EPS 66 Meluruskan Pemahaman Kemajuan Abbassiyah
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the rise and decline of the Abbasid Caliphate, highlighting the brief 'golden age' under Harun al-Rashid. It emphasizes that while the Abbasids were instrumental in advancing Islamic civilization, their peak lasted only about 99 years of their 508-year rule. The decline began with Caliph al-Mutawakkil and culminated with the fall of Baghdad in 1258. The speaker stresses that later generations, like Imam al-Zarnuji, inherited a period of decline rather than progress, challenging the conventional view of an uninterrupted era of glory for the Abbasid dynasty.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Abbasid Caliphate's achievements were built upon the foundations laid by the Umayyad dynasty, particularly in territorial expansion and military campaigns.
- 😀 Harun al-Rashid's reign marked the golden age of the Abbasid dynasty, characterized by cultural and intellectual flourishing.
- 😀 The intellectual contributions during the Abbasid period were significant, with notable figures in law (Imam Abu Hanifah, Imam Malik, etc.), theology (Abu al-Hasan al-Ash'ari), mysticism (Rabi'ah al-Adawiyah), and philosophy (Al-Kindi, Ibn Sina).
- 😀 The scientific advancements during the Abbasid period were revolutionary, including contributions from Al-Khwarizmi (mathematics), Jabir ibn Hayyan (chemistry), and Al-Biruni (gravitational theory).
- 😀 Despite the golden age, the peak of the Abbasid Caliphate only lasted for 99 years of its more than 500-year existence.
- 😀 The Abbasid Caliphate began its decline during the reign of Caliph Al-Mutawakkil, leading to centuries of political and economic stagnation.
- 😀 The fall of Baghdad in 1258 at the hands of the Mongols under Hulagu Khan marked the definitive end of the Abbasid political power.
- 😀 The Abbasid era should not be seen as uniformly prosperous; much of their rule was marked by decline, especially after the reign of Al-Mutawakkil.
- 😀 While Harun al-Rashid's reign was highly celebrated, the later period saw the caliphs becoming more symbolic than powerful.
- 😀 The destruction of Baghdad by the Mongols demonstrated the vulnerability of the Abbasid Caliphate despite its formal status as a major power.
- 😀 Imam al-Zarnuji's work, created during the later, more troubled Abbasid period, reflects the intellectual inheritance of the past rather than the flourishing of the golden age.
Q & A
What role did the Umayyad dynasty play in the Abbasid Caliphate's success?
-The Umayyad dynasty laid the groundwork for the Abbasid Caliphate's expansion by engaging in wars with the Byzantine Empire and expanding Islamic territory across North Africa, Spain, and parts of Europe and Asia. The Abbasids inherited these territorial gains and continued to spread Islam, inheriting a vast empire.
What was the significance of Harun al-Rashid's rule for the Abbasid Caliphate?
-Harun al-Rashid's reign is considered the peak of the Abbasid Caliphate, characterized by cultural, intellectual, and scientific prosperity. His rule was marked by advancements in philosophy, law, and the sciences, and he became a legendary figure in both Islamic history and literature, especially in works like 'One Thousand and One Nights.'
How did Harun al-Rashid's reign influence global literature?
-Harun al-Rashid's reign was romanticized in the literary work 'One Thousand and One Nights,' where he is depicted as an ideal ruler. This portrayal contributed to his lasting legacy as one of the greatest rulers of the Islamic world, representing the splendor and achievements of the Abbasid period.
What contributions did scholars during the Abbasid period make?
-The Abbasid period saw the emergence of many influential scholars, including jurists like Imam Abu Hanifa, Imam Malik, Imam Shafi'i, and Imam Ahmad, as well as philosophers like Al-Kindi and Ibn Sina. These scholars made significant contributions to fields such as Islamic law, theology, philosophy, and science.
Why is it incorrect to view the entire Abbasid era as a period of uninterrupted prosperity?
-The Abbasid Caliphate, while marked by periods of significant cultural and intellectual achievement, was also subject to long periods of decline. After Harun al-Rashid's death, the caliphate experienced political instability, internal strife, and external threats, leading to a steady weakening of its power, culminating in the fall of Baghdad to the Mongols in 1258.
How long did the Abbasid Caliphate experience its peak period?
-The Abbasid Caliphate's peak period lasted for about 99 years, from the reign of the first caliph, Abul Abbas as-Saffah, to the reign of Al-Wathiq. This period was characterized by significant achievements in governance, culture, and intellectual life.
What factors contributed to the decline of the Abbasid Caliphate?
-The decline of the Abbasid Caliphate was influenced by several factors, including political fragmentation, the weakening of central authority, and external invasions. The empire's fragmentation began with the reign of Al-Mutawakkil, and by the 13th century, it was further exacerbated by the Mongol invasion, which led to the fall of Baghdad in 1258.
What is the significance of the Mongol invasion of Baghdad in 1258?
-The Mongol invasion of Baghdad in 1258 is considered the symbolic end of the Abbasid Caliphate. Despite still being a formal political entity, the caliphate was effectively destroyed when Hulagu Khan's forces sacked the city, marking the end of its influence in the Islamic world.
What did Imam al-Zarnuji inherit during the decline of the Abbasid Caliphate?
-Imam al-Zarnuji lived during the last days of the Abbasid Caliphate, particularly under the reign of the last caliph, Al-Mustasim. Rather than inheriting the golden age of the Abbasids, he inherited a period of decline, with the caliphate's power and influence diminishing significantly by his time.
How did the fall of the Abbasid Caliphate compare to the rise of the Mamluks?
-The fall of the Abbasid Caliphate was swiftly followed by the rise of the Mamluks in Egypt, who were able to defeat the Mongols at the Battle of Ain Jalut. This contrast highlights the vulnerability of the Abbasids despite their vast empire, whereas the smaller Mamluk forces were able to repel the Mongol invasion, marking a new chapter in Islamic history.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

