industrial revolution.
How does carbon act as both a reducing agent and a fuel in the production of iron?
-As a reducing agent, carbon removes oxygen from iron oxide, thereby reducing it to iron. Simultaneously, carbon serves as a fuel by burning to produce the high temperatures necessary for the reaction to occur.
What is the chemical process involved in reducing iron oxide to iron?
-The reduction process involves three steps: First, carbon burns to produce carbon dioxide. Then, carbon dioxide reacts with more carbon to form carbon monoxide, which ultimately reduces iron oxide to iron.
What are redox reactions, and how do they apply to iron production?
-Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons. In iron production, carbon is oxidized (losing electrons) to form carbon dioxide, while iron oxide is reduced (gaining electrons) to form iron.
Why is copper extraction less harsh than iron extraction?
-Copper is a less reactive metal compared to iron, so it can be extracted under less extreme conditions. This is part of the reason why copper extraction was discovered earlier than iron extraction.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)