PAI Kelas 8 Bab 13 Bag 1 Pemerintahan Daulah Abbasiyah

Sejarah Dinasti Bani Abbasiyah, Dunia Islam Pusat Pengetahuan Dunia

Materi PAI 8 : Masa Keemasan Islam Era Daulah Abbasiyah (750-1258 M) @Kur.Merdeka

SOSOK KHALIFAH DAULAH ABBASIYAH -- Bagian I

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman PAI Kelas 8 Bab 5 Daulah Abbasiyah
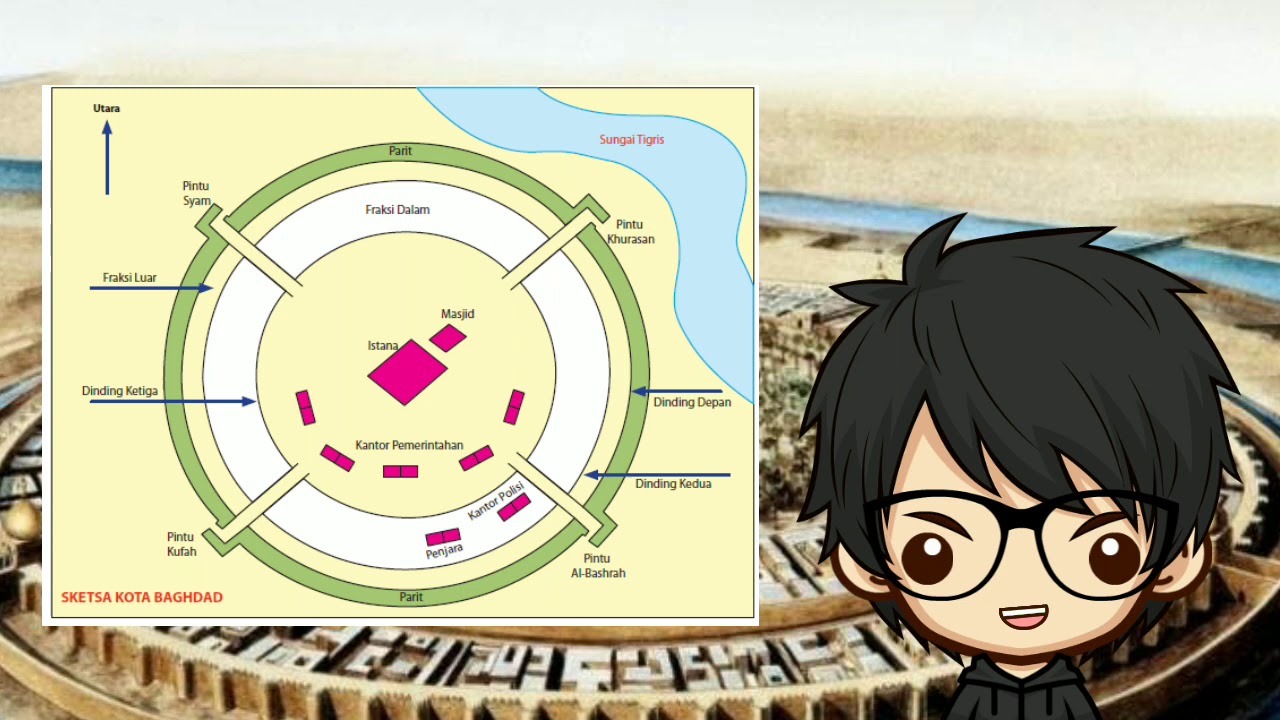
Fase-fase atau Periode Pemerintahan Dinasti Abbasiyah
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